Bohr`s model of the atom
... back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
... back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... molecule can absorb a photon only if the photon energy precisely matches the pigment energy level • More realistically (C), a range of energies is absorbed • Quantum mechanics and the existence of quantized energies for both photons and pigment molecules are ...
... molecule can absorb a photon only if the photon energy precisely matches the pigment energy level • More realistically (C), a range of energies is absorbed • Quantum mechanics and the existence of quantized energies for both photons and pigment molecules are ...
Ch. 5 Notes: Electrons in Atoms Big Idea: The Atoms of each
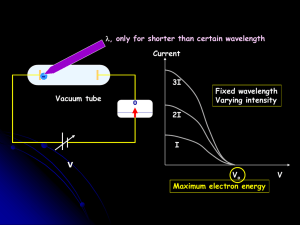
... b. Energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency increases. 4. According to Planck’s theory, for a given frequency, matter can emit or absorb energy only in whole-number multiples of hv. b. The Photoelectric Effect a. Electrons, called photoelectrons, are emitted from a metal’s surface ...
... b. Energy of radiation increases as the radiation’s frequency increases. 4. According to Planck’s theory, for a given frequency, matter can emit or absorb energy only in whole-number multiples of hv. b. The Photoelectric Effect a. Electrons, called photoelectrons, are emitted from a metal’s surface ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
... Most likely outcome of a measurement of position, for a system (or particle) in state y: ...
... Most likely outcome of a measurement of position, for a system (or particle) in state y: ...
Quantum Model of the Atom Power point
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle •The idea of electrons having a dual wave-particle nature troubled scientists. If electrons are both particles and waves, then where are they in the atom? •Heisenberg’s idea involved the detection of electrons. Electrons are detected by their interaction with ph ...
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle •The idea of electrons having a dual wave-particle nature troubled scientists. If electrons are both particles and waves, then where are they in the atom? •Heisenberg’s idea involved the detection of electrons. Electrons are detected by their interaction with ph ...
Chapter 4: Electrons in Atoms I. Properties of Light A
... Translated: “The more certain I am about where it is, the less certain I can be about where it is going. The more certain I am about where it is going, the less certain I can be about where it is.” 2. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both ...
... Translated: “The more certain I am about where it is, the less certain I can be about where it is going. The more certain I am about where it is going, the less certain I can be about where it is.” 2. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both ...
Chapter 4
... outside the nucleus – Why the e- did not crash into the nucleus – Why atoms produce spectra (colors) at specific wavelengths when energy is added ...
... outside the nucleus – Why the e- did not crash into the nucleus – Why atoms produce spectra (colors) at specific wavelengths when energy is added ...
honors-chapter6-reading
... 2. Explain the relationship between quantum of energy and Planck’s constant. Be sure to include the equation for energy in your discussion. 3. Explain the photoelectric effect and role of photons. 4. Why is light (electromagnetic radiation) described as having both wavelike and particle-like charact ...
... 2. Explain the relationship between quantum of energy and Planck’s constant. Be sure to include the equation for energy in your discussion. 3. Explain the photoelectric effect and role of photons. 4. Why is light (electromagnetic radiation) described as having both wavelike and particle-like charact ...
Statistical laws
... For example, there are about 6×1023 molecules for 1 mol gas at standard conditions. The macroscopic properties (pressure, specific heat, phase transition, etc.) are the average of motions of many molecules. Within the framework of classic mechanics, one needs to solve Newton’s equations of 6×1023 ...
... For example, there are about 6×1023 molecules for 1 mol gas at standard conditions. The macroscopic properties (pressure, specific heat, phase transition, etc.) are the average of motions of many molecules. Within the framework of classic mechanics, one needs to solve Newton’s equations of 6×1023 ...
are WAVES. PARTICLES!
... …without knowing which one. Release the particle It should interfere with itself like a bunch of waves that came from each box. ...
... …without knowing which one. Release the particle It should interfere with itself like a bunch of waves that came from each box. ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... negative numbers: #P-hard Estimating a sum of exponentially many nonnegative numbers: Still hard, but known to be in PH ...
... negative numbers: #P-hard Estimating a sum of exponentially many nonnegative numbers: Still hard, but known to be in PH ...
Document
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
Topic 14
... Since, in this case the particle is confined by INFINITE potential barriers, we know particle must be located between x=0 and x=L →Normalisation condition reduces to : ...
... Since, in this case the particle is confined by INFINITE potential barriers, we know particle must be located between x=0 and x=L →Normalisation condition reduces to : ...