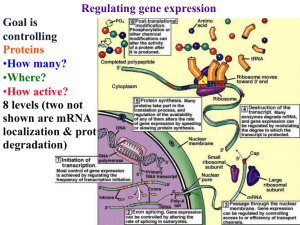
Chapter 18 Gene Regulation
... • Histone acetylation adds a acetyl groups to amino acids that make histones, thus making chromatin less tightly packed and increasing transcription ...
... • Histone acetylation adds a acetyl groups to amino acids that make histones, thus making chromatin less tightly packed and increasing transcription ...
presentation (spanish ppt format, 4.7 MB)
... from exogenous dsRNA but must undergo post-transcriptional modification. miRNA’s are expressed from longer RNA-coding gene as a primary transcript (pri-miRNA) which is processed within the cell nucleus to a 70 bp stem-loop structure (pre-miRNA) by the microprocessor complex (RNase III Drosha and dsR ...
... from exogenous dsRNA but must undergo post-transcriptional modification. miRNA’s are expressed from longer RNA-coding gene as a primary transcript (pri-miRNA) which is processed within the cell nucleus to a 70 bp stem-loop structure (pre-miRNA) by the microprocessor complex (RNase III Drosha and dsR ...
NMPDRposter - Edwards @ SDSU
... a separate gene in pyogenes, but it has fused with the next function in the pathway, EC 4.1.2.25, in both pneumo and Fus. nuc. The different structures of the operons in the two species of Strep may provide insight to differing sulfonamide resistance in these organisms. If the gene of interest plays ...
... a separate gene in pyogenes, but it has fused with the next function in the pathway, EC 4.1.2.25, in both pneumo and Fus. nuc. The different structures of the operons in the two species of Strep may provide insight to differing sulfonamide resistance in these organisms. If the gene of interest plays ...
Genome Analysis
... human DNA, but they represent the major biological function of the genome and the main focus of interest by biologists Human genes tend to have small exons (encoding an average of only 50 codons) separated by long introns (some exceeding 10 kb) This creates a signal-to-noise problem, with the resu ...
... human DNA, but they represent the major biological function of the genome and the main focus of interest by biologists Human genes tend to have small exons (encoding an average of only 50 codons) separated by long introns (some exceeding 10 kb) This creates a signal-to-noise problem, with the resu ...
Chapter 14: Gene Transcription and RNA Modification
... _____ 6. Removes the introns from the pre-mRNA. _____ 7. May produce an mRNA with different combinations of introns. _____ 8. Identifies the consensus sequence AAUAAA in the pre-mRNA. _____ 9. Attaches a guanosine monophosphate to the pre-mRNA. For questions 10 to 14, identify the type of splicing t ...
... _____ 6. Removes the introns from the pre-mRNA. _____ 7. May produce an mRNA with different combinations of introns. _____ 8. Identifies the consensus sequence AAUAAA in the pre-mRNA. _____ 9. Attaches a guanosine monophosphate to the pre-mRNA. For questions 10 to 14, identify the type of splicing t ...
Chapter 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes and Their
... The repressor gene encodes a repressor. The repressor binds (under appropriate conditions) to the operator. Binding is regulated by the presence or absence of the effector molecule (inducer or co-repressor). The promoter is the site of transcription initiation for the structural gene(s). Trans ...
... The repressor gene encodes a repressor. The repressor binds (under appropriate conditions) to the operator. Binding is regulated by the presence or absence of the effector molecule (inducer or co-repressor). The promoter is the site of transcription initiation for the structural gene(s). Trans ...
Mapping Regulatory Network from a Model Organism to a Non
... We have used Saccharomyces cerevisiae as the source genome and Arabidopsis thaliana as the target genome for experimentation in this work. We evaluated the mapped transcription factors (TF) and target genes (TG) by comparing them to the available transcription factor data and binding site data of Ar ...
... We have used Saccharomyces cerevisiae as the source genome and Arabidopsis thaliana as the target genome for experimentation in this work. We evaluated the mapped transcription factors (TF) and target genes (TG) by comparing them to the available transcription factor data and binding site data of Ar ...
S. cerevisiae
... Module = group of genes co-regulated by the same regulatory system * Evolution of individual gene targets * Evolution of activating signals * Wholesale evolution of the entire module Transcription factor sites occur upstream of totally different genes, ...
... Module = group of genes co-regulated by the same regulatory system * Evolution of individual gene targets * Evolution of activating signals * Wholesale evolution of the entire module Transcription factor sites occur upstream of totally different genes, ...
Powerpoint - Wishart Research Group
... – Tandem gene families (250 copies of rRNA, 500-1000 tRNA gene copies) – Pseudogenes (dead genes) – Short interspersed elements (SINEs) • 200-300 bp long, 100,000+ copies, scattered • Alu repeats are good examples ...
... – Tandem gene families (250 copies of rRNA, 500-1000 tRNA gene copies) – Pseudogenes (dead genes) – Short interspersed elements (SINEs) • 200-300 bp long, 100,000+ copies, scattered • Alu repeats are good examples ...
View attached file
... most likely forced to switch from a system that recognizes short intronic sequences within exons to one that recognizes short exons amid a sea of introns. The average human protein-coding gene, for example, is 28,000 nucleotides long, with 8.8 exons separated by 7.8 introns. The exons are relatively ...
... most likely forced to switch from a system that recognizes short intronic sequences within exons to one that recognizes short exons amid a sea of introns. The average human protein-coding gene, for example, is 28,000 nucleotides long, with 8.8 exons separated by 7.8 introns. The exons are relatively ...
Lecture 5
... Features of chloroplast translation (similar to prokaryotic translation) 1) Makes use of 70S ribosomes. 2) Uses fMet-initiator tRNA for the translation initiation codon. 3) The mRNAs are not capped. 4) The mRNAs are not poly-adenylated. 5) Ribosome binding occur in Shine-Delgarno-like sequence moti ...
... Features of chloroplast translation (similar to prokaryotic translation) 1) Makes use of 70S ribosomes. 2) Uses fMet-initiator tRNA for the translation initiation codon. 3) The mRNAs are not capped. 4) The mRNAs are not poly-adenylated. 5) Ribosome binding occur in Shine-Delgarno-like sequence moti ...
Future Directions Project Objectives Why Sequence Ferns?
... and complexities of ferns is critical for lineages comprising both homosporous and understanding the evolutionary genomics of heterosporous species, as well as the most land plants as a whole. As sister to the seed recently diverged lineage to have an plants, ferns are the required outgroup for inde ...
... and complexities of ferns is critical for lineages comprising both homosporous and understanding the evolutionary genomics of heterosporous species, as well as the most land plants as a whole. As sister to the seed recently diverged lineage to have an plants, ferns are the required outgroup for inde ...
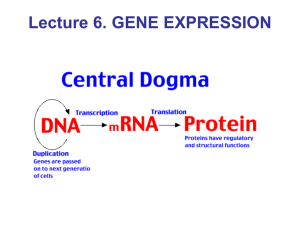
Lecture 6
... • A minimal set of 256 genes has been proposed by comparison of Haemophilus influenzae (G-) with M. genitalium (G+) complete genomes. ...
... • A minimal set of 256 genes has been proposed by comparison of Haemophilus influenzae (G-) with M. genitalium (G+) complete genomes. ...
Document
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
Learning Objectives for Final Exam , BIO105 Learning Objectives for
... After attending lecture, reviewing their notes, and reading the chapter, a student should be able to: - Explain how RNA differs from DNA. - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Describe where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukar ...
... After attending lecture, reviewing their notes, and reading the chapter, a student should be able to: - Explain how RNA differs from DNA. - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Describe where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukar ...
The Epigenetics of Non
... siRNA pathway B) [25]. siRNA-based mechanisms have been well-studied in plants and fission yeast [9,26]. Although at first siRNAs in animals were mostly considered to be from foreign DNA or RNA (i.e. viral-induced exo-siRNAs), recent studies have characterized many more endogenously encoded siRNAs ( ...
... siRNA pathway B) [25]. siRNA-based mechanisms have been well-studied in plants and fission yeast [9,26]. Although at first siRNAs in animals were mostly considered to be from foreign DNA or RNA (i.e. viral-induced exo-siRNAs), recent studies have characterized many more endogenously encoded siRNAs ( ...
Chapter 4. The Epigenetics of Non
... siRNA pathway B) [25]. siRNA-based mechanisms have been well-studied in plants and fission yeast [9,26]. Although at first siRNAs in animals were mostly considered to be from foreign DNA or RNA (i.e. viral-induced exo-siRNAs), recent studies have characterized many more endogenously encoded siRNAs ( ...
... siRNA pathway B) [25]. siRNA-based mechanisms have been well-studied in plants and fission yeast [9,26]. Although at first siRNAs in animals were mostly considered to be from foreign DNA or RNA (i.e. viral-induced exo-siRNAs), recent studies have characterized many more endogenously encoded siRNAs ( ...
Homework Assignment #1
... b. You isolate clones for each of these bands. Two correspond to the ACT1 and ACT2 genes you have already identified. The third you name ACT3. Now you prepare labeled probes specific for each individual actin gene (i.e., they will not cross-hybridize with either of the other actin genes) and use the ...
... b. You isolate clones for each of these bands. Two correspond to the ACT1 and ACT2 genes you have already identified. The third you name ACT3. Now you prepare labeled probes specific for each individual actin gene (i.e., they will not cross-hybridize with either of the other actin genes) and use the ...
Chapter 15 Outline - Adelphi University
... Chapter 15 Outline Genes and How They Work Advanced Placement Biology Roslyn High School The Central Dogma Traces The Flow Of Gene-Encoded Information. How Do Cells Use RNA To Make Protein? ...
... Chapter 15 Outline Genes and How They Work Advanced Placement Biology Roslyn High School The Central Dogma Traces The Flow Of Gene-Encoded Information. How Do Cells Use RNA To Make Protein? ...
Alternative hypotheses explaining the presence of RIP genes in
... With comparison purposes, the plausibility of both hypotheses was evaluated by counting the minimal needed number of losses on the phylogeny of Bilateria lineage. To do this, a loss event was considered when no RIP genes were detected in species with fully-sequenced genomes (Figure 2). The Assembly ...
... With comparison purposes, the plausibility of both hypotheses was evaluated by counting the minimal needed number of losses on the phylogeny of Bilateria lineage. To do this, a loss event was considered when no RIP genes were detected in species with fully-sequenced genomes (Figure 2). The Assembly ...
Slide 1
... • Detect potential coding regions by looking at ORFs – A genome of length n is comprised of (n/3) codons – Stop codons break genome into segments between consecutive Stop codons – The subsegments of these that start from the Start codon (ATG) are ORFs • ORFs in different frames may overlap ATG ...
... • Detect potential coding regions by looking at ORFs – A genome of length n is comprised of (n/3) codons – Stop codons break genome into segments between consecutive Stop codons – The subsegments of these that start from the Start codon (ATG) are ORFs • ORFs in different frames may overlap ATG ...
In prokaryotes, replication, transcription, and translation take place
... A particular DNA sequence reads TCGAGGTCACCG. A mutation occurs in which the first "A" in the sequence is deleted. What will happen to the protein produced? A ...
... A particular DNA sequence reads TCGAGGTCACCG. A mutation occurs in which the first "A" in the sequence is deleted. What will happen to the protein produced? A ...
CHAPTER 14
... mRNA molecules would bind to this column because they have a polyA tail. The string of adenine nucleotides in the polyA tail is complementary to stretch of thymine in the poly-dT column, so the two would hydrogen bond to each other. To purify mRNAs, one begins with a sample of cells; the cells need ...
... mRNA molecules would bind to this column because they have a polyA tail. The string of adenine nucleotides in the polyA tail is complementary to stretch of thymine in the poly-dT column, so the two would hydrogen bond to each other. To purify mRNAs, one begins with a sample of cells; the cells need ...
Lecture7
... Exons and Introns • In eukaryotes, the gene is a combination of coding segments (exons) that are interrupted by non-coding segments (introns) • This makes computational gene prediction in eukaryotes even more difficult • Prokaryotes don’t have introns - Genes in prokaryotes are continuous ...
... Exons and Introns • In eukaryotes, the gene is a combination of coding segments (exons) that are interrupted by non-coding segments (introns) • This makes computational gene prediction in eukaryotes even more difficult • Prokaryotes don’t have introns - Genes in prokaryotes are continuous ...