DVD Check-out List - Center for Reproductive Biology
... Dr. Jennifer Graves, Australian National University, "Sex Chromosomes and the Future of Men", January 2007 Dr. Grant MacGregor, University of California-Irvine, "FNDC3-a novel protein family with multiple roles in reproduction and development", February 2007 Cathryn Hogarth, Monash Institute of Medi ...
... Dr. Jennifer Graves, Australian National University, "Sex Chromosomes and the Future of Men", January 2007 Dr. Grant MacGregor, University of California-Irvine, "FNDC3-a novel protein family with multiple roles in reproduction and development", February 2007 Cathryn Hogarth, Monash Institute of Medi ...
Molecular Genetics Review
... Leading strand vs. lagging strand Okazaki fragments Pro vs. Eukaryotic replication ...
... Leading strand vs. lagging strand Okazaki fragments Pro vs. Eukaryotic replication ...
Objectives Unit 5
... 1)The student is able to construct scientific explanations that use the structures and mechanisms of DNA and RNA to support the claim that DNA and, in some cases, that RNA are the primary sources of heritable information. 2) The student is able to justify the selection of data from historical invest ...
... 1)The student is able to construct scientific explanations that use the structures and mechanisms of DNA and RNA to support the claim that DNA and, in some cases, that RNA are the primary sources of heritable information. 2) The student is able to justify the selection of data from historical invest ...
Document
... 5. Transcription and Translation summary: 17.26; DNA sequence determines protein shape 6. Protein shape determines function (5.20, 18.13) H. Gene Expression: 1. Characteristics of a cell depend on which genes are expressed within it 2. Tissue-specific gene expression vs. house-keeping genes (pg. 36 ...
... 5. Transcription and Translation summary: 17.26; DNA sequence determines protein shape 6. Protein shape determines function (5.20, 18.13) H. Gene Expression: 1. Characteristics of a cell depend on which genes are expressed within it 2. Tissue-specific gene expression vs. house-keeping genes (pg. 36 ...
Organism Genome (kb) Form
... chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different typ ...
... chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different typ ...
Case name Owner Website description Integrates DNA Methylation
... Integrates DNA Methylation and Chromatin Structure Assessment to Better Predict Chance of Disease This integrated DNA test kit helps diagnose disease by measuring methylation and chromatin structure at the same time, giving it an edge over disease detection kits that employ separate evaluations. Loc ...
... Integrates DNA Methylation and Chromatin Structure Assessment to Better Predict Chance of Disease This integrated DNA test kit helps diagnose disease by measuring methylation and chromatin structure at the same time, giving it an edge over disease detection kits that employ separate evaluations. Loc ...
Review (12/13/16)
... • H3K4me2/3 is associated with transcriptional activity. • Methylation of H3K9me2/3 is associated with repression ...
... • H3K4me2/3 is associated with transcriptional activity. • Methylation of H3K9me2/3 is associated with repression ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
Présentation PowerPoint
... -How do we explore the nutritional factors and their effects on C1 metabolism? -Can human cell-based models be used effectively to study epigenetic programming in vitro? -What kind of environmental variables initiate the emergence of an epigenetic phenotype? -Is there a genetic basis to epigenetic i ...
... -How do we explore the nutritional factors and their effects on C1 metabolism? -Can human cell-based models be used effectively to study epigenetic programming in vitro? -What kind of environmental variables initiate the emergence of an epigenetic phenotype? -Is there a genetic basis to epigenetic i ...
Epigenetics Article
... smoke—can affect our gene expression and that of future generations. Epigenetics introduces the concept of free will into our idea of genetics." Scientists are still coming to understand the many ways that epigenetic changes unfold at the biochemical level. One form of epigenetic change physically ...
... smoke—can affect our gene expression and that of future generations. Epigenetics introduces the concept of free will into our idea of genetics." Scientists are still coming to understand the many ways that epigenetic changes unfold at the biochemical level. One form of epigenetic change physically ...
13 4 (a) Genetic modification of organisms uses a
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
Christine Yiwen Yeh - The Second Draft: The Human Epigenome for novel Diagnoses and Therapies
... efficient and more precise genome annotation of regulatory elements. With the genome annotation on this second level of gene expression it is more possible to pinpoint functional or cell type-specific regions in studies. (2) Cell Identity Epigenomic maps can also provide more information than simple ...
... efficient and more precise genome annotation of regulatory elements. With the genome annotation on this second level of gene expression it is more possible to pinpoint functional or cell type-specific regions in studies. (2) Cell Identity Epigenomic maps can also provide more information than simple ...
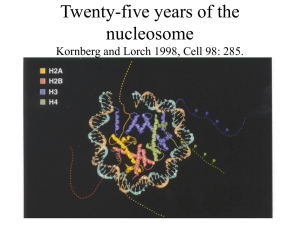
Twenty-five years of the nucleosome Kornberg and Lorch 1998, Cell
... 2. Immunocytochemistry- observe phospho-H3 throughout chromosomes during cell division Thus, this must play a role is chromosome condensation during mitosis 3. Models1. Phosphorylation + acetylation allows activation of gene expression, depending on context 2. Phospho-H3 loosens chromatin, enhancin ...
... 2. Immunocytochemistry- observe phospho-H3 throughout chromosomes during cell division Thus, this must play a role is chromosome condensation during mitosis 3. Models1. Phosphorylation + acetylation allows activation of gene expression, depending on context 2. Phospho-H3 loosens chromatin, enhancin ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of crossing over ...
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of crossing over ...
Some Problems with Genetic Horoscopes
... Since the apoE molecule helps to transport cholesterol around in the blood, and the population surveys have shown that people with allele 4 do have, on average, high cholesterol, the conclusion that allele 4 leads to high cholesterol seemed logical. However, the combination of high cholesterol and a ...
... Since the apoE molecule helps to transport cholesterol around in the blood, and the population surveys have shown that people with allele 4 do have, on average, high cholesterol, the conclusion that allele 4 leads to high cholesterol seemed logical. However, the combination of high cholesterol and a ...
A THREE-GENERATION APPROACH IN BIODEMOGRAPHY IS
... Understanding the biochemical and cellular processes by which telomere extension occurs is important for analyzing the processes of human senescence and of carcinogenesis. Epigenetic maternalization (or initiation of new imprints) continues in the F(n-1) generation during maturation of growing oocyt ...
... Understanding the biochemical and cellular processes by which telomere extension occurs is important for analyzing the processes of human senescence and of carcinogenesis. Epigenetic maternalization (or initiation of new imprints) continues in the F(n-1) generation during maturation of growing oocyt ...
2 points - Triton Science
... • The genome changes slowly, through the processes of random mutation and natural selection. It takes many generations for a genetic trait to become common in a population. • The epigenome, on the other hand, can change rapidly in response to signals from the environment. • Epigenetic inheritance ma ...
... • The genome changes slowly, through the processes of random mutation and natural selection. It takes many generations for a genetic trait to become common in a population. • The epigenome, on the other hand, can change rapidly in response to signals from the environment. • Epigenetic inheritance ma ...
Epigenetics
... How many genes do we have ? The answer to this question is almost meaningless because: • Each gene can give rise to several proteins by alternative splicing • And each protein can be modified in multiple ways by phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, glycosylation etc. • These modified proteins ...
... How many genes do we have ? The answer to this question is almost meaningless because: • Each gene can give rise to several proteins by alternative splicing • And each protein can be modified in multiple ways by phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, glycosylation etc. • These modified proteins ...
DNA - VanityWolveriine
... Basically, DNA contains genetics in all life forms. The genetics in DNA is developed and stored by the different combinations and orders of stored information. ...
... Basically, DNA contains genetics in all life forms. The genetics in DNA is developed and stored by the different combinations and orders of stored information. ...
powerpoint
... methylation of cytosine at position C5 in CpG dinucleotides Other main group is epigenetic posttranslational modification of histones ...
... methylation of cytosine at position C5 in CpG dinucleotides Other main group is epigenetic posttranslational modification of histones ...
PDF
... in genes involved in suppressing TE activity in germ cells, and the expression of these genes is activated during two phases of DNA demethylation in PGCs. These findings suggest that unique reliance on promoter DNA methylation acts as a highly tuned sensor of global DNA demethylation and allows PGCs ...
... in genes involved in suppressing TE activity in germ cells, and the expression of these genes is activated during two phases of DNA demethylation in PGCs. These findings suggest that unique reliance on promoter DNA methylation acts as a highly tuned sensor of global DNA demethylation and allows PGCs ...
Presentation
... heterochromatin are usually not expressed Chemical modifications to histones and DNA of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression Acetylation prevents histones from packing tightly, which allows genes to be expressed. Methylation causes histones to pack tightly so that g ...
... heterochromatin are usually not expressed Chemical modifications to histones and DNA of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression Acetylation prevents histones from packing tightly, which allows genes to be expressed. Methylation causes histones to pack tightly so that g ...
BIOD19H3 Epigenetics in Health and Disease Professor: Winter 2015
... Professor: Patrick McGowan; TA: Wilfred de Vega ...
... Professor: Patrick McGowan; TA: Wilfred de Vega ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA code for? What are the products of mtDNA transcription and translation? 13 proteins for aerobic cellular respiration; 22 tRNA for translatio ...
... mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA code for? What are the products of mtDNA transcription and translation? 13 proteins for aerobic cellular respiration; 22 tRNA for translatio ...
Epigenetics

Epigenetics is the study, in the field of genetics, of cellular and physiological phenotypic trait variations that are caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Hence, epigenetic research seeks to describe dynamic alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell. These alterations may or may not be heritable, although the use of the term ""epigenetic"" to describe processes that are not heritable is controversial. Unlike genetics based on changes to the DNA sequence (the genotype), the changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype of epigenetics have other causes, thus use of the prefix epi- (Greek: επί- over, outside of, around).The term also refers to the changes themselves: functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave (or ""express themselves"") differently.One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis, totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo, which in turn become fully differentiated cells. In other words, as a single fertilized egg cell – the zygote – continues to divide, the resulting daughter cells change into all the different cell types in an organism, including neurons, muscle cells, epithelium, endothelium of blood vessels, etc., by activating some genes while inhibiting the expression of others.