An Approximate Approach to DNA Denaturation
... modern biophysics because it is at the basis of life. However, it also is a very difficult problem due to the complex role played by RNA polymerases in the process. It is now well established (Freifelder 1987) t h a t local denaturation of DNA is involved so t h a t it is interesting to investigate ...
... modern biophysics because it is at the basis of life. However, it also is a very difficult problem due to the complex role played by RNA polymerases in the process. It is now well established (Freifelder 1987) t h a t local denaturation of DNA is involved so t h a t it is interesting to investigate ...
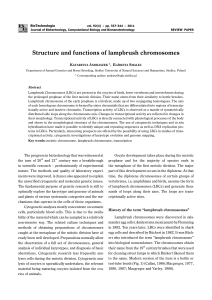
Structure and functions of lampbrush chromosomes
... (chromomeres visible as dark irregular structures and also observed in the interphase nucleus) and side loops of decondensed chromatin. In the homologous sections of the bivalent, chromatin is condensed (spirally twisted) or decondensed in the form of side loops – two per each chromosome and four at ...
... (chromomeres visible as dark irregular structures and also observed in the interphase nucleus) and side loops of decondensed chromatin. In the homologous sections of the bivalent, chromatin is condensed (spirally twisted) or decondensed in the form of side loops – two per each chromosome and four at ...
Pierre MADL Div. of Material Sciences Dep
... Conrad Waddington (1905-1975) is often credited with coining the term epigenetics in 1942 as “the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. Epigenetics appears in the literature as far back as the mid 19th century ...
... Conrad Waddington (1905-1975) is often credited with coining the term epigenetics in 1942 as “the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. Epigenetics appears in the literature as far back as the mid 19th century ...
Aberrant DNA methylation in cancer: potential clinical
... occurring modification of human DNA (Fig. 1) and results from the activity of a family of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzymes that catalyse the addition of a methyl group to cytosine residues at CpG dinucleotides (Ref. 1). Alterations in DNA methylation are regarded as epigenetic, and not genetic, ...
... occurring modification of human DNA (Fig. 1) and results from the activity of a family of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzymes that catalyse the addition of a methyl group to cytosine residues at CpG dinucleotides (Ref. 1). Alterations in DNA methylation are regarded as epigenetic, and not genetic, ...
Analyzing the Changes in DNA Flexibility Due to Base Modifications
... When the water and ions are placed, they are placed randomly, and there may be high energy clashes that would apply very large forces at the beginning of any subsequent simulations. The DNA double helix is fairly fragile, and it is possible that hydrogen bonds could be broken early on in the simulat ...
... When the water and ions are placed, they are placed randomly, and there may be high energy clashes that would apply very large forces at the beginning of any subsequent simulations. The DNA double helix is fairly fragile, and it is possible that hydrogen bonds could be broken early on in the simulat ...
Molecular and Cellular Biology, September 2000, p
... general control of chromatin remodeling during cell differentiation. Indeed, through the control of a specific group of genes encoding chromatin-associated proteins (such as H10), these molecules may regulate chromatin structure and function. Transcription factors interacting with the H10 promoter a ...
... general control of chromatin remodeling during cell differentiation. Indeed, through the control of a specific group of genes encoding chromatin-associated proteins (such as H10), these molecules may regulate chromatin structure and function. Transcription factors interacting with the H10 promoter a ...
non mendelian inheritance
... To predict phenotype, we must consider several factors. These include the dominant/recessive relationship of alleles, gene interactions that may affect the expression of a single trait, and the roles that sex and the environment play in influencing the individual’s phenotype. Once these factors are ...
... To predict phenotype, we must consider several factors. These include the dominant/recessive relationship of alleles, gene interactions that may affect the expression of a single trait, and the roles that sex and the environment play in influencing the individual’s phenotype. Once these factors are ...
The use of the twin model to investigate the genetics and
... genetics of ageing took the opportunity to investigate whether an excess of naevi may be a marker of delayed ageing. A study of 1897 twins on whom white cell telomere length data were available was performed to establish the correlation between telomere length and naevus counts.12 Telomere length is ...
... genetics of ageing took the opportunity to investigate whether an excess of naevi may be a marker of delayed ageing. A study of 1897 twins on whom white cell telomere length data were available was performed to establish the correlation between telomere length and naevus counts.12 Telomere length is ...
Supercoils in plant DNA: nucleoid
... have been conducted. Plants share many common features with the other eukaryotes, but there are also many peculiarities distinguishing them. For example, they possess unusually large genomes, highly variable in size and organization from species to species, a lot of repetitive DNA, low relative amou ...
... have been conducted. Plants share many common features with the other eukaryotes, but there are also many peculiarities distinguishing them. For example, they possess unusually large genomes, highly variable in size and organization from species to species, a lot of repetitive DNA, low relative amou ...
Restriction Enzyme digestion of DNA
... endonucleases (RE), digest DNA by breaking bonds only within a specific short sequence of bases. These base sequences usually ran in size from 48 base pairs but can be as long as 23 base pairs. • Restriction endonucleases confer an adaptive advantage on bacteria by digesting foreign DNA usually from ...
... endonucleases (RE), digest DNA by breaking bonds only within a specific short sequence of bases. These base sequences usually ran in size from 48 base pairs but can be as long as 23 base pairs. • Restriction endonucleases confer an adaptive advantage on bacteria by digesting foreign DNA usually from ...
localization of histone gene transcripts in newt lampbrush
... sequences during oogenesis in Amphibia and certain other animals. The other favourable situation is provided by polytene chromosomes of larval Diptera, where many identical DNA sequences lie in lateral register with one another. There is yet another favourable situation which has hitherto been littl ...
... sequences during oogenesis in Amphibia and certain other animals. The other favourable situation is provided by polytene chromosomes of larval Diptera, where many identical DNA sequences lie in lateral register with one another. There is yet another favourable situation which has hitherto been littl ...
E.coli
... setting or transferred to transgenic mice in a living animal YACs need origin, a centromere, and ...
... setting or transferred to transgenic mice in a living animal YACs need origin, a centromere, and ...
Parental Legacy Determines Methylation and Expression of an
... during inheritance from the parent. The distinctive information imparted by passage of these genes through the male and female parents evidently allows them to act collaboratively in the embryo. This concept of differential expression of paternally and maternally derived genes might explain the fail ...
... during inheritance from the parent. The distinctive information imparted by passage of these genes through the male and female parents evidently allows them to act collaboratively in the embryo. This concept of differential expression of paternally and maternally derived genes might explain the fail ...
Tutorial - QIAGEN Bioinformatics
... Figure 1: Toolbox folder structure after installation of the Bisulfite Sequencing plugin. Bisulfite sequencing is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. Changes in cytosin ...
... Figure 1: Toolbox folder structure after installation of the Bisulfite Sequencing plugin. Bisulfite sequencing is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. Changes in cytosin ...
Gill: Gene Regulation II
... Histone Code Hypothesis Histone modifications serve to recruit other proteins by specific recognition of the modified histone via protein domains specialized for such purposes, rather than through simply stabilizing or destabilizing the interaction between histone and the underlying DNA. histone mo ...
... Histone Code Hypothesis Histone modifications serve to recruit other proteins by specific recognition of the modified histone via protein domains specialized for such purposes, rather than through simply stabilizing or destabilizing the interaction between histone and the underlying DNA. histone mo ...
R - Genetics
... either with the specific DNA (from a capsule-deficient strain) responsible for their production or with the DNA extracted from cells of their own strain (clone). This finding suggests genotypic identity of the capsule-deficient transformants with the capsule-deficient donor cells. The spontaneous ca ...
... either with the specific DNA (from a capsule-deficient strain) responsible for their production or with the DNA extracted from cells of their own strain (clone). This finding suggests genotypic identity of the capsule-deficient transformants with the capsule-deficient donor cells. The spontaneous ca ...
Chromatin DNA Methylayion
... Repetitive, satellite, centromeric and pericentromeric sequences are hypomethylated in cancer. ...
... Repetitive, satellite, centromeric and pericentromeric sequences are hypomethylated in cancer. ...
development, the Linker histone H1 is essential for Drosophila
... However, its elimination by gene inactivation led to partially decondensed chromatin, supporting an in vivo role for H1 in chromatin folding. Mammals express at least eight nonallelic H1 subtypes that differ in their expression during development. Although none of the eight individual subtypes appea ...
... However, its elimination by gene inactivation led to partially decondensed chromatin, supporting an in vivo role for H1 in chromatin folding. Mammals express at least eight nonallelic H1 subtypes that differ in their expression during development. Although none of the eight individual subtypes appea ...
Student`s guide -
... Loading the gel a. Pour slightly more than 10 mL of TBE buffer solution into the gel tank. The liquid should just cover the surface of the gel and flood into the areas at either end. b. Very gently ease the comb from the gel, allowing the buffer solution to fill the wells left behind. Take care no ...
... Loading the gel a. Pour slightly more than 10 mL of TBE buffer solution into the gel tank. The liquid should just cover the surface of the gel and flood into the areas at either end. b. Very gently ease the comb from the gel, allowing the buffer solution to fill the wells left behind. Take care no ...
Chapter 13
... It goes into the complex as one doublestranded molecule, and emerges as two double-stranded molecules. ...
... It goes into the complex as one doublestranded molecule, and emerges as two double-stranded molecules. ...
Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape
... a number of them were determined in complex with cofactors or/and DNA (Table 2). The classification of nucleases in terms of their 3D structures provides more defined properties, since it is accepted that the 3D structures are much less diverged and more closely related to the functions than the pri ...
... a number of them were determined in complex with cofactors or/and DNA (Table 2). The classification of nucleases in terms of their 3D structures provides more defined properties, since it is accepted that the 3D structures are much less diverged and more closely related to the functions than the pri ...
Biology, 8th Edition
... breakdown by modifying it after replication. An enzyme adds a methyl group to one or more bases in each restriction site so that the restriction enzyme does not recognize and cut the bacterial DNA. Restriction enzymes enable scientists to cut DNA from chromosomes into shorter fragments in a controll ...
... breakdown by modifying it after replication. An enzyme adds a methyl group to one or more bases in each restriction site so that the restriction enzyme does not recognize and cut the bacterial DNA. Restriction enzymes enable scientists to cut DNA from chromosomes into shorter fragments in a controll ...
Smchd1 regulates a subset of autosomal genes subject to
... [9-11], and (d) the apparently random widespread monoallelic expression of possibly hundreds of individual genes spread throughout the genome [12,13]. While the molecular mechanisms underlying the different forms of monoallelic expression have unique characteristics, they may be expected to share co ...
... [9-11], and (d) the apparently random widespread monoallelic expression of possibly hundreds of individual genes spread throughout the genome [12,13]. While the molecular mechanisms underlying the different forms of monoallelic expression have unique characteristics, they may be expected to share co ...
Epigenetics

Epigenetics is the study, in the field of genetics, of cellular and physiological phenotypic trait variations that are caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Hence, epigenetic research seeks to describe dynamic alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell. These alterations may or may not be heritable, although the use of the term ""epigenetic"" to describe processes that are not heritable is controversial. Unlike genetics based on changes to the DNA sequence (the genotype), the changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype of epigenetics have other causes, thus use of the prefix epi- (Greek: επί- over, outside of, around).The term also refers to the changes themselves: functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave (or ""express themselves"") differently.One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis, totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo, which in turn become fully differentiated cells. In other words, as a single fertilized egg cell – the zygote – continues to divide, the resulting daughter cells change into all the different cell types in an organism, including neurons, muscle cells, epithelium, endothelium of blood vessels, etc., by activating some genes while inhibiting the expression of others.