physiol mcq - WordPress.com
... Dr S Programme Physiology MCQ [File MCQPHYS3] Respiration/alimentary tract/kidney Type A ...
... Dr S Programme Physiology MCQ [File MCQPHYS3] Respiration/alimentary tract/kidney Type A ...
LIFE Bringing Research to
... Patients had to comply with the study which required them to use their CPAP machine every night for a minimum of four hours over the course of a year. Each of the CPAP devices contained a chip that would record usage date, allowing Jassal to confirm that patients were compliant. “When we followed th ...
... Patients had to comply with the study which required them to use their CPAP machine every night for a minimum of four hours over the course of a year. Each of the CPAP devices contained a chip that would record usage date, allowing Jassal to confirm that patients were compliant. “When we followed th ...
Regulation of Blood
... unchanged. However, as plasma volume is restored [as a result of increased aldosterone levels (see the answer to Question 8), increased capillary absorption of fluid, and the infusion of saline], plasma volume increases, but red blood cell volume does riot. (It takes about 7 days for a stem cell to ...
... unchanged. However, as plasma volume is restored [as a result of increased aldosterone levels (see the answer to Question 8), increased capillary absorption of fluid, and the infusion of saline], plasma volume increases, but red blood cell volume does riot. (It takes about 7 days for a stem cell to ...
Q = HR x SV
... science concerned with the function of organisms and their parts. Exercise physiology is a branch of physiology that deals with the functioning of the body during exercise. ...
... science concerned with the function of organisms and their parts. Exercise physiology is a branch of physiology that deals with the functioning of the body during exercise. ...
Hypotension
... CO = Stroke Volume x Heart rate Remember: normal valves sinus rhythm no hypovolaemia obstruction BP sensed by: ...
... CO = Stroke Volume x Heart rate Remember: normal valves sinus rhythm no hypovolaemia obstruction BP sensed by: ...
Exam #3
... 34) You are sitting in the woods after eating a very messy sandwich, so you are covered with sandwich drippings, when all of a sudden you realize that your feet are resting on a bear cub, and his mother is out to get you like you got the sandwich. So you stand up and run like mad. In this situation ...
... 34) You are sitting in the woods after eating a very messy sandwich, so you are covered with sandwich drippings, when all of a sudden you realize that your feet are resting on a bear cub, and his mother is out to get you like you got the sandwich. So you stand up and run like mad. In this situation ...
Pulse
... bath given. S.Niggemeier RN---------------------------4:45pm T-102.2 A P- 88 R-18 BP 130/78 taking fluids, feels “better than before”. S.Niggemeier RN----------------------------- ...
... bath given. S.Niggemeier RN---------------------------4:45pm T-102.2 A P- 88 R-18 BP 130/78 taking fluids, feels “better than before”. S.Niggemeier RN----------------------------- ...
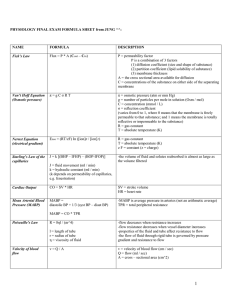
Cumulative Formula Sheet
... k = hydraulic constant (ml / min) (k depends on permeability of capillaries, e.g. fenestration) Cardiac Output ...
... k = hydraulic constant (ml / min) (k depends on permeability of capillaries, e.g. fenestration) Cardiac Output ...
Flight Physiology - San Juan Island EMS and MedEvac
... nitrogen itself is not a problem. Eventually, it would reach a state of equilibrium and stop on-gassing (packing in). The problem begins when the diver ascends and reduces the pressure his body is under, making the nitrogen less soluble in his tissues. If the diver comes up too fast (releases the pr ...
... nitrogen itself is not a problem. Eventually, it would reach a state of equilibrium and stop on-gassing (packing in). The problem begins when the diver ascends and reduces the pressure his body is under, making the nitrogen less soluble in his tissues. If the diver comes up too fast (releases the pr ...
Physiology of blood vessels. Systemic circulation
... Functional types of vessels Resistive vessels or arterioles, smallest arteries; lead to capillary beds Sphincters Shunts Arterial anastomoses provide alternate pathways (collateral channels) for blood to reach a given body region. If one branch is blocked, the collateral channel can supply the area ...
... Functional types of vessels Resistive vessels or arterioles, smallest arteries; lead to capillary beds Sphincters Shunts Arterial anastomoses provide alternate pathways (collateral channels) for blood to reach a given body region. If one branch is blocked, the collateral channel can supply the area ...
Bermingham, M
... OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect of an 8-week, water-based exercise program (experimental group) with that of an upper-extremity function program (control group) to increase cardiovascular fitness within a community setting for people with stroke. DESIGN: Single-blind randomized controlled trial. S ...
... OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect of an 8-week, water-based exercise program (experimental group) with that of an upper-extremity function program (control group) to increase cardiovascular fitness within a community setting for people with stroke. DESIGN: Single-blind randomized controlled trial. S ...
Biology Lesson 1 Keeping Healthy Learning Objectives: In this
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
System Responses to Exercise and Disease
... heart rate and TPR. Remember that the regulated variable here is mean arterial pressure. In this example, the blood loss is mild (no more than about 1 liter for a 60-70 Kg person) and the reflexive compensation is able to protect MAP while slower responses can restore the lost fluid, electrolytes an ...
... heart rate and TPR. Remember that the regulated variable here is mean arterial pressure. In this example, the blood loss is mild (no more than about 1 liter for a 60-70 Kg person) and the reflexive compensation is able to protect MAP while slower responses can restore the lost fluid, electrolytes an ...
Fundamentals II
... aspects of well being. Circulation is monitored through assessment of Vital Signs along with other collected data. The patient’s physiological status is reflected by their vital signs. ...
... aspects of well being. Circulation is monitored through assessment of Vital Signs along with other collected data. The patient’s physiological status is reflected by their vital signs. ...
Document
... of blood pumped/min by the heart and = approximately 5000ml or 5L/min Stroke Volume (SV) is the amount of blood ejected from the L ventricle with each contraction. ...
... of blood pumped/min by the heart and = approximately 5000ml or 5L/min Stroke Volume (SV) is the amount of blood ejected from the L ventricle with each contraction. ...
General Physiology – Biology 115, Fall 2016 Instructor: H. Bernheim
... sciences and computational methods Be mindful of ethical considerations and societal outcomes in research and in technological advancement Knowledge Base Competencies Covered in Bio 115 An understanding of the major paradigms in biology, including evolution, cell theory, genetic inheritance, the cen ...
... sciences and computational methods Be mindful of ethical considerations and societal outcomes in research and in technological advancement Knowledge Base Competencies Covered in Bio 115 An understanding of the major paradigms in biology, including evolution, cell theory, genetic inheritance, the cen ...
Arterial blood pressure
... Total peripheral resistance & Blood pressure It is the sum of all the vascular resistances. The PR is essential for maintenance of the arterial B.P. particularly the diastolic BP. It is produced mainly in the arterioles. It is determined by 3 factors: (a) The radius (or diameter) of the vesse ...
... Total peripheral resistance & Blood pressure It is the sum of all the vascular resistances. The PR is essential for maintenance of the arterial B.P. particularly the diastolic BP. It is produced mainly in the arterioles. It is determined by 3 factors: (a) The radius (or diameter) of the vesse ...
Michael Zundel, MD (MARC Presenter) Handout
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
Heart Rate The interval between two successive R waves
... Blood pressure is most commonly measured by the indirect method. An inflatable rubber cuff attached to a manometer is placed around the upper arm of the sitting patient (Fig.15). This is inflated until the brachial artery is completely occluded (the radial pulse can no longer be felt). Now the press ...
... Blood pressure is most commonly measured by the indirect method. An inflatable rubber cuff attached to a manometer is placed around the upper arm of the sitting patient (Fig.15). This is inflated until the brachial artery is completely occluded (the radial pulse can no longer be felt). Now the press ...
AV shunt
... Jugular venous pressure is the vertical distance, measured in cm, between the venous pulsation in the neck and the sternal angle (junction of the second rib with the sternum) when the patient is propped up on pillows at 45 to the horizontal. In this position, the sternal angle marks the level of the ...
... Jugular venous pressure is the vertical distance, measured in cm, between the venous pulsation in the neck and the sternal angle (junction of the second rib with the sternum) when the patient is propped up on pillows at 45 to the horizontal. In this position, the sternal angle marks the level of the ...
Editorial Comment Hyperthermia: A Hyperadrenergic
... Central venous pressure falls in proportion to the rise in cardiac output; that is, such a high blood flow raises pressures and volumes in the compliant cutaneous vasculature so that blood volume shifts away from the body core to the body surface, further promoting the gain of heat. Despite the fall ...
... Central venous pressure falls in proportion to the rise in cardiac output; that is, such a high blood flow raises pressures and volumes in the compliant cutaneous vasculature so that blood volume shifts away from the body core to the body surface, further promoting the gain of heat. Despite the fall ...
Editorial Comment Hyperthermia: A Hyperadrenergic
... Central venous pressure falls in proportion to the rise in cardiac output; that is, such a high blood flow raises pressures and volumes in the compliant cutaneous vasculature so that blood volume shifts away from the body core to the body surface, further promoting the gain of heat. Despite the fall ...
... Central venous pressure falls in proportion to the rise in cardiac output; that is, such a high blood flow raises pressures and volumes in the compliant cutaneous vasculature so that blood volume shifts away from the body core to the body surface, further promoting the gain of heat. Despite the fall ...
Primary Exam Workshop
... combined with methaemoglobin c) the O2 saturation of arterial blood with a PO2 of 40mmHg is about 85% d) anaemia decreases O2 saturation e) O2 affinity for Hb is reduced by decreased blood pH ...
... combined with methaemoglobin c) the O2 saturation of arterial blood with a PO2 of 40mmHg is about 85% d) anaemia decreases O2 saturation e) O2 affinity for Hb is reduced by decreased blood pH ...
1 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... – S3 – a faint sound associated with blood flowing into the ventricles – S4 – another faint sound associated with atrial contraction ...
... – S3 – a faint sound associated with blood flowing into the ventricles – S4 – another faint sound associated with atrial contraction ...