DNA Structure - Colorado State University
... them slightly differently (in the same manner that English usage in Britain is slightly different from English usage in the U.S.). More distantly related species, such as burning bush and American bittersweet (Celastrus scandens), still generally have the same proteins, but make them very differentl ...
... them slightly differently (in the same manner that English usage in Britain is slightly different from English usage in the U.S.). More distantly related species, such as burning bush and American bittersweet (Celastrus scandens), still generally have the same proteins, but make them very differentl ...
Chapter 43 – Immune System
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
Document
... ____ 14. In which part of the cell does this process shown in Figure 11-1 take place? a. in the nucleus c. at the ribosomes b. in food vacuoles d. on the chromosome ____ 15. Which of the structures in Figure 11-1 are composed of RNA? a. II and IV c. I and V b. III and IV d. III and V ____ 16. Struct ...
... ____ 14. In which part of the cell does this process shown in Figure 11-1 take place? a. in the nucleus c. at the ribosomes b. in food vacuoles d. on the chromosome ____ 15. Which of the structures in Figure 11-1 are composed of RNA? a. II and IV c. I and V b. III and IV d. III and V ____ 16. Struct ...
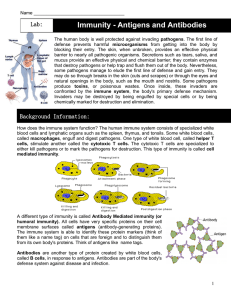
Antigens and Antibodies
... complex. Antibodies have two binding sites, so they can attach to two antigen molecules. They deal with pathogens by clumping or linking them together to make it easier for them to be engulfed by phagocytes. They can also rupture foreign cells and inactivate any toxins they produce. Some of the anti ...
... complex. Antibodies have two binding sites, so they can attach to two antigen molecules. They deal with pathogens by clumping or linking them together to make it easier for them to be engulfed by phagocytes. They can also rupture foreign cells and inactivate any toxins they produce. Some of the anti ...
pBMN-LacZ - Allele Biotech
... etroviruses are one of the most efficient tools for delivering genes into dividing mammalian cells. The pBMN-Z Retroviral Expression Vector is a Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (MMULV) based vector containing retroviral LTRs and packaging signal. It also contains the gene encoding β-galactosidase (lac ...
... etroviruses are one of the most efficient tools for delivering genes into dividing mammalian cells. The pBMN-Z Retroviral Expression Vector is a Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (MMULV) based vector containing retroviral LTRs and packaging signal. It also contains the gene encoding β-galactosidase (lac ...
Immunity Ch. 11.1-6
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
DNA Structure and Lab
... ____________________ (C) The Genetic Code (p. 132) DNA makes up _____________. Genes control _____________________________________________________________________ The order of _________________ bases along a gene forms a __________________ code that specifies what type of _______________ will be pro ...
... ____________________ (C) The Genetic Code (p. 132) DNA makes up _____________. Genes control _____________________________________________________________________ The order of _________________ bases along a gene forms a __________________ code that specifies what type of _______________ will be pro ...
BIO 402/502 Advanced Cell & Developmental Biology
... deletions/duplications following meiosis (unequal cross-over) and loss of viability. ...
... deletions/duplications following meiosis (unequal cross-over) and loss of viability. ...
1 The structure and replication of DNA
... expressing the genes characteristic for that type of cell. - Differentiation into specialised cells from meristems in plants; embryonic and tissue (adult) stem cells in animals. - Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. - Stem cells are relatively un ...
... expressing the genes characteristic for that type of cell. - Differentiation into specialised cells from meristems in plants; embryonic and tissue (adult) stem cells in animals. - Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. - Stem cells are relatively un ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Notes Part 1
... The production (synthesis) of polypeptide chains (proteins) Two phases: Transcription & Translation mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
... The production (synthesis) of polypeptide chains (proteins) Two phases: Transcription & Translation mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
gene control regions?
... Introns Evolution: Early vs Late? Getting Bigger or Getting Smaller? Both genes have identical Patterns of introns (66) -Illustrate… -Common ancestor -If not early, at least they’ve been around for a while… Human HD = 180,000 bps F. Rubripes HD = 24,000 bps -Difference due to intron size Difference ...
... Introns Evolution: Early vs Late? Getting Bigger or Getting Smaller? Both genes have identical Patterns of introns (66) -Illustrate… -Common ancestor -If not early, at least they’ve been around for a while… Human HD = 180,000 bps F. Rubripes HD = 24,000 bps -Difference due to intron size Difference ...
Cow DNA: How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
File
... a. Primary immune response by an organism because the pathogen is typically being recognized as many antigens & not just one b. For example, a virus is typically made up of several different kinds of proteins & each protein type can cause an immune response c. Thus several different kinds of B cells ...
... a. Primary immune response by an organism because the pathogen is typically being recognized as many antigens & not just one b. For example, a virus is typically made up of several different kinds of proteins & each protein type can cause an immune response c. Thus several different kinds of B cells ...
Immune System Concept Maps
... 2. IMMUNE RESPONSE, PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, PATHOGEN, ANTIGEN, TCELL, B-CELL, ANTIBODY, PLASMA CELLS, MEMORY B-CELLS, ANTIBODIES, PHAGOCYTES, KILLER T-CELL (CYTOTOXIC T-CELL), HELPER T-CELL, SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, SUPPRESSOR T-CELL (10 points) ...
... 2. IMMUNE RESPONSE, PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, PATHOGEN, ANTIGEN, TCELL, B-CELL, ANTIBODY, PLASMA CELLS, MEMORY B-CELLS, ANTIBODIES, PHAGOCYTES, KILLER T-CELL (CYTOTOXIC T-CELL), HELPER T-CELL, SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE, SUPPRESSOR T-CELL (10 points) ...
Checkpoints
... Square: arrest with MBC, release and X-ray Triangle: arrest with MBC, x-ray and hold in MBC for 4 hr ...
... Square: arrest with MBC, release and X-ray Triangle: arrest with MBC, x-ray and hold in MBC for 4 hr ...
Genetic Engineering
... the required gene is cut out of the DNA strand by an endonuclease (enzyme) - this enzyme cuts the DNA at specific points - it leaves “sticky-ends” – which allow other genes to rejoin the same restriction enzyme (endonuclease) is used to cut the bacterial plasmid (leaving the same sticky ends) the re ...
... the required gene is cut out of the DNA strand by an endonuclease (enzyme) - this enzyme cuts the DNA at specific points - it leaves “sticky-ends” – which allow other genes to rejoin the same restriction enzyme (endonuclease) is used to cut the bacterial plasmid (leaving the same sticky ends) the re ...
II. Principles of Cell
... number of independent clones = genome size/average size insert For a human genomic DNA library of 40 kb average insert size ...
... number of independent clones = genome size/average size insert For a human genomic DNA library of 40 kb average insert size ...
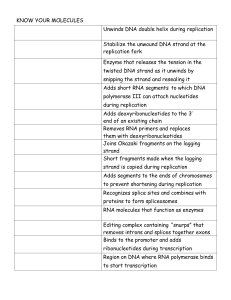
Know your molecules organizer
... to prevent shortening during replication Recognizes splice sites and combines with proteins to form spliceosomes RNA molecules that function as enzymes Editing complex containing “snurps” that removes introns and splices together exons Binds to the promoter and adds ribonucleotides during transcript ...
... to prevent shortening during replication Recognizes splice sites and combines with proteins to form spliceosomes RNA molecules that function as enzymes Editing complex containing “snurps” that removes introns and splices together exons Binds to the promoter and adds ribonucleotides during transcript ...
Section 2: Figures
... M of tris [hydroxyl methyl] amino methane was used to stop the reactions. Controls were taken as DNA alone, DNA with 0.2 M tris [hydroxyl methyl] amino methane, and 500 µM CuNPs. The separation and visualization of DNA bands were performed as mentioned above. The band intensity was measured using “q ...
... M of tris [hydroxyl methyl] amino methane was used to stop the reactions. Controls were taken as DNA alone, DNA with 0.2 M tris [hydroxyl methyl] amino methane, and 500 µM CuNPs. The separation and visualization of DNA bands were performed as mentioned above. The band intensity was measured using “q ...
CREDGREW power point
... chemical that genes are made of G = Grow; all organisms grow R = Response; all organisms respond to stimuli E = Exchange; all organisms exchange gasses; take in CO2 and let out O2 ...
... chemical that genes are made of G = Grow; all organisms grow R = Response; all organisms respond to stimuli E = Exchange; all organisms exchange gasses; take in CO2 and let out O2 ...
Unit 4
... 5. List the nitrogen bases found in DNA, and distinguish between pyrimidine and purine. The nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine and purine are adenine and guanine. 7. Explain the "base-pairing rule" and describe its significanc ...
... 5. List the nitrogen bases found in DNA, and distinguish between pyrimidine and purine. The nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine and purine are adenine and guanine. 7. Explain the "base-pairing rule" and describe its significanc ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.