cardiac output
... requires a given amount of oxygen, HR at any given intensity will be lower due to an increased SV. A trained individual will have to work at higher intensities to achieve the same HR he or she achieved prior to physical ...
... requires a given amount of oxygen, HR at any given intensity will be lower due to an increased SV. A trained individual will have to work at higher intensities to achieve the same HR he or she achieved prior to physical ...
Key Questions for Understanding Respiratory Physiology
... Key Questions for Understanding Respiratory Physiology ...
... Key Questions for Understanding Respiratory Physiology ...
Placenta - Academics
... (b) Systemic vascular resistance decreases by 25--30%, the effect mediated by progesterone, prostacyclin and oestrogen. (c) Central venous pressure and pulmonary artery pressure are unchanged during normal pregnancy. During labour each uterine contraction expels 500 ml of blood into the circulation ...
... (b) Systemic vascular resistance decreases by 25--30%, the effect mediated by progesterone, prostacyclin and oestrogen. (c) Central venous pressure and pulmonary artery pressure are unchanged during normal pregnancy. During labour each uterine contraction expels 500 ml of blood into the circulation ...
Blood Pressure Controls
... Note: In an elastic system like blood vessels, the overall size of the system responds to the volume of its contents somewhat like a balloon with a minimal and maximal overall size. It also responds to access to vessels that can be controlled by muscles. In blood vessels, if something decreases the ...
... Note: In an elastic system like blood vessels, the overall size of the system responds to the volume of its contents somewhat like a balloon with a minimal and maximal overall size. It also responds to access to vessels that can be controlled by muscles. In blood vessels, if something decreases the ...
The Diagnosis of Uterine Rupture with VBAC
... • May require dose adjustment • Rapid decrease in clearance in the first two weeks postpartum Tran TA, et al. Neurology 2002; 59: 251-55. ...
... • May require dose adjustment • Rapid decrease in clearance in the first two weeks postpartum Tran TA, et al. Neurology 2002; 59: 251-55. ...
The Diagnosis of Uterine Rupture with VBAC
... • May require dose adjustment • Rapid decrease in clearance in the first two weeks postpartum Tran TA, et al. Neurology 2002; 59: 251-55. ...
... • May require dose adjustment • Rapid decrease in clearance in the first two weeks postpartum Tran TA, et al. Neurology 2002; 59: 251-55. ...
Unit Four Essential Questions
... oxygenated. After the blood is oxygenated it then reenters the heart through the pulmonary veins and into the left atrium. It then enters the left ventricle by using the bicuspid/ mitral valve then leaves to go throughout the body using the aortic valve and then through the aorta. ...
... oxygenated. After the blood is oxygenated it then reenters the heart through the pulmonary veins and into the left atrium. It then enters the left ventricle by using the bicuspid/ mitral valve then leaves to go throughout the body using the aortic valve and then through the aorta. ...
13/mhso2/015 course code: phs212 physiology of
... musculature and the smooth muscles of the arteriolar and arterial wall, plays a key role in the erectile process, in the flaccid state, these smooth muscles are tonically contracted, allowing only small amount of arterial flow for nutritional purposes. The blood partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) is a ...
... musculature and the smooth muscles of the arteriolar and arterial wall, plays a key role in the erectile process, in the flaccid state, these smooth muscles are tonically contracted, allowing only small amount of arterial flow for nutritional purposes. The blood partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) is a ...
Blood Pressure and Pulse BIOL 204, Section 550 Lab Report By
... also able to recover faster than the poor conditioned subject, showing a lower heart rate and blood pressure after two minutes (from 92 bpm and 130/80 mmHg immediately following exercise to 75 bpm and 100/68 mmHg two minutes after exercise). The poorly conditioned subject’s heart rate took the full ...
... also able to recover faster than the poor conditioned subject, showing a lower heart rate and blood pressure after two minutes (from 92 bpm and 130/80 mmHg immediately following exercise to 75 bpm and 100/68 mmHg two minutes after exercise). The poorly conditioned subject’s heart rate took the full ...
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
... measure of the amount of friction blood encounters as it passes through vessels. • Blood Pressure =the force per unit area exerted on a vessel wall by the blood contained within it (expressed in mm Hg). • Blood flow =the volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation i ...
... measure of the amount of friction blood encounters as it passes through vessels. • Blood Pressure =the force per unit area exerted on a vessel wall by the blood contained within it (expressed in mm Hg). • Blood flow =the volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation i ...
circ and homeo
... through a closed circuit of blood vessels. • This closed system keeps blood contained as it passes through various “circulations” of the body. ...
... through a closed circuit of blood vessels. • This closed system keeps blood contained as it passes through various “circulations” of the body. ...
1-Acute Control of Local Blood Flow
... leads to formation of the vascular growth factors (also called "angiogenic factors").They cause new vessels to sprout from other small vessels. So oxygen is important not only for acute control of local blood flow but also for long-term control. One example of this is increased vascularity in tissue ...
... leads to formation of the vascular growth factors (also called "angiogenic factors").They cause new vessels to sprout from other small vessels. So oxygen is important not only for acute control of local blood flow but also for long-term control. One example of this is increased vascularity in tissue ...
Cardiovascular - Cambridge Electronic Design
... Output pulse trains, variable amplitude pulses, ramp, sine and arbitrary waveforms during sampling Responds in real-time to changes or features in the sampled data Graphical sequence editor ...
... Output pulse trains, variable amplitude pulses, ramp, sine and arbitrary waveforms during sampling Responds in real-time to changes or features in the sampled data Graphical sequence editor ...
Schedules
... designed to clinical standards, but it feels weird. You should experience it for yourself. Although small shocks are uncomfortable rather than painful, large shocks can be painful. Remember that the pain results not from damage to your body, but from action potentials set off in the nerve fibres tha ...
... designed to clinical standards, but it feels weird. You should experience it for yourself. Although small shocks are uncomfortable rather than painful, large shocks can be painful. Remember that the pain results not from damage to your body, but from action potentials set off in the nerve fibres tha ...
PHS_204_ASSIGNMENT_1
... Coitus is the sexual union between a male and female involving insertion of penis into the vagina in which there is excitement until orgasm and ejaculation occur. Considered from this viewpoint, the process of coitus with the subsequent climax may be profitably studied in both sexes in human which t ...
... Coitus is the sexual union between a male and female involving insertion of penis into the vagina in which there is excitement until orgasm and ejaculation occur. Considered from this viewpoint, the process of coitus with the subsequent climax may be profitably studied in both sexes in human which t ...
PHS_204_ASSIGNMENTT_1
... Coitus is the sexual union between a male and female involving insertion of penis into the vagina in which there is excitement until orgasm and ejaculation occur. Considered from this viewpoint, the process of coitus with the subsequent climax may be profitably studied in both sexes in human which t ...
... Coitus is the sexual union between a male and female involving insertion of penis into the vagina in which there is excitement until orgasm and ejaculation occur. Considered from this viewpoint, the process of coitus with the subsequent climax may be profitably studied in both sexes in human which t ...
File
... • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels through the systemic circulation • Is inversely related to the total cross-sectional area • Is fastest in the aorta, slowest in the capillaries, increases again in veins • Slow ...
... • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels through the systemic circulation • Is inversely related to the total cross-sectional area • Is fastest in the aorta, slowest in the capillaries, increases again in veins • Slow ...
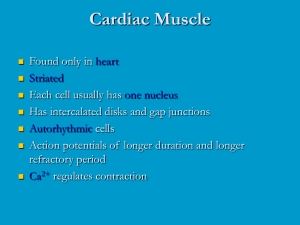
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer ...
... Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer ...
Models of Cheyne-Stokes Respiration with Cardiovascular
... The model assumes that the peripheral chemoreceptors (at the carotid bodies) monitor concentration in arterial blood (indirectly through pH of carbonic acid). [Ref. Lorenzi-Filho et al. (1999)] If the level increases, the brain stimulates an increase in the ventilation rate (and similarly for a decr ...
... The model assumes that the peripheral chemoreceptors (at the carotid bodies) monitor concentration in arterial blood (indirectly through pH of carbonic acid). [Ref. Lorenzi-Filho et al. (1999)] If the level increases, the brain stimulates an increase in the ventilation rate (and similarly for a decr ...
1 Physiology week 9 – Cardiovascular (flow/BP)
... ‘flow varies directly and resistance inversely with the fourth power of the radius’ Critical closing pressure – the pressure within a vessel lumen at which blood flow ceases. Law of Laplace P=T/r (for spherical structure this is 2T/r) W can be ignored in thin walled structures. (transmural P = P ins ...
... ‘flow varies directly and resistance inversely with the fourth power of the radius’ Critical closing pressure – the pressure within a vessel lumen at which blood flow ceases. Law of Laplace P=T/r (for spherical structure this is 2T/r) W can be ignored in thin walled structures. (transmural P = P ins ...
File - Doctorswriting
... A. resistance is inversely proportional to the square of the radius B. the wall tension necessary to balance transmural pressure is inversely proportional to the radius (PT/R) C. velocity is equal to flow for any given diameter D. flow and resistance are both related, reciprocally, to the radius to ...
... A. resistance is inversely proportional to the square of the radius B. the wall tension necessary to balance transmural pressure is inversely proportional to the radius (PT/R) C. velocity is equal to flow for any given diameter D. flow and resistance are both related, reciprocally, to the radius to ...
File - Doctorswriting
... 39. All of the following are true of venule walls except A. Are slightly thinner than capillaries B. Are thin and easily distended C. Contain relatively little smooth muscle D. Venoconstriction is caused by noradrenergic nerves and noradrenaline E. All are correct 40. Which of the following is inco ...
... 39. All of the following are true of venule walls except A. Are slightly thinner than capillaries B. Are thin and easily distended C. Contain relatively little smooth muscle D. Venoconstriction is caused by noradrenergic nerves and noradrenaline E. All are correct 40. Which of the following is inco ...
Chapter5 Respiration
... Chemical Regulation of Respiration The respiratory control system are very sensitive to alterations in the internal environment of the body. Changes in the body PCO2, pH and PO2 cause changes in alveolar ventilation designed to restore these variable to their normal values. 1.Carbon dioxide (CO2) T ...
... Chemical Regulation of Respiration The respiratory control system are very sensitive to alterations in the internal environment of the body. Changes in the body PCO2, pH and PO2 cause changes in alveolar ventilation designed to restore these variable to their normal values. 1.Carbon dioxide (CO2) T ...
PP Chapter 19-Blood Vessels
... this prevents blood from reentering the heart the walls of the aorta recoil which helps to maintain adequate pressure on the reducing blood volume to keep blood flowing forward in small vessels – diastolic pressure (70-80 mmHg) ...
... this prevents blood from reentering the heart the walls of the aorta recoil which helps to maintain adequate pressure on the reducing blood volume to keep blood flowing forward in small vessels – diastolic pressure (70-80 mmHg) ...
CHAPTER 2 - PULMONARY FUNCTION, TRANSPORT OF BLOOD
... • To increase stimulation of the SA node. • Thereby increasing heart rate. 9) Running a marathon in hot conditions sets up a competition between the active muscles and the skin for limited blood supply. How does the human body respond to meet the needs of supplying oxygen to exercising muscle an ...
... • To increase stimulation of the SA node. • Thereby increasing heart rate. 9) Running a marathon in hot conditions sets up a competition between the active muscles and the skin for limited blood supply. How does the human body respond to meet the needs of supplying oxygen to exercising muscle an ...