Slide 1
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine pairs with Guanine through 3 Hydrogen bonds Gregor Mendel was the first to suggest that heritable factors were passed from parent to offspring, determining characteristics Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome (its entire heredita ...
... Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine pairs with Guanine through 3 Hydrogen bonds Gregor Mendel was the first to suggest that heritable factors were passed from parent to offspring, determining characteristics Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome (its entire heredita ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
DNA in classifying species
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
DNA Test Study Guide
... ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that there are two types of chromosomes, ____________ and ________________. In order for a hum ...
... ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that there are two types of chromosomes, ____________ and ________________. In order for a hum ...
How does my immune system react when I puncture my skin on
... While some viral proteins assemble new virus , others are cut up by the proteosome and then selected by MHCI and promptly presented on the cells surface (Here is an animation showing this series of events ) Cytotoxic T-cell, with corresponding CD8 receptor ...
... While some viral proteins assemble new virus , others are cut up by the proteosome and then selected by MHCI and promptly presented on the cells surface (Here is an animation showing this series of events ) Cytotoxic T-cell, with corresponding CD8 receptor ...
Test Study Guide
... How did Griffith arrive at the conclusion that a gene from one kind of bacteria transformed another kind of bacteria? Avery, Macleod and McCarty – What did Avery conclude caused transformation? Hershey and Chase – ...
... How did Griffith arrive at the conclusion that a gene from one kind of bacteria transformed another kind of bacteria? Avery, Macleod and McCarty – What did Avery conclude caused transformation? Hershey and Chase – ...
Reproduction
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
Acc_Bio_Biotechnology_12
... They isolated the gene that codes for rRNA from the DNA of an African clawed frog. They inserted the gene into E. coli bacteria. During transcription, the bacteria produced frog rRNA! ...
... They isolated the gene that codes for rRNA from the DNA of an African clawed frog. They inserted the gene into E. coli bacteria. During transcription, the bacteria produced frog rRNA! ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
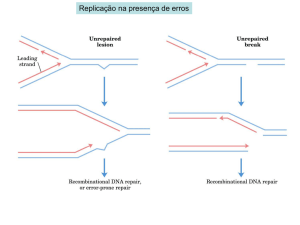
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Misconceptions relating to DNA and RNA
... Genes are traits A gene and the expression of the gene as a characteristic or trait are the same thing There are some types of organisms that do not have DNA Only animals have DNA, plants and mushrooms do not have DNA Each DNA molecule is made of more than one chromosome The different cell types fou ...
... Genes are traits A gene and the expression of the gene as a characteristic or trait are the same thing There are some types of organisms that do not have DNA Only animals have DNA, plants and mushrooms do not have DNA Each DNA molecule is made of more than one chromosome The different cell types fou ...
DNA: Sample Storage - Sacramento County District Attorney
... Amplified DNA from casework will be retained in frozen storage until the case has been technically and administratively reviewed. After the review process has been completed, the amplified DNA may be destroyed. NOTE: Exceptions to this process are when ...
... Amplified DNA from casework will be retained in frozen storage until the case has been technically and administratively reviewed. After the review process has been completed, the amplified DNA may be destroyed. NOTE: Exceptions to this process are when ...
Whole Genome Scale DNA Methylation Differences in
... Summary of Results: We identified 132 different CpG sites at which the direction of the intra-MZ pair DNA methylation difference significantly correlated with the diabetic state i.e. T1D-associated methylation variable positions (T1D-MVPs). We confirmed these T1D-MVPs display statistically significa ...
... Summary of Results: We identified 132 different CpG sites at which the direction of the intra-MZ pair DNA methylation difference significantly correlated with the diabetic state i.e. T1D-associated methylation variable positions (T1D-MVPs). We confirmed these T1D-MVPs display statistically significa ...
Lab 6 DNA ISOLN
... Purification of the DNA of interest from soluble proteins and other nucleic acids ...
... Purification of the DNA of interest from soluble proteins and other nucleic acids ...
DNA experiments exercise
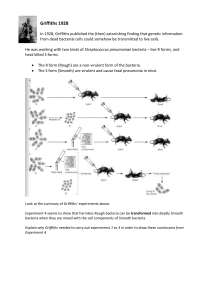
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Natural Defenses for Healthy Animals
... immunostimulatory motifs). Its structure is typical for the genetic material of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The animal’s immune system can therefore identify these DNA sequences easily – they are like a red flag to the immune system. ...
... immunostimulatory motifs). Its structure is typical for the genetic material of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The animal’s immune system can therefore identify these DNA sequences easily – they are like a red flag to the immune system. ...
Gene Technology
... Selection: breeding organisms with certain traits so that the offspring will have those traits. • A. Mass Selection- Crossing and growing plants with desired traits until the trait appears consistently Exbreeding wheat with more protein; rice with more iron ...
... Selection: breeding organisms with certain traits so that the offspring will have those traits. • A. Mass Selection- Crossing and growing plants with desired traits until the trait appears consistently Exbreeding wheat with more protein; rice with more iron ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.