PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ___________ individuals by a ...
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ___________ individuals by a ...
File
... What is a GENOME? A genome is the total collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
... What is a GENOME? A genome is the total collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
Introduction to the biology and technology of DNA microarrays
... – (ii) translation, during which mRNA is translated to produce a protein. ...
... – (ii) translation, during which mRNA is translated to produce a protein. ...
File
... What is a GENOME? A genome is the total collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
... What is a GENOME? A genome is the total collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
11. Use the following mRNA codon key as needed to... GCC Alanine AAU
... A type of human dwarfism results from the production of mutant SHR-1 protein. You look at the length of the mutant SHR-1 and the normal (wild-type) SHR-1 protein, and discover that the mutant SHR-1 protein has fewer amino acids. What do you expect to find when you examine the DNA sequence? A. nucleo ...
... A type of human dwarfism results from the production of mutant SHR-1 protein. You look at the length of the mutant SHR-1 and the normal (wild-type) SHR-1 protein, and discover that the mutant SHR-1 protein has fewer amino acids. What do you expect to find when you examine the DNA sequence? A. nucleo ...
Workshop IX Fungal Genomics Chair: Peter Philippsen 206
... We have sequenced the genome of the filamentous ascomycete Ashbya gossypii and produced a complete annotation of the 4718 protein coding genes. (GenBank accession numbers AE016814-AE016821). The systematic gene nomenclature follows that used for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This facilitated the alignme ...
... We have sequenced the genome of the filamentous ascomycete Ashbya gossypii and produced a complete annotation of the 4718 protein coding genes. (GenBank accession numbers AE016814-AE016821). The systematic gene nomenclature follows that used for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This facilitated the alignme ...
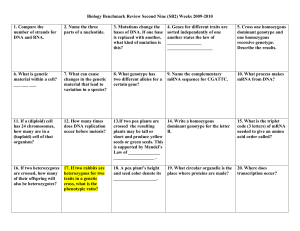
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
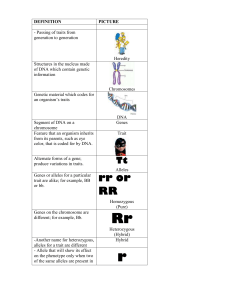
definition - Humble ISD
... chromosome Feature that an organism inherits from its parents, such as eye color, that is coded for by DNA. Alternate forms of a gene; produce variations in traits. ...
... chromosome Feature that an organism inherits from its parents, such as eye color, that is coded for by DNA. Alternate forms of a gene; produce variations in traits. ...
Genetic Engineering
... II. Genetic Engineering and Genetically Modified Organisms 1. What is genetic engineering? • Genetic engineering is altering the genetic makeup of an organism by CUTTING DNA from one organism and INSERTING FRAGMENTS into a host. • The end result is RECOMBINANT DNA, or DNA made from two or ...
... II. Genetic Engineering and Genetically Modified Organisms 1. What is genetic engineering? • Genetic engineering is altering the genetic makeup of an organism by CUTTING DNA from one organism and INSERTING FRAGMENTS into a host. • The end result is RECOMBINANT DNA, or DNA made from two or ...
Biology 303 EXAM III
... Assume that in this imaginary world the genetic code is nonoverlapping and utilizes the smallest possible size for a codon that accommodates all amino acids unambiguously. In this particular world, which of the following mutations in the coding region of a gene would not cause a frame-shift? 1. an i ...
... Assume that in this imaginary world the genetic code is nonoverlapping and utilizes the smallest possible size for a codon that accommodates all amino acids unambiguously. In this particular world, which of the following mutations in the coding region of a gene would not cause a frame-shift? 1. an i ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
TRPGR: Sequencing the barley gene-space
... Another important preliminary step towards sequencing the large genome of barley is to obtain a glimpse to the genome structure and how it compares to other related sequenced genomes. As barley is expected to have a low gene density (approximately 1 gene every 100 kbp), contiguous sequences in the m ...
... Another important preliminary step towards sequencing the large genome of barley is to obtain a glimpse to the genome structure and how it compares to other related sequenced genomes. As barley is expected to have a low gene density (approximately 1 gene every 100 kbp), contiguous sequences in the m ...
DNA_Project - Berkeley Cosmology Group
... between the exons, which don’t work in coding for protein synthesis. Exons are segments of a gene that does code for protein synthesis that is transcribed to messenger RNA. Both introns and exons sequences are transcribed into RNA. RNA splicing is done by spliceosomes, which are large group ofRNA an ...
... between the exons, which don’t work in coding for protein synthesis. Exons are segments of a gene that does code for protein synthesis that is transcribed to messenger RNA. Both introns and exons sequences are transcribed into RNA. RNA splicing is done by spliceosomes, which are large group ofRNA an ...
Cribado genético del cáncer colorrectal mediante el estudio del
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
state-of-the-art genome engineering in plant biotechnology
... It is now easy to achieve such knockouts in most plant species, thus accelerating plant breeding and allowing the generation of transgene-free plants as this technology is deregulated in multiple countries. Alternatively, allele replacements and gene knock-in events can be achieved by providing a re ...
... It is now easy to achieve such knockouts in most plant species, thus accelerating plant breeding and allowing the generation of transgene-free plants as this technology is deregulated in multiple countries. Alternatively, allele replacements and gene knock-in events can be achieved by providing a re ...
BIN-2002
... into contigs (up to the complete chromosome size) – required for identification of complete genes and their annotation. Assembly provides also information on the genome architecture (linear or circular chromosomes, their number etc.). Contigs may be up to millions of nucleotides in size. An average ...
... into contigs (up to the complete chromosome size) – required for identification of complete genes and their annotation. Assembly provides also information on the genome architecture (linear or circular chromosomes, their number etc.). Contigs may be up to millions of nucleotides in size. An average ...
Repeated DNA sequences - lecture 1
... Two of these (CAG and CCG) are involved in human genetic disease. In the genes that contain them, the copy number (n) of the repeat is variable. If n<40, there are no symptoms. But if n>50, symptoms of the disease start to show (these thresholds are slightly different in different diseases). In many ...
... Two of these (CAG and CCG) are involved in human genetic disease. In the genes that contain them, the copy number (n) of the repeat is variable. If n<40, there are no symptoms. But if n>50, symptoms of the disease start to show (these thresholds are slightly different in different diseases). In many ...
Scott Skellenger Vice President, Technology Product Engineering
... The Center of Engagement with the Genomic Informed Health Record ...
... The Center of Engagement with the Genomic Informed Health Record ...
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON THE UCL CANCER INSTITUTE
... group has a broad interest in genome organization and its influence on gene regulation. We use molecular methods (Hi-C, 4C-Seq, ChIP and 3D microscopy) and computational analysis to investigate the organisation of mammalian chromosomes. Recent work has shown that a set of chromatin proteins, called ...
... group has a broad interest in genome organization and its influence on gene regulation. We use molecular methods (Hi-C, 4C-Seq, ChIP and 3D microscopy) and computational analysis to investigate the organisation of mammalian chromosomes. Recent work has shown that a set of chromatin proteins, called ...
S-strain (virulent)
... center and meet each other in pairs (rungs of the ladder). The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Adenine - Thymine Cytosine - Guanine ...
... center and meet each other in pairs (rungs of the ladder). The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Adenine - Thymine Cytosine - Guanine ...
A History of Genetics and Genomics
... The information age is essential to genomics. The electronic analysis, distribution and storage of genomic data is a hallmark of the science. Critical to this was the development of computers, both large and small, which put computing power in the hands of all scientists. The free distribution of an ...
... The information age is essential to genomics. The electronic analysis, distribution and storage of genomic data is a hallmark of the science. Critical to this was the development of computers, both large and small, which put computing power in the hands of all scientists. The free distribution of an ...
Lab - Protein Synthesis
... Biology Lab Transcription & Translation Background: The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the ...
... Biology Lab Transcription & Translation Background: The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the ...
Evolution process by which species change over time
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...