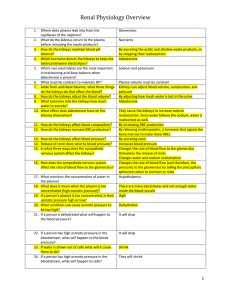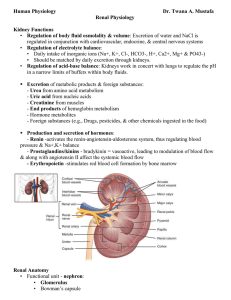
Renal Physiology
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... – Has a transport maximum, Tm, for most substances besides Na+ • Tm is the rate at which solutes can be transported, e.g., 375 mg/min • Renal threshold is the plasma level (concentration) above which a particular solute will appear in urine, e.g., 180 mg/dl ...
... – Has a transport maximum, Tm, for most substances besides Na+ • Tm is the rate at which solutes can be transported, e.g., 375 mg/min • Renal threshold is the plasma level (concentration) above which a particular solute will appear in urine, e.g., 180 mg/dl ...
Which pressures and where
... Repetition of physiology & basic terms Microcirculation, perfusion & blood pressure Regulators of perfusion & blood pressure Central role of kidneys in regulation of circulating volume & blood pressure ...
... Repetition of physiology & basic terms Microcirculation, perfusion & blood pressure Regulators of perfusion & blood pressure Central role of kidneys in regulation of circulating volume & blood pressure ...
Respiratory physiology - Assets - Cambridge
... The subject takes a maximal inspiration, and then breathes out into a spirometer in steps of 500 ml. The lungs are given a few seconds to stabilise after each exhalation and then the oesophageal pressure is recorded. This process is repeated until the patient has breathed out their total lung capaci ...
... The subject takes a maximal inspiration, and then breathes out into a spirometer in steps of 500 ml. The lungs are given a few seconds to stabilise after each exhalation and then the oesophageal pressure is recorded. This process is repeated until the patient has breathed out their total lung capaci ...
Relation of the Lungs to the Thoracic (Chest) Wall
... Where P is the pressure of the gas, V is its volume, and subscripts 1 and 2 represent the initial and resulting conditions respectively. Gases always fill their container. Therefore, in a large container, the molecules in a given amount of gas will be far apart and the pressure will be low. But if ...
... Where P is the pressure of the gas, V is its volume, and subscripts 1 and 2 represent the initial and resulting conditions respectively. Gases always fill their container. Therefore, in a large container, the molecules in a given amount of gas will be far apart and the pressure will be low. But if ...
GFR - gserianne.com
... adult male; less in females due to greater proportion of body fat) Major forces affecting movement of fluid between compartments: 1) Hydrostatic pressure 2) Osmotic pressure ...
... adult male; less in females due to greater proportion of body fat) Major forces affecting movement of fluid between compartments: 1) Hydrostatic pressure 2) Osmotic pressure ...
Physiology Objectives 43
... 100 ml of blood/mmHg of pressure), and therefore, oxygen transport in blood primarily relies on hemoglobin (oxygen is highly soluble in hemoglobin). Factors that alter hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve: fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 than regular hemoglobin, and thus, shifts the cu ...
... 100 ml of blood/mmHg of pressure), and therefore, oxygen transport in blood primarily relies on hemoglobin (oxygen is highly soluble in hemoglobin). Factors that alter hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve: fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 than regular hemoglobin, and thus, shifts the cu ...
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... current condition of the blood pressure? 38. If osmotic pressure is too high what is the eventual effect on the blood pressure? 39. If blood pressure is too high what two hormones will be released? 40. If osmotic pressure is too low what is the current condition of the blood pressure? 41. If osmotic ...
... current condition of the blood pressure? 38. If osmotic pressure is too high what is the eventual effect on the blood pressure? 39. If blood pressure is too high what two hormones will be released? 40. If osmotic pressure is too low what is the current condition of the blood pressure? 41. If osmotic ...
16 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... the peritubular space, and then enter the bloodstream? 70. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 71. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 72. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 73. What is another name for this hormone? 74. What effect do ...
... the peritubular space, and then enter the bloodstream? 70. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 71. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 72. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 73. What is another name for this hormone? 74. What effect do ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... the peritubular space, and then enter the bloodstream? 70. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 71. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 72. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 73. What is another name for this hormone? 74. What effect do ...
... the peritubular space, and then enter the bloodstream? 70. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 71. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 72. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 73. What is another name for this hormone? 74. What effect do ...
2. Physiology_Respiratory_System
... Increased capillary permeability ♦ Substance P ♦ Histamine and related substances ♦ Kinins, etc., Inadequate lymph flow ♦ Pulmonary capillary pressure is about 10mmHg, where as the oncotic pressure is 25mm of Hg, so that an inward-directed pressure gradient of about 15mm Hg keeps the alveoli free of ...
... Increased capillary permeability ♦ Substance P ♦ Histamine and related substances ♦ Kinins, etc., Inadequate lymph flow ♦ Pulmonary capillary pressure is about 10mmHg, where as the oncotic pressure is 25mm of Hg, so that an inward-directed pressure gradient of about 15mm Hg keeps the alveoli free of ...
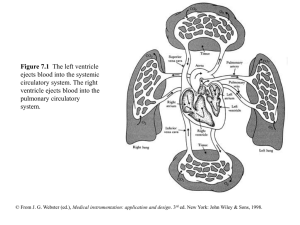
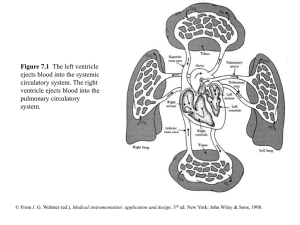
chapter07
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
Figure 1.1 Generalized instrumentation system The sensor
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
... Pressure is then slowly released, and blood flow under the cuff is monitored by a microphone or stethoscope placed over a downstream artery. The first Korotkoff sound detected indicates systolic pressure, whereas the transition from muffling to silence brackets diastolic pressure. (From R. F. Rushme ...
Optimization of axial-pump pressure sensitivity for a
... internal autoregulation at constant pump speeds can be achieved by varying the inflow pressures.3 In the present study, we achieved a similar experimental demonstration of this responsivity by varying the outflow pressure and leaving the inflow pressure constant, thereby changing the pressure differ ...
... internal autoregulation at constant pump speeds can be achieved by varying the inflow pressures.3 In the present study, we achieved a similar experimental demonstration of this responsivity by varying the outflow pressure and leaving the inflow pressure constant, thereby changing the pressure differ ...
Shock - Doctors2Be
... tissue perfusion with relatively or absolutely inadequate cardiac out put. Depending upon the cause of inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood volume for tissue perfusion circulatory shock can be divided into different types ...
... tissue perfusion with relatively or absolutely inadequate cardiac out put. Depending upon the cause of inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood volume for tissue perfusion circulatory shock can be divided into different types ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Micturition-process by which the urinary bladder empties when it becomes filled a. The bladder fills progressively until the tension within the walls rises above a threshold level b. The micturition reflex empties the bladder or stimulates a conscious desire to urinate c. It is an autonomic reflex ...
... • Micturition-process by which the urinary bladder empties when it becomes filled a. The bladder fills progressively until the tension within the walls rises above a threshold level b. The micturition reflex empties the bladder or stimulates a conscious desire to urinate c. It is an autonomic reflex ...
Work Physiology
... Blood flow to muscles (rest): 3.6 mL/min Blood flow to muscles (work): 90 mL/min Cardiac output (rest): 5.5 L Cardiac output (work): 30 L During work: ↑ Blood flow to muscles ↑ stroke volume (50%) ↑ heart rate (270%) ...
... Blood flow to muscles (rest): 3.6 mL/min Blood flow to muscles (work): 90 mL/min Cardiac output (rest): 5.5 L Cardiac output (work): 30 L During work: ↑ Blood flow to muscles ↑ stroke volume (50%) ↑ heart rate (270%) ...
Blood Vessels
... • Goes up as diameter is reduced • Arteriole diameter dominates • Viscosity of blood • Depends on hematocrit • Turbulence • Cause of pathological sounds ...
... • Goes up as diameter is reduced • Arteriole diameter dominates • Viscosity of blood • Depends on hematocrit • Turbulence • Cause of pathological sounds ...
File
... delivered to the working muscles. These changes include increases in body temperature, breathing rate, blood flow, and heart rate. An individual who is physically fit has a higher stroke volume than those who are not physically fit; this means that those who are active can deliver more oxygen to the ...
... delivered to the working muscles. These changes include increases in body temperature, breathing rate, blood flow, and heart rate. An individual who is physically fit has a higher stroke volume than those who are not physically fit; this means that those who are active can deliver more oxygen to the ...
renal physiology tutorial discussion
... more permeable or less permeable than other capillaries. Give reason. ...
... more permeable or less permeable than other capillaries. Give reason. ...
cardiovascular system
... it. Increased preload = increase output i.e. as blood flows into the heart, it must be pumped out. During increased exercise venous return increases. 2. Neural Regulation: a. The cardiovascular (CV) center and vasomotor center are located in the medulla of the brain stem. b. Baroreceptors (or presso ...
... it. Increased preload = increase output i.e. as blood flows into the heart, it must be pumped out. During increased exercise venous return increases. 2. Neural Regulation: a. The cardiovascular (CV) center and vasomotor center are located in the medulla of the brain stem. b. Baroreceptors (or presso ...
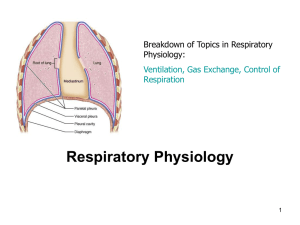
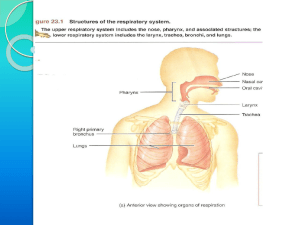
Cardiovascular System, Respiratory System
... and bronchia, pleural cavities, lungs, surface anatomy of the thorax. Histology: conduct part, respiratory part, pleura, blood circulation. Physiology: lung ventilation, gas exchange between air and blood, transport of the breathing gases between lungs and tissues, regulation of the lung ventilation ...
... and bronchia, pleural cavities, lungs, surface anatomy of the thorax. Histology: conduct part, respiratory part, pleura, blood circulation. Physiology: lung ventilation, gas exchange between air and blood, transport of the breathing gases between lungs and tissues, regulation of the lung ventilation ...