Midterm 2 - Creighton Biology
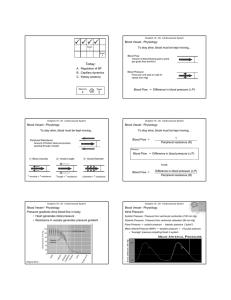
... 20. Which of the following statements about the formation of lymph is true? a. Hydrostatic pressure driving fluid out of the capillaries is slightly greater than osmotic pressure in the opposite direction, resulting in the formation of about 4 liters of fluid per day. b. Hydrostatic pressure driving ...
... 20. Which of the following statements about the formation of lymph is true? a. Hydrostatic pressure driving fluid out of the capillaries is slightly greater than osmotic pressure in the opposite direction, resulting in the formation of about 4 liters of fluid per day. b. Hydrostatic pressure driving ...
BRS Physiology
... calculated HCO3– of 32 mEq/L. His serum cortisol and urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) are normal, his serum aldosterone is increased, and his plasma renin activity is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hypertension? ...
... calculated HCO3– of 32 mEq/L. His serum cortisol and urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) are normal, his serum aldosterone is increased, and his plasma renin activity is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hypertension? ...
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions
... impermeable to water, and urine is dilute.] b. When blood volume drops, venous return to the right heart drops, decreasing the secretion of atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH). The decreased ANH causes more Na+ reabsorbtion in the collecting duct, causing more water reabsorption. This hormonal reflex h ...
... impermeable to water, and urine is dilute.] b. When blood volume drops, venous return to the right heart drops, decreasing the secretion of atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH). The decreased ANH causes more Na+ reabsorbtion in the collecting duct, causing more water reabsorption. This hormonal reflex h ...
One-and-a-Half Ventricular Repair through the Right Lateral
... ventricular outflow to the main pulmonary artery was verified, and no sinusoidal communications were observed. Diameters of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves were found to be 61% and 74%, respectively, of the anticipated normal values. These diameters corresponded to Z values of –4.6 and –3.1, resp ...
... ventricular outflow to the main pulmonary artery was verified, and no sinusoidal communications were observed. Diameters of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves were found to be 61% and 74%, respectively, of the anticipated normal values. These diameters corresponded to Z values of –4.6 and –3.1, resp ...
Musculoskeletal system - Responses to exercise PPT
... You need to make sure your group researches your particular area thoroughly and covers the following responses depending on what system has been assigned. Your group will then present back the findings to the rest of the group through a detailed and informative A3 poster. • Musculoskeletal response: ...
... You need to make sure your group researches your particular area thoroughly and covers the following responses depending on what system has been assigned. Your group will then present back the findings to the rest of the group through a detailed and informative A3 poster. • Musculoskeletal response: ...
Physiology د. نصير جواد المختار Lecture X: Acid – Base Balance The
... The H ion concentration has always to be kept with normal range, otherwise enzymatic activities might be affected as increasing or decreasing the level and this might either stimulate or depress the activity. In general the H+ concentration of extracellular fluid represented by blood is usually cons ...
... The H ion concentration has always to be kept with normal range, otherwise enzymatic activities might be affected as increasing or decreasing the level and this might either stimulate or depress the activity. In general the H+ concentration of extracellular fluid represented by blood is usually cons ...
BRS Physiology
... is directly proportional to volume and inversely proportional to pressure. describes how volume changes in response to a change in pressure. is much greater for veins than for arteries. As a result, more blood volume is contained in the veins (unstressed volume) than in the arteries (stressed volume ...
... is directly proportional to volume and inversely proportional to pressure. describes how volume changes in response to a change in pressure. is much greater for veins than for arteries. As a result, more blood volume is contained in the veins (unstressed volume) than in the arteries (stressed volume ...
Blood Vessel - Oregon State University
... 1) Osmotic Pressure: Diffusion of water (↓ [solute] to ↑ [solute]) a) Capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure (OPC): ...
... 1) Osmotic Pressure: Diffusion of water (↓ [solute] to ↑ [solute]) a) Capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure (OPC): ...
hey every body, this is the 1st lec. Of the renal system by dr. Saleem
... sometimes to 30%-40% because these animals (like rabbits) need to keep water in their bodies. ...
... sometimes to 30%-40% because these animals (like rabbits) need to keep water in their bodies. ...
Physiology – spinal anesthesia MGMC
... medullary blood flow Not advisable to control IPPV decreases venous return and cardiac output ...
... medullary blood flow Not advisable to control IPPV decreases venous return and cardiac output ...
Respiratory Physiology Part I
... • During inspiration, respiratory muscles contract, and thoracic cavity expands (more volume), lowering the pressure in the thoracic cavity • Pressure in lungs is now greater than the pressure in thoracic cavity so they expand (increase in volume, decrease in pressure) • PATM > Palv Air flows in to ...
... • During inspiration, respiratory muscles contract, and thoracic cavity expands (more volume), lowering the pressure in the thoracic cavity • Pressure in lungs is now greater than the pressure in thoracic cavity so they expand (increase in volume, decrease in pressure) • PATM > Palv Air flows in to ...
הצעה למבנה הקוריקולום לקורסים הקדם
... of systolic and diastolic pressures. Given systolic and diastolic blood pressures, calculate the pulse pressure and the mean arterial pressure. 2) Describe how arterial systolic, diastolic, mean, and pulse pressure are affected by changes in a) stroke volume, b) heart rate, c) arterial compliance, a ...
... of systolic and diastolic pressures. Given systolic and diastolic blood pressures, calculate the pulse pressure and the mean arterial pressure. 2) Describe how arterial systolic, diastolic, mean, and pulse pressure are affected by changes in a) stroke volume, b) heart rate, c) arterial compliance, a ...
Physiology of Circulation
... the slower the velocity. [capillaries, as a group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
... the slower the velocity. [capillaries, as a group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
Inotropes - GEOCITIES.ws
... • B high flow oxygen and ventilatory support if required • C circulatory access; relevant blood tests; fluid bolus if hypovolaemia suspected and repeated depending on response (HR, BP, UO, CVP,PAWP, peripheral perfusion, MVO2, lactate, ABG); antibiotics; cardioversion, inotropes when intravascular v ...
... • B high flow oxygen and ventilatory support if required • C circulatory access; relevant blood tests; fluid bolus if hypovolaemia suspected and repeated depending on response (HR, BP, UO, CVP,PAWP, peripheral perfusion, MVO2, lactate, ABG); antibiotics; cardioversion, inotropes when intravascular v ...
Cardiac Pharmacology
... preload, (or both) and therefore drop BP • Some dilate arterioles – Decreases PVR (afterload) – Hydralazine ...
... preload, (or both) and therefore drop BP • Some dilate arterioles – Decreases PVR (afterload) – Hydralazine ...
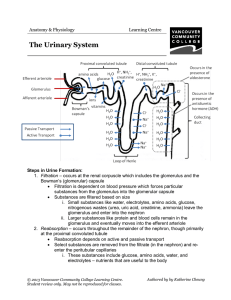
Urinary System - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
International Mentee Application
... outside the United States. The objectives of this program are: 1) to help young physicians, clinicians and scientists develop their professional careers; 2) to promote the highest possible quality of science and practice in cardiovascular and cerebral vascular disease throughout the world by enrichi ...
... outside the United States. The objectives of this program are: 1) to help young physicians, clinicians and scientists develop their professional careers; 2) to promote the highest possible quality of science and practice in cardiovascular and cerebral vascular disease throughout the world by enrichi ...
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... the slower the velocity. [capillaries, as a group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
... the slower the velocity. [capillaries, as a group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
Building a Comprehensive Nutritional Practice
... The volume of blood within a ventricle immediately before a contraction is known as the end-diastolic volume (EDV) . Similarly, the volume of blood left in a ventricle at the end of contraction is endsystolic volume. The difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volumes (ESV) re ...
... The volume of blood within a ventricle immediately before a contraction is known as the end-diastolic volume (EDV) . Similarly, the volume of blood left in a ventricle at the end of contraction is endsystolic volume. The difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volumes (ESV) re ...
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... are considering the diffusion of a gas, the concentration gradient (C1 – C2) will generally be reported as a partial pressure gradient (P1 – P2), but do not confuse this partial pressure gradient with the (hydrostatic) pressure gradient in Poiseuille’s law; these are two very different kinds of pres ...
... are considering the diffusion of a gas, the concentration gradient (C1 – C2) will generally be reported as a partial pressure gradient (P1 – P2), but do not confuse this partial pressure gradient with the (hydrostatic) pressure gradient in Poiseuille’s law; these are two very different kinds of pres ...
CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 2 Physiology and Health
... I can identify obesity as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes. I can state that limiting fats in the diet reduces high calorific value and limiting free sugars removes the issue of having no metabolic energy expended in their digestion. I can calculate body mass ...
... I can identify obesity as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes. I can state that limiting fats in the diet reduces high calorific value and limiting free sugars removes the issue of having no metabolic energy expended in their digestion. I can calculate body mass ...
Physiology of Circulation
... group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
... group, make up the largest total cross – sectional area in the cardiovascular system, as a result allow the slowest velocity of blood flow]. ...
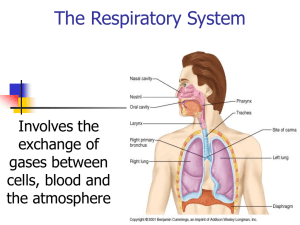
The Respiratory System
... epithelium Type I and type II alveolar cells Diffusion of gases takes place across an alveolar-capillary respiratory membrane ...
... epithelium Type I and type II alveolar cells Diffusion of gases takes place across an alveolar-capillary respiratory membrane ...