CVT 109 - University Health
... to teach physiology relavant to noninvasive vascular technology. Major areas of interrogation Intracranial cerebrovascular Extracranial cerebrovascular Abdominal visceral vascular Peripheral arterial Peripheral venous ...
... to teach physiology relavant to noninvasive vascular technology. Major areas of interrogation Intracranial cerebrovascular Extracranial cerebrovascular Abdominal visceral vascular Peripheral arterial Peripheral venous ...
Vascular Tone
... • Gravity forces blood to pool in the lower extremities. – Thus pressure in the lower veins is greater than that of the higher veins. ...
... • Gravity forces blood to pool in the lower extremities. – Thus pressure in the lower veins is greater than that of the higher veins. ...
Smoking can cost an arm and a leg KEY
... Only blood pressure is taken. Nothing is painful. The gel may be cold. ...
... Only blood pressure is taken. Nothing is painful. The gel may be cold. ...
Methods S1.
... obstruct the same caliber vessels as affected by human PVD (<100µm)[3], noting that >99.8% of 50µm diameter microspheres lodge in the baboon pulmonary circulation[4]. Of note, the use of microspheres did not affect post procedural recovery. Post Procedural Animal Care At the end of the procedure, th ...
... obstruct the same caliber vessels as affected by human PVD (<100µm)[3], noting that >99.8% of 50µm diameter microspheres lodge in the baboon pulmonary circulation[4]. Of note, the use of microspheres did not affect post procedural recovery. Post Procedural Animal Care At the end of the procedure, th ...
Blood Pressure - Doctor Jade Main
... located in carotid arteries & aorta monitor stretch in walls due to pressure of blood flowing to brain two types-carotid sinus reflex & aortic reflex ...
... located in carotid arteries & aorta monitor stretch in walls due to pressure of blood flowing to brain two types-carotid sinus reflex & aortic reflex ...
Laboratory Exercise 10: Physiology of Ventilation (Breathing)
... breathing muscles relax, the thoracic cage recoils, pressure gradients are reversed. The greater intrathoracic pressure causes air to be expired. A breathing cycle (one breath) includes inspiration and expiration. A normal breathing rate at rest for an adult is 12-18 breaths/minute. This called eupn ...
... breathing muscles relax, the thoracic cage recoils, pressure gradients are reversed. The greater intrathoracic pressure causes air to be expired. A breathing cycle (one breath) includes inspiration and expiration. A normal breathing rate at rest for an adult is 12-18 breaths/minute. This called eupn ...
Circulatory system I: Blood Circulatory system I: Blood
... – Volume of blood flowing through vessel, organ, or circulatory system (=CO) – Varies within body organs ...
... – Volume of blood flowing through vessel, organ, or circulatory system (=CO) – Varies within body organs ...
Lab_respiration - Ping Pong
... As is well know, the volume of gases varies with pressure and temperature. In order to measure the lung volumes, we breathe into a spirometer or pneumotachograph. The volume measured must then be correct for the temperature difference between the lungs and the measuring apparatus as well as for the ...
... As is well know, the volume of gases varies with pressure and temperature. In order to measure the lung volumes, we breathe into a spirometer or pneumotachograph. The volume measured must then be correct for the temperature difference between the lungs and the measuring apparatus as well as for the ...
Human homeostasis
... and retention resulting in changed viscosity may also effect the delicate balance of blood volume and pressure made available to brain areas. Refer to wikipedia article on cerebral blood flow. Physical activity or restlessness, physical exhibitions of nervousness, all also likely slightly modify or ...
... and retention resulting in changed viscosity may also effect the delicate balance of blood volume and pressure made available to brain areas. Refer to wikipedia article on cerebral blood flow. Physical activity or restlessness, physical exhibitions of nervousness, all also likely slightly modify or ...
Urinary System - Mohawk Medicinals
... Up to 99% of water can be reabsorbed Causes aquaporins to be inserted into the walls of the collecting duct (more ADH = more aquaporins) Controls water reabsorption ...
... Up to 99% of water can be reabsorbed Causes aquaporins to be inserted into the walls of the collecting duct (more ADH = more aquaporins) Controls water reabsorption ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Endothelial cells move it to the interstitial space between the two layers of the artery Macrophages consume it and become lipid filled foam cells – In response they release cytokines which causes smooth muscle growth in the area & forms a lesion on the arterial wall ...
... Endothelial cells move it to the interstitial space between the two layers of the artery Macrophages consume it and become lipid filled foam cells – In response they release cytokines which causes smooth muscle growth in the area & forms a lesion on the arterial wall ...
vein - Highline Canvas
... Used for small or fragile veins that are difficult to draw Winged needle inserted at about 5° angle then threaded into vein ...
... Used for small or fragile veins that are difficult to draw Winged needle inserted at about 5° angle then threaded into vein ...
The Renal System
... plasma level is constant. urine is collected for a timed period to get urine flow rate and urinary concentration of ...
... plasma level is constant. urine is collected for a timed period to get urine flow rate and urinary concentration of ...
3. Respiration - Ping Pong
... To create a flow of air in to the lungs, the surrounding tissues need to create and change the pressure surrounding the lungs. These pressures are relatively small and are usually described in cmH2O. The air pressure is set at zero and the other pressures are described as deviations from this. After ...
... To create a flow of air in to the lungs, the surrounding tissues need to create and change the pressure surrounding the lungs. These pressures are relatively small and are usually described in cmH2O. The air pressure is set at zero and the other pressures are described as deviations from this. After ...
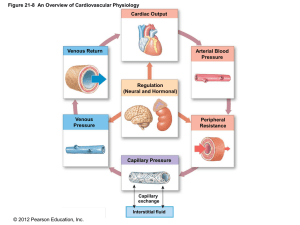
Physiology of Circulation
... arterial end , hydrostatic pressure gradient = blood pressure- tissue pressure = 35-2=33 mmHg pushing fluid out (filtration). oncotic pressure gradient = plasma oncotic pressure – tissue oncotic pressure = 25-2=23 mmHg pulling fluid in (reabsorption) . The net result at the arterial end is 33-23=10 ...
... arterial end , hydrostatic pressure gradient = blood pressure- tissue pressure = 35-2=33 mmHg pushing fluid out (filtration). oncotic pressure gradient = plasma oncotic pressure – tissue oncotic pressure = 25-2=23 mmHg pulling fluid in (reabsorption) . The net result at the arterial end is 33-23=10 ...
Cerebellum
... • Venous BP is steady and changes little during the cardiac cycle • The pressure gradient in the venous system is only about 20 ...
... • Venous BP is steady and changes little during the cardiac cycle • The pressure gradient in the venous system is only about 20 ...
Review for Medical Physiology
... positive-feedback increase in sodium permeability caused by the transient opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. At almost the same time, the permeability to potassium decreases as certain potassium channels close, which contributes to the membrane depolarization. These potassium channels remain ...
... positive-feedback increase in sodium permeability caused by the transient opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. At almost the same time, the permeability to potassium decreases as certain potassium channels close, which contributes to the membrane depolarization. These potassium channels remain ...
(Renal haemodynamic and GFR).
... • Describe that the mechanism of urine formation include three basic processes; glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, ...
... • Describe that the mechanism of urine formation include three basic processes; glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, ...
Sympathetic reflex compensations in shock
... Readjustment of blood volume may require 1 to 48 hours. ...
... Readjustment of blood volume may require 1 to 48 hours. ...
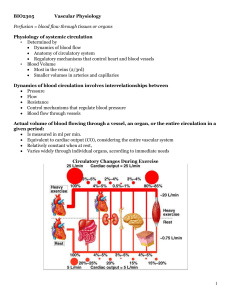
Chapter 10 - Vascular Physiology
... Pressure of arterial blood is regulated by blood volume, TPR, and cardiac rate. • MAP=CO TPR • Arteriole resistance is greatest because they have the smallest diameter. • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total cross-sectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase ...
... Pressure of arterial blood is regulated by blood volume, TPR, and cardiac rate. • MAP=CO TPR • Arteriole resistance is greatest because they have the smallest diameter. • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total cross-sectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase ...
Diastolic pressure
... elevation of blood pressure by sympathetic stimulation of the heart and peripheral vasoconstriction ...
... elevation of blood pressure by sympathetic stimulation of the heart and peripheral vasoconstriction ...
[j26] Chapter 14#
... specifically operate to control the work of the heart (cardiac output) and to ensure normal regulation of blood flow and blood pressure throughout the body. It is not surprising to learn that blood will always flow from higherpressure blood vessels toward lower-pressure blood vessels. This physical ...
... specifically operate to control the work of the heart (cardiac output) and to ensure normal regulation of blood flow and blood pressure throughout the body. It is not surprising to learn that blood will always flow from higherpressure blood vessels toward lower-pressure blood vessels. This physical ...


















![[j26] Chapter 14#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000367221_1-b8dd3faa03e0a519508f460a9af94122-300x300.png)