Power Point for Lecture 9
... 1. Interaction between the AR1 of the downstream CAP subunit and one copy of CTD. 2. The AR1-CTD interaction facilitates the binding of CTD to the DNA downstream of CAP. 3. Possibly, interaction between same copy of CTD and the 70 bound at the –35 element. 4. The interaction between the second ...
... 1. Interaction between the AR1 of the downstream CAP subunit and one copy of CTD. 2. The AR1-CTD interaction facilitates the binding of CTD to the DNA downstream of CAP. 3. Possibly, interaction between same copy of CTD and the 70 bound at the –35 element. 4. The interaction between the second ...
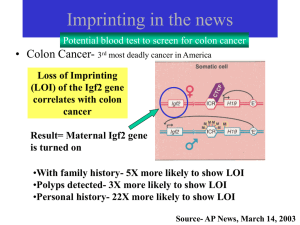
Imprinting
... MechanismMethylation serves two purposes 1. Inactivate a gene (e.g. H19) 2. Prevent binding of epigenetic marker so that Igf2 is activated ...
... MechanismMethylation serves two purposes 1. Inactivate a gene (e.g. H19) 2. Prevent binding of epigenetic marker so that Igf2 is activated ...
Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA
... (middle) panel displays all the genes along a number line. The genes are color coded by strand and gene type and labeled with the gene name. When a gene in the middle panel is selected, details about that gene appear in the top panel. DOGMA displays both strands of the genome’s nucleotide sequence, ...
... (middle) panel displays all the genes along a number line. The genes are color coded by strand and gene type and labeled with the gene name. When a gene in the middle panel is selected, details about that gene appear in the top panel. DOGMA displays both strands of the genome’s nucleotide sequence, ...
Supplementary Figures
... lincRNAs and protein coding genes (Supplementary Figure 4). We compared and contrasted the TE composition of protein coding and lincRNA promoters. The upstream promoter regions of protein coding genes are known to harbor TEs, which in some cases shape transcriptional regulation[2-4]. We confirmed th ...
... lincRNAs and protein coding genes (Supplementary Figure 4). We compared and contrasted the TE composition of protein coding and lincRNA promoters. The upstream promoter regions of protein coding genes are known to harbor TEs, which in some cases shape transcriptional regulation[2-4]. We confirmed th ...
Charles G. Kurland
... proteome is in fact not made up of bacterial descendents. They are eukaryotic proteins with no allignable homologues in bacteria or in archaea. Some of the characteristic organelle-specific functions such as ATP export are carried out by such eukaryotic add-ons to the mitochondrial proteome. The lab ...
... proteome is in fact not made up of bacterial descendents. They are eukaryotic proteins with no allignable homologues in bacteria or in archaea. Some of the characteristic organelle-specific functions such as ATP export are carried out by such eukaryotic add-ons to the mitochondrial proteome. The lab ...
Gene Section E2F6 (E2F transcription factor 6) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... (2413 bp mRNA), compared to variant 1, that causes a frameshift leading to an early stop codon. This transcript may function in a regulatory role with no protein translated. The predicted protein (isoform b) is much shorter than isoform a. Transcript variants 2 and 4 encode isoform b. Transcript var ...
... (2413 bp mRNA), compared to variant 1, that causes a frameshift leading to an early stop codon. This transcript may function in a regulatory role with no protein translated. The predicted protein (isoform b) is much shorter than isoform a. Transcript variants 2 and 4 encode isoform b. Transcript var ...
Genes and RNA
... In order to recognize their promoters, bacterial RNA polymerase enzymes require a specialized subunit called the sigma factor (σ), which directly contacts the promoter sequence. The complex formed by the sigma subunit with the remaining polymerase core subunits constitutes the bacterial holoenzyme. ...
... In order to recognize their promoters, bacterial RNA polymerase enzymes require a specialized subunit called the sigma factor (σ), which directly contacts the promoter sequence. The complex formed by the sigma subunit with the remaining polymerase core subunits constitutes the bacterial holoenzyme. ...
SF Genetics Lecture_Central Dogma_3.1 BY2208
... •! typically about 3-500 bases long •! encodes protein •! multiple types, usually not abundant, unstable 3) Transfer RNA (tRNA) •! very small - less than 100 bases long •! key role in translation •! abundant and stable ...
... •! typically about 3-500 bases long •! encodes protein •! multiple types, usually not abundant, unstable 3) Transfer RNA (tRNA) •! very small - less than 100 bases long •! key role in translation •! abundant and stable ...
Gene Expression
... RNA polymerase transcribes both the exons and introns, producing a long RNA molecule. Enzymes in the nucleus then add further nucleotides at the beginning (cap) and end (tail) of the RNA transcript. Other enzymes cut out the RNA introns and splice together the exons to form the true mRNA, which move ...
... RNA polymerase transcribes both the exons and introns, producing a long RNA molecule. Enzymes in the nucleus then add further nucleotides at the beginning (cap) and end (tail) of the RNA transcript. Other enzymes cut out the RNA introns and splice together the exons to form the true mRNA, which move ...
File
... in bacterial cells, RNA polymerase III does not require that a hairpin structure precede the string of Us. • In many of the genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, transcription can end at multiple sites located within a span of hundreds or thousands of base pairs. ...
... in bacterial cells, RNA polymerase III does not require that a hairpin structure precede the string of Us. • In many of the genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, transcription can end at multiple sites located within a span of hundreds or thousands of base pairs. ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;21)(q26;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... AML1-EVI1: 180 kDa; breakpoint after exon 5 or 6 in AML1, at the very 5' end of EVI1 → translocation protein includes N-term AML1 with the Runt domain and most of the gene EVI1, from the second untranslated exon to C-term, which includes the 2 zinc fingers. ...
... AML1-EVI1: 180 kDa; breakpoint after exon 5 or 6 in AML1, at the very 5' end of EVI1 → translocation protein includes N-term AML1 with the Runt domain and most of the gene EVI1, from the second untranslated exon to C-term, which includes the 2 zinc fingers. ...
Lecture Notes
... GENERAL IMPORTANCE: The decision to transcribe a gene or not is often regulated at initiation and mediated by physiological controls. ...
... GENERAL IMPORTANCE: The decision to transcribe a gene or not is often regulated at initiation and mediated by physiological controls. ...
INTRODUCTION: - the BIOTECH Project
... of rRNA with genomic DNA to measure the similarity of rRNAs in various species. These experiments demonstrated that rRNA-based methods are applicable to directly comparing a broader range of organisms (i.e., spanning greater phylogenetic distances) than is whole genome DNA-DNA hybridization. However ...
... of rRNA with genomic DNA to measure the similarity of rRNAs in various species. These experiments demonstrated that rRNA-based methods are applicable to directly comparing a broader range of organisms (i.e., spanning greater phylogenetic distances) than is whole genome DNA-DNA hybridization. However ...
Learning Regulatory Networks from Sparsely Sampled Time Series
... overlaps between cluster Xi and Yj: g is the total number of genes Nxi is the number of genes in cluster Xi Nyj is the number of genes in cluster Yj Kij is the number of overlapped genes in Xi and Yj ...
... overlaps between cluster Xi and Yj: g is the total number of genes Nxi is the number of genes in cluster Xi Nyj is the number of genes in cluster Yj Kij is the number of overlapped genes in Xi and Yj ...
Know Before You Buy! Teacher Guide - Science Take-Out
... food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food source. The structural genes in the lac operon contain the DNA code that produces three proteins. ...
... food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food source. The structural genes in the lac operon contain the DNA code that produces three proteins. ...
Gene Section MIR7-1 (microRNA 7-1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... gene, a ribonucleoprotein. There are two other microRNAs in the human genome that yield mature miR-7, with all three miR-7 loci found on different chromosomes. ...
... gene, a ribonucleoprotein. There are two other microRNAs in the human genome that yield mature miR-7, with all three miR-7 loci found on different chromosomes. ...
Working with ribonucleic acid (RNA)-based biotechnologies)
... RNA-based approaches to regulate gene activity have been practiced in the lab for some time. Significant technical advances and validation of strategies now mean they are likely to see application in animals in the field soon. There are a variety of RNA-based biotechnologies differing in technical a ...
... RNA-based approaches to regulate gene activity have been practiced in the lab for some time. Significant technical advances and validation of strategies now mean they are likely to see application in animals in the field soon. There are a variety of RNA-based biotechnologies differing in technical a ...
Genoombrowsers - Radboud Universiteit
... • People do not only vary at the nucleotide level (SNPs); short pieces genome can be present in varying number of copies (Copy Number Polymorphisms (CNPs) or Copy Number Variants (CNVs) • When there are genes in the CNV areas, this can lead to variations in the number of gene copies between individu ...
... • People do not only vary at the nucleotide level (SNPs); short pieces genome can be present in varying number of copies (Copy Number Polymorphisms (CNPs) or Copy Number Variants (CNVs) • When there are genes in the CNV areas, this can lead to variations in the number of gene copies between individu ...
Chapter 19. - Kenston Local Schools
... "reproduces" by copying itself & inserting into new chromosome locations AP Biology ...
... "reproduces" by copying itself & inserting into new chromosome locations AP Biology ...
Chapter 20 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... Activators are proteins that recognize specific short DNA sequences inducing the efficiency of the promoters. Co-activators are proteins required for a more efficient transcription. They do not bind DNA. Regulators of chromatin structure Figure 25.2 ...
... Activators are proteins that recognize specific short DNA sequences inducing the efficiency of the promoters. Co-activators are proteins required for a more efficient transcription. They do not bind DNA. Regulators of chromatin structure Figure 25.2 ...
Gene Concept - Govt. College Aron
... messenger RNA, uracil nucleotides are removed and cytocine nucleotides are replaced by uracil after transcription. The information for this process comes either from the gene involved or alternatively from outside it ...
... messenger RNA, uracil nucleotides are removed and cytocine nucleotides are replaced by uracil after transcription. The information for this process comes either from the gene involved or alternatively from outside it ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... Origin of eukaryotic miRNA machinery • Comparative genomic analysis shows that the protein machinery of RNAi is conserved in all major eukaryotic lineages, independent loss in many unicellular forms notwithstanding. • It appears most likely that LECA possessed relatively complex RNAi machinery. At ...
... Origin of eukaryotic miRNA machinery • Comparative genomic analysis shows that the protein machinery of RNAi is conserved in all major eukaryotic lineages, independent loss in many unicellular forms notwithstanding. • It appears most likely that LECA possessed relatively complex RNAi machinery. At ...
H_Pylori_MicroArray_Data_Analysis
... • MAPPFinder was used to determine the most upregulated and downregulated genes • Data indicated that many of the top 10 most significant genes dealt with transcription • Data shows that RpoN dependent genes were not among the most significantly changed ...
... • MAPPFinder was used to determine the most upregulated and downregulated genes • Data indicated that many of the top 10 most significant genes dealt with transcription • Data shows that RpoN dependent genes were not among the most significantly changed ...
New Title - Gravette School District
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation The general principles of gene regulation in prokaryotes also apply to eukaryotic cells, although there are some important differences. Operons are generally not found in eukaryotes. Most eukaryotic genes are controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are m ...
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation The general principles of gene regulation in prokaryotes also apply to eukaryotic cells, although there are some important differences. Operons are generally not found in eukaryotes. Most eukaryotic genes are controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are m ...