Line Spectra and the Bohr Model
... • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can have both wave and particle properties. ...
... • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can have both wave and particle properties. ...
Section 5-1
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
PowerPoint
... theories that are used to explain what is happening in the modern version of Young’s experiment. ...
... theories that are used to explain what is happening in the modern version of Young’s experiment. ...
Energy levels and atomic structures lectures
... Electrons from states with ni > 2 can return, initially, to the first-excited state (nf = 2), emitting one photon and then to the ground state emitting a second photon, with Eph = 10.2 eV, which is part of the Lyman series. Photons from transitions to the first-excited, (n = 2) state of the hydrogen ...
... Electrons from states with ni > 2 can return, initially, to the first-excited state (nf = 2), emitting one photon and then to the ground state emitting a second photon, with Eph = 10.2 eV, which is part of the Lyman series. Photons from transitions to the first-excited, (n = 2) state of the hydrogen ...
Isra University Faculty of Arts and science Course Calendar 2016
... (dual and quad-polar), Hamiltonian corn, the elements of the matrix and the principle of symmetry, the equations of motion for transitions binaries electrodes and magnetic, vibration operations, the behavior of the case for the transition of dual-electrode, properties, transit behavior for the trans ...
... (dual and quad-polar), Hamiltonian corn, the elements of the matrix and the principle of symmetry, the equations of motion for transitions binaries electrodes and magnetic, vibration operations, the behavior of the case for the transition of dual-electrode, properties, transit behavior for the trans ...
presentation source
... The W and Z are extremely short-lived, but can be identified by their decay modes, also predicted by electroweak theory ene ...
... The W and Z are extremely short-lived, but can be identified by their decay modes, also predicted by electroweak theory ene ...
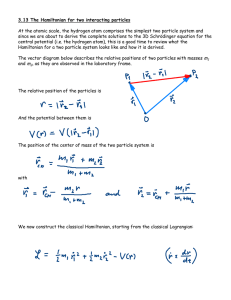
3.13 The Hamiltonian for two interacting particles At the atomic scale
... central potential (i.e. the hydrogen atom), this is a good time to review what the Hamiltonian for a two particle system looks like and how it is derived. The vector diagram below describes the relative positions of two particles with masses m1 and m2, as they are observed in the laboratory frame. ...
... central potential (i.e. the hydrogen atom), this is a good time to review what the Hamiltonian for a two particle system looks like and how it is derived. The vector diagram below describes the relative positions of two particles with masses m1 and m2, as they are observed in the laboratory frame. ...
Chapter 7
... • The energy of a photon given off can be calculated by subtracting the lower energy level from the higher energy level (energy of a photon is positive) ...
... • The energy of a photon given off can be calculated by subtracting the lower energy level from the higher energy level (energy of a photon is positive) ...
The problem states
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. ...
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. ...
Wave-Particle Duality
... problems throws new light on perhaps the oldest philosophical problem, the ancient question about the existential status of ideas, and the relation between the ideal and the material. Put most simply, the quantum wave function is an idea, pure information about the possible places that matter may be ...
... problems throws new light on perhaps the oldest philosophical problem, the ancient question about the existential status of ideas, and the relation between the ideal and the material. Put most simply, the quantum wave function is an idea, pure information about the possible places that matter may be ...
The Blind Men and the Quantum
... Paradox 4 (non-locality): EPR Experiments Malus and Furry An EPR Experiment measures the correlated polarizations of a pair of entangled photons, obeying Malus’ Law [P(qrel) = Cos2qrel] The measurement gives the same result as if both filters were in the same arm. Furry proposed to place both photo ...
... Paradox 4 (non-locality): EPR Experiments Malus and Furry An EPR Experiment measures the correlated polarizations of a pair of entangled photons, obeying Malus’ Law [P(qrel) = Cos2qrel] The measurement gives the same result as if both filters were in the same arm. Furry proposed to place both photo ...
Problem set 6
... equation and give a quasi-physical interpretation of any new quantities that appear in your answer. 3. Consider the classical mechanics of a particle of mass m in an SHO potential V(x) = 12 mω2 x2 . Suppose x(t) is a classical trajectory between xi (ti ) and x f (t f ) and let x(t)+δx(t) be a neighb ...
... equation and give a quasi-physical interpretation of any new quantities that appear in your answer. 3. Consider the classical mechanics of a particle of mass m in an SHO potential V(x) = 12 mω2 x2 . Suppose x(t) is a classical trajectory between xi (ti ) and x f (t f ) and let x(t)+δx(t) be a neighb ...
Physics and the Search for Ultimate BuildingBlocks
... through slit A or slit B, then one can say it goes through either slit A or slit B. [otherwise] one may not say that an electron goes through either slit A or slit B. If one does say that, and starts to make any deductions from the statement, he will make errors in the analysis. This is the logical ...
... through slit A or slit B, then one can say it goes through either slit A or slit B. [otherwise] one may not say that an electron goes through either slit A or slit B. If one does say that, and starts to make any deductions from the statement, he will make errors in the analysis. This is the logical ...
Introduction to Quantum Mechanic
... concept that all matter and energy exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. A central concept of quantum mechanics, duality, addresses the inadequacy of classical concepts like "particle" and "wave" in fully describing the behavior of small-scale objects. Various interpretations of quan ...
... concept that all matter and energy exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. A central concept of quantum mechanics, duality, addresses the inadequacy of classical concepts like "particle" and "wave" in fully describing the behavior of small-scale objects. Various interpretations of quan ...