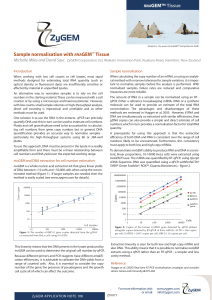
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... The amount of RNA in a sample can be normalised using an RTqPCR. Either a reference housekeeping mRNA, rRNA or a synthetic molecule can be used to provide an estimate of the total RNA concentration. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA ...
... The amount of RNA in a sample can be normalised using an RTqPCR. Either a reference housekeeping mRNA, rRNA or a synthetic molecule can be used to provide an estimate of the total RNA concentration. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA ...
发现次级代谢途径特异性转录调控因子
... orthologous regulators restores pimaricin production DNA fragment: pimM,amphRIV, nysRIV, pteF Vector: pSET152 giving rise to pSETpimM pMamphRIV, pMnysRIV, pMpteF Transfermation by conjugation As expected,given its highest identity to PimM, pimaricin yield was the highest in the strain complemented w ...
... orthologous regulators restores pimaricin production DNA fragment: pimM,amphRIV, nysRIV, pteF Vector: pSET152 giving rise to pSETpimM pMamphRIV, pMnysRIV, pMpteF Transfermation by conjugation As expected,given its highest identity to PimM, pimaricin yield was the highest in the strain complemented w ...
Recombinant Human GM-CSF
... that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. It is produced by a number of different cell types (including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts) in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besi ...
... that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. It is produced by a number of different cell types (including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts) in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besi ...
2-centrioles & fibers disappear
... • When the tRNA matches its anticodons to the mRNA’s codons at the ribosomes, it brings with it a particular amino acid. After the tRNA’s drops off amino acids from the start to the stop codon, the protein is complete. ...
... • When the tRNA matches its anticodons to the mRNA’s codons at the ribosomes, it brings with it a particular amino acid. After the tRNA’s drops off amino acids from the start to the stop codon, the protein is complete. ...
Selfish DNA and the wonderful world of RNA
... They have been called "junk" DNA and "selfish" DNA. "selfish" because their only function seems to make more copies of themselves and "junk" because there is no obvious benefit to their host. ...
... They have been called "junk" DNA and "selfish" DNA. "selfish" because their only function seems to make more copies of themselves and "junk" because there is no obvious benefit to their host. ...
Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis
... are underlined. Non-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotides were also generated with the non-labeled single-stranded complementary oligonucleotides using the same methods. Binding reactions and electrophoresis have been described previously (Rokudai et al., 2002), and detection of the biotin-labele ...
... are underlined. Non-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotides were also generated with the non-labeled single-stranded complementary oligonucleotides using the same methods. Binding reactions and electrophoresis have been described previously (Rokudai et al., 2002), and detection of the biotin-labele ...
BIO 304 Genetics
... 1. Purine bases commonly found in DNA are guanine and ____adenine_____. 2. The normal phenotype that is typical of most individuals in a population is called __wild type___ . 3. A mutation of an enzyme-encoding gene that completely abolishes activity of the enzyme is called a ____null______________ ...
... 1. Purine bases commonly found in DNA are guanine and ____adenine_____. 2. The normal phenotype that is typical of most individuals in a population is called __wild type___ . 3. A mutation of an enzyme-encoding gene that completely abolishes activity of the enzyme is called a ____null______________ ...
Computational Immunology An Introduction
... • Both identify and attack foreign tissues and organisms • Have different strengths • In a constant dialogue with each other • Complement each other ...
... • Both identify and attack foreign tissues and organisms • Have different strengths • In a constant dialogue with each other • Complement each other ...
PPT 23
... BHK monolayers could be used for the growth and titration of FMDV, Mowat and Chapman (1962). BHK cells grown in suspension, Capstick et al. (1962) Suspension cells produced in large scale fermenters, Telling and Elsworth ...
... BHK monolayers could be used for the growth and titration of FMDV, Mowat and Chapman (1962). BHK cells grown in suspension, Capstick et al. (1962) Suspension cells produced in large scale fermenters, Telling and Elsworth ...
Chromatin Structure and Function
... unmodified or methylated histones silence or repress genes, acetylation allows gene expression, and phosphorylation is involved in mitotic chrom. condensation. ...
... unmodified or methylated histones silence or repress genes, acetylation allows gene expression, and phosphorylation is involved in mitotic chrom. condensation. ...
BSc in Applied Biotechnology 5 BO0055 ‑ PLANT AND ANIMAL
... These cells are then incorporated into an embryo at the blastocyst stage of development. The result is a chimeric animal. ES cell-mediated gene transfer is the method of choice for gene inactivation, the so-called knock-out method. This technique is of particular importance for the study of the gene ...
... These cells are then incorporated into an embryo at the blastocyst stage of development. The result is a chimeric animal. ES cell-mediated gene transfer is the method of choice for gene inactivation, the so-called knock-out method. This technique is of particular importance for the study of the gene ...
In the DNA Double Helix, complementary base pairs are held
... sequences in each gene) come together. ...
... sequences in each gene) come together. ...
explaining the forensic use of dna to the average american
... Series of triplet sequences that repeat numerous times. B. The length of these sequences differ from individual to individual and are used as a means of DNA typing. C. The length differences associated with DNA strands are called RFLP. D. Once these sequences are cut, they are sorted out using elect ...
... Series of triplet sequences that repeat numerous times. B. The length of these sequences differ from individual to individual and are used as a means of DNA typing. C. The length differences associated with DNA strands are called RFLP. D. Once these sequences are cut, they are sorted out using elect ...
File
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
Evolution process by which species change over time
... • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic make up • DNA strands can ...
... • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic make up • DNA strands can ...
7echap20guidedreading
... 6. Using the diagram below – label the steps to cloning a human gene in a bacterial plasmid ...
... 6. Using the diagram below – label the steps to cloning a human gene in a bacterial plasmid ...
Hygiene III The Hugiene Hypothesis
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
CHAPTER 24
... development of vaccines to counteract their effects. With increased fast mobility of humans from one area to another, infected individuals could spread the pathogens into populations not intended for infection. Spread of pathogens is indiscriminate and so large numbers of nontarget individuals (e.g. ...
... development of vaccines to counteract their effects. With increased fast mobility of humans from one area to another, infected individuals could spread the pathogens into populations not intended for infection. Spread of pathogens is indiscriminate and so large numbers of nontarget individuals (e.g. ...
Go to Classzone - Issaquah Connect
... 4. Which organelle must bind to the RNA before translation can take place? __________________. 5. When you are translating your mRNA into your protein, littellase, make sure to line the ____________ up directly with their complementary base pair. 6. Which organelle in the cytoplasm processes, packag ...
... 4. Which organelle must bind to the RNA before translation can take place? __________________. 5. When you are translating your mRNA into your protein, littellase, make sure to line the ____________ up directly with their complementary base pair. 6. Which organelle in the cytoplasm processes, packag ...
NAME___________________________________TA__________
... determinant) that this particular antibody recognizes. Polyclonal antibodies would give more information about the identity of more of the unidentified proteins. In a polyclonal antiserum, there are antibodies to many different epitopes on the same protein (remember, epitopes are relatively small re ...
... determinant) that this particular antibody recognizes. Polyclonal antibodies would give more information about the identity of more of the unidentified proteins. In a polyclonal antiserum, there are antibodies to many different epitopes on the same protein (remember, epitopes are relatively small re ...
AP Bio - Semester 2 Review
... 2. F factor (If a bacteria possess this gene, they are considered “male”.) (Shown as F+); (F- are “female”.)(They do NOT possess the F factor gene.) a. Pili – This structure is a “sex whip” for pulling the “female” close so that a conjugation tube can be made between the two bacteria. The pili is cr ...
... 2. F factor (If a bacteria possess this gene, they are considered “male”.) (Shown as F+); (F- are “female”.)(They do NOT possess the F factor gene.) a. Pili – This structure is a “sex whip” for pulling the “female” close so that a conjugation tube can be made between the two bacteria. The pili is cr ...
Chapter 16 Review
... and selects for the mutation or against the mutation. Thus, organisms that have a mutation that is selected will have their fitness increased, while organisms that have mutations that are selected against will have their fitness decreased. Exactly what is natural selection acting on in the selection ...
... and selects for the mutation or against the mutation. Thus, organisms that have a mutation that is selected will have their fitness increased, while organisms that have mutations that are selected against will have their fitness decreased. Exactly what is natural selection acting on in the selection ...
Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance
... Lipids - (also known as fats) - long term energy storage Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) - the instructions the cell uses to build proteins Proteins: The highly variable macromolecules that make each organism unique Structural - these make up the physical body of many organisms Functional (enzymes) - th ...
... Lipids - (also known as fats) - long term energy storage Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) - the instructions the cell uses to build proteins Proteins: The highly variable macromolecules that make each organism unique Structural - these make up the physical body of many organisms Functional (enzymes) - th ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.























