Maintenance of DNA Methylation during the Arabidopsis Life Cycle
... (GUS) (Luo et al., 2000), respectively. However, this transcriptional control may affect only the corresponding transcriptional reporter. Silencing in endosperm has been shown for the paternal copy of reporter constructs inserted at several loci, leading to the hypothesis of global silencing of the ...
... (GUS) (Luo et al., 2000), respectively. However, this transcriptional control may affect only the corresponding transcriptional reporter. Silencing in endosperm has been shown for the paternal copy of reporter constructs inserted at several loci, leading to the hypothesis of global silencing of the ...
Exercise 10 - DNA Fingerprinting - Lake
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a double stranded genetic molecule consisting of many monomers called nucleotides, hence DNA is a polynucleotide. The two strands of DNA are connected to one another by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of each strand. The DNA base pair sequence and DNA quan ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a double stranded genetic molecule consisting of many monomers called nucleotides, hence DNA is a polynucleotide. The two strands of DNA are connected to one another by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of each strand. The DNA base pair sequence and DNA quan ...
SMN1 - IS MU
... (b) In patients with FSHD, the chromatin structure of D4Z4 adopts a more open configuration (open springs and open circles) leading to inefficient transcriptional repression (black arrows) of the D4Z4 repeat. (c) The DUX4 gene is located within each D4Z4 unit. On permissive chromosomes, the last cop ...
... (b) In patients with FSHD, the chromatin structure of D4Z4 adopts a more open configuration (open springs and open circles) leading to inefficient transcriptional repression (black arrows) of the D4Z4 repeat. (c) The DUX4 gene is located within each D4Z4 unit. On permissive chromosomes, the last cop ...
Interfacial Behavior of a Hairpin DNA Probe Immobilized on Gold
... may be highlighted. For biophysics studies, a major advantage of reflectivity over other scattering techniques is that the required sample quantity is very small (<10-6 g); therefore, it is suitable for work with expensive or rare macromolecules. In this article, neutron reflectivity was used to sho ...
... may be highlighted. For biophysics studies, a major advantage of reflectivity over other scattering techniques is that the required sample quantity is very small (<10-6 g); therefore, it is suitable for work with expensive or rare macromolecules. In this article, neutron reflectivity was used to sho ...
Epigenetic inheritance of acquired traits through sperm RNAs and
... is transferred to the other. The transvection phenomenon in mice was first noticed during transgene manipulation38–40. In these cases, induced DNA methylation on one allele (triggered by transgene manipulations at this allele) was transferred to the other allele, the genotype of which remained wild ...
... is transferred to the other. The transvection phenomenon in mice was first noticed during transgene manipulation38–40. In these cases, induced DNA methylation on one allele (triggered by transgene manipulations at this allele) was transferred to the other allele, the genotype of which remained wild ...
Document
... identical copies of a gene-carrying piece of DNA – Recombinant DNA is formed by joining DNA sequences from two different sources – One source contains the gene that will be cloned – Another source is a gene carrier, called a vector ...
... identical copies of a gene-carrying piece of DNA – Recombinant DNA is formed by joining DNA sequences from two different sources – One source contains the gene that will be cloned – Another source is a gene carrier, called a vector ...
Presentation
... Key features of DNA: • A double-stranded helix, uniform diameter • It is right-handed • It is antiparallel • Outer edges of nitrogenous bases are exposed in the major and minor grooves ...
... Key features of DNA: • A double-stranded helix, uniform diameter • It is right-handed • It is antiparallel • Outer edges of nitrogenous bases are exposed in the major and minor grooves ...
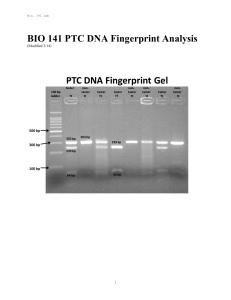
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take advantage of the C to T change at nucleotide position 785. The nucleotide sequence surrounding this ...
... interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take advantage of the C to T change at nucleotide position 785. The nucleotide sequence surrounding this ...
Lin, R., C. D. Allis and S. J. Elledge. 1996. PAT1
... Rpd3p (Taunton et al. 1996). Taken together, these data indicate that the steady-state balance of histone acetylation plays a direct role in the modulation of chromatin structure to create new patterns of transcription (Brownell & Allis 1996). Histone H1, unlike core histones, is highly diverged in ...
... Rpd3p (Taunton et al. 1996). Taken together, these data indicate that the steady-state balance of histone acetylation plays a direct role in the modulation of chromatin structure to create new patterns of transcription (Brownell & Allis 1996). Histone H1, unlike core histones, is highly diverged in ...
11-17-11 DNA Lecture - Kings County Criminal Bar Association
... • Loci are not independent of one another and therefore rare random match probabilities cannot be generated with the product rule; must use haplotypes (combination of alleles observed at all tested loci) ...
... • Loci are not independent of one another and therefore rare random match probabilities cannot be generated with the product rule; must use haplotypes (combination of alleles observed at all tested loci) ...
Where Is DNA Found?
... Greater automation of the DNA typing process Use of SNPs—single nucleotide polymorphism, which measures a one-nucleotide change or difference from one individual to another. More sites are needed to differentiate between individuals (30 to 50 SNPs to attain the frequencies of the 13 STR loci), but i ...
... Greater automation of the DNA typing process Use of SNPs—single nucleotide polymorphism, which measures a one-nucleotide change or difference from one individual to another. More sites are needed to differentiate between individuals (30 to 50 SNPs to attain the frequencies of the 13 STR loci), but i ...
Objective 2.1 Lesson D Recombinant Organisms
... genes. Mark in pencil the name of the gene on your plasmid. Your teacher should display a color coded plasmid. 5. Cut out the PLASMID as strips. You should end up with 6 strips. Discard ANY TWO of the strips (except for the strip which contains the “origin of replication” site. Shuffle the strips an ...
... genes. Mark in pencil the name of the gene on your plasmid. Your teacher should display a color coded plasmid. 5. Cut out the PLASMID as strips. You should end up with 6 strips. Discard ANY TWO of the strips (except for the strip which contains the “origin of replication” site. Shuffle the strips an ...
Mary Ann Osley*, Alastair Fleming, and Cheng
... Ubiquitylated histones have been estimated to account for between 1-20% of total cellular histones - levels that are in part accounted for by the dynamic nature of histone ubiquitylation. The ubiquitin mark turns over continually throughout mitotic cell growth, and during mitosis the core histones a ...
... Ubiquitylated histones have been estimated to account for between 1-20% of total cellular histones - levels that are in part accounted for by the dynamic nature of histone ubiquitylation. The ubiquitin mark turns over continually throughout mitotic cell growth, and during mitosis the core histones a ...
DNA the Crown Jewels 2012
... determines the shape and therefore the function of the protein. Example- hemoglobin- found in our red blood cells and responsible for carrying oxygen to our body cells. Hemoglobin is made of 4 polypeptide chains. Consider the problem with sickle cell anemia- ...
... determines the shape and therefore the function of the protein. Example- hemoglobin- found in our red blood cells and responsible for carrying oxygen to our body cells. Hemoglobin is made of 4 polypeptide chains. Consider the problem with sickle cell anemia- ...
How DNA Evidence Works The Science of DNA Fingerprinting
... Sequence polymorphisms are usually simple substitutions of one or two bases in the genes themselves. Genes are the pieces of the chromosome that actually serve as templates for the production of proteins. Amazingly, despite our complexity, genes make up only 5 percent of the human genome. Individual ...
... Sequence polymorphisms are usually simple substitutions of one or two bases in the genes themselves. Genes are the pieces of the chromosome that actually serve as templates for the production of proteins. Amazingly, despite our complexity, genes make up only 5 percent of the human genome. Individual ...
Chapter 16 Lecture Notes
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
Chapter 16 Outline
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
CHAPTER 16 THE MOLECULE BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
Lesson Plan - beyond benign
... analyzed for the presence of cancer genes her extracted DNA must be prepared, or “chopped up”, into pieces with proteins called restriction enzymes. These pieces of DNA are then tested and the results are interpreted. It may seem very complicated but, as you will learn, it’s fairly simple. So, what ...
... analyzed for the presence of cancer genes her extracted DNA must be prepared, or “chopped up”, into pieces with proteins called restriction enzymes. These pieces of DNA are then tested and the results are interpreted. It may seem very complicated but, as you will learn, it’s fairly simple. So, what ...
Frequent and histological type-specific inactivation of 14-3
... Figure 4 Immunohistochemical analysis (IHC) and methylation of primary lung tumor specimens. A panel of 30 lung tumors consisting of eight small cell carcinomas, 13 adenocarcinomas, seven squamous carcinomas, and two large cell carcinomas, were examined in this study. Sections 3 mm thick from 10% fo ...
... Figure 4 Immunohistochemical analysis (IHC) and methylation of primary lung tumor specimens. A panel of 30 lung tumors consisting of eight small cell carcinomas, 13 adenocarcinomas, seven squamous carcinomas, and two large cell carcinomas, were examined in this study. Sections 3 mm thick from 10% fo ...
word
... active. Chromosome silencing of one X chromosome, normally chosen at random, then occurs coincident with cellular differentiation. Once chromosome silencing has been established it is stably maintained through all subsequent cell divisions. We are trying to understand developmental regulation of X i ...
... active. Chromosome silencing of one X chromosome, normally chosen at random, then occurs coincident with cellular differentiation. Once chromosome silencing has been established it is stably maintained through all subsequent cell divisions. We are trying to understand developmental regulation of X i ...
An Apple a Day: Extracting DNA from Any Living Thing
... students to identify which objects contain DNA. Have students sort the objects into the three categories (living, never living, or previously living) based on their identifications. Ask students to explain how and why they categorized each object the way they did. Most likely, students will sort obj ...
... students to identify which objects contain DNA. Have students sort the objects into the three categories (living, never living, or previously living) based on their identifications. Ask students to explain how and why they categorized each object the way they did. Most likely, students will sort obj ...
Export To Word
... in different tissues express different genes? A basic notion in biology that most high school students fail to conceptualize is the fact that all cells in the animal or human body contain the same DNA, yet different cells in different tissues express, on the one hand, a set of common genes, and on t ...
... in different tissues express different genes? A basic notion in biology that most high school students fail to conceptualize is the fact that all cells in the animal or human body contain the same DNA, yet different cells in different tissues express, on the one hand, a set of common genes, and on t ...
C-Collate3 740..903
... among 23 chromosome pairs. This 2 m of DNA must be organized within a nucleus that is approximately 10 mm in diameter so that it can be separated easily during cell division and replicated rapidly. In addition, selected regions must be identi®ed and read quickly by the transcriptional machinery, all ...
... among 23 chromosome pairs. This 2 m of DNA must be organized within a nucleus that is approximately 10 mm in diameter so that it can be separated easily during cell division and replicated rapidly. In addition, selected regions must be identi®ed and read quickly by the transcriptional machinery, all ...
Development and validation of a diagnostic service for epimutations
... LOMM at GNAS exon 1A. This epigenotype has been associated with maternally inherited microdeletions in STX16 gene. Sporadic PHP-1b Variable GNAS imprinting defects that may involve the upstream DMRs NESP55 & NESPAS, in addition to GNAS exon 1A. This epigenotype can result from: - maternally inherite ...
... LOMM at GNAS exon 1A. This epigenotype has been associated with maternally inherited microdeletions in STX16 gene. Sporadic PHP-1b Variable GNAS imprinting defects that may involve the upstream DMRs NESP55 & NESPAS, in addition to GNAS exon 1A. This epigenotype can result from: - maternally inherite ...
Epigenetics

Epigenetics is the study, in the field of genetics, of cellular and physiological phenotypic trait variations that are caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Hence, epigenetic research seeks to describe dynamic alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell. These alterations may or may not be heritable, although the use of the term ""epigenetic"" to describe processes that are not heritable is controversial. Unlike genetics based on changes to the DNA sequence (the genotype), the changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype of epigenetics have other causes, thus use of the prefix epi- (Greek: επί- over, outside of, around).The term also refers to the changes themselves: functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave (or ""express themselves"") differently.One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis, totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo, which in turn become fully differentiated cells. In other words, as a single fertilized egg cell – the zygote – continues to divide, the resulting daughter cells change into all the different cell types in an organism, including neurons, muscle cells, epithelium, endothelium of blood vessels, etc., by activating some genes while inhibiting the expression of others.