Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... to transport genetic material into a target organism? 13. What are the two most commonly used vectors for getting DNA into organisms? 14. How does replication of a bacterial chromosome occur? 15. How is the leading strand in DNA replication different from the lagging strand? ...
... to transport genetic material into a target organism? 13. What are the two most commonly used vectors for getting DNA into organisms? 14. How does replication of a bacterial chromosome occur? 15. How is the leading strand in DNA replication different from the lagging strand? ...
Genetic Engineering
... medicine, and agriculture • Transgenic organisms • Gene therapy –Sheep alpha-1 antitrypsin for treatment of emphysema –Goats CFTR protein for treatment of Cystic Fibrosis ...
... medicine, and agriculture • Transgenic organisms • Gene therapy –Sheep alpha-1 antitrypsin for treatment of emphysema –Goats CFTR protein for treatment of Cystic Fibrosis ...
File
... 5. Label the parts of a Chromosome below with the following: Exon, Intron, Gene, Centromere, Chromatid. ...
... 5. Label the parts of a Chromosome below with the following: Exon, Intron, Gene, Centromere, Chromatid. ...
Part I, for Exam 1: 1. Based on Chargaff`s rules, which of the
... conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation. C) a replication origin, which permits it to replicate autonomously. D) resistance to two different antibiotics, which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA. E) small overall size, which facili ...
... conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation. C) a replication origin, which permits it to replicate autonomously. D) resistance to two different antibiotics, which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA. E) small overall size, which facili ...
What holds chromosomes together: Researchers
... structure of a ring-shaped protein complex (SMC- In humans the DNA packaging machinery is kleisin), which ensures order in this packaging similarly organized. "We suspect that this process. Together with their cooperation partners asymmetric structure plays an important role in the at the Korea Adva ...
... structure of a ring-shaped protein complex (SMC- In humans the DNA packaging machinery is kleisin), which ensures order in this packaging similarly organized. "We suspect that this process. Together with their cooperation partners asymmetric structure plays an important role in the at the Korea Adva ...
presentation source
... • DNA strands can be spliced into the plasmid, and the plasmid re-inserted into a bacterium • As the bacteria divides, the spliced DNA becomes part of the genome and is also replicated • Certain viruses can also be used as vectors ...
... • DNA strands can be spliced into the plasmid, and the plasmid re-inserted into a bacterium • As the bacteria divides, the spliced DNA becomes part of the genome and is also replicated • Certain viruses can also be used as vectors ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
Biology Assessment #3:
... 6. Identify the number of chromosomes in human haploid cells, diploid cells, sex cells, gametes, and somatic cells. 7. What is the meaning of n and 2n? 8. How is a zygote formed? 9. What is the chromosome # in a zygote? Why or how? 10. Compare parent and daughter cells before and after mitosis (disc ...
... 6. Identify the number of chromosomes in human haploid cells, diploid cells, sex cells, gametes, and somatic cells. 7. What is the meaning of n and 2n? 8. How is a zygote formed? 9. What is the chromosome # in a zygote? Why or how? 10. Compare parent and daughter cells before and after mitosis (disc ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... - Making changes to the DNA code of an organism. How can I take a gene from one organism and insert it into another completely different organism? A. Recombinant DNA - DNA made by connecting fragments of DNA from different sources. A + B =C ...
... - Making changes to the DNA code of an organism. How can I take a gene from one organism and insert it into another completely different organism? A. Recombinant DNA - DNA made by connecting fragments of DNA from different sources. A + B =C ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology & Genomics
... of organisms/components to make desired products Ex. Making wine & cheese with yeast, selective breeding of organisms, recombinant DNA products Genetic Direct ...
... of organisms/components to make desired products Ex. Making wine & cheese with yeast, selective breeding of organisms, recombinant DNA products Genetic Direct ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... Genes • Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering invol ...
... Genes • Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering invol ...
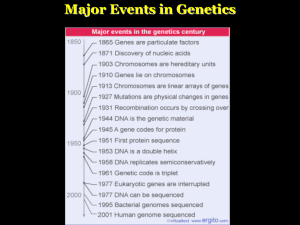
Major Events in Genetics
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... a. Scientist(s) b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experimental design/procedures d. One sentence conclusion 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bas ...
... a. Scientist(s) b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experimental design/procedures d. One sentence conclusion 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bas ...
Biotechnology - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... enabled scientists to completely sequence the human genome. A rough draft was complete in 2000. ...
... enabled scientists to completely sequence the human genome. A rough draft was complete in 2000. ...
Goal 3 Guided Worksheet
... Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of protein. ...
... Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of protein. ...
Gene Technology
... • Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) gene that produces insecticide is inserted to many crops. • Transgenic rice with added vitamin A reduced vision impairment in Asian countries. • Crops can also be modified to make them easier to grow and to increase nutrition values. ...
... • Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) gene that produces insecticide is inserted to many crops. • Transgenic rice with added vitamin A reduced vision impairment in Asian countries. • Crops can also be modified to make them easier to grow and to increase nutrition values. ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
... 2. Explain what the human genome is. Why do scientists want to study it? ...
... 2. Explain what the human genome is. Why do scientists want to study it? ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... The place in the body from which cells are ...
... The place in the body from which cells are ...
DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis with Answers
... Which process is most directly affected by the arrangements of components 1 through 4? a. diffusion through cell membranes b. fertilization of a sex cell c. sequencing of amino acids in cells d. increasing the number of cells in an organism ...
... Which process is most directly affected by the arrangements of components 1 through 4? a. diffusion through cell membranes b. fertilization of a sex cell c. sequencing of amino acids in cells d. increasing the number of cells in an organism ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.