PPT Version - OMICS International
... I- Passive acquired immunity Ready made Ab transferred to individual giving rapid protection and short lasting immunity: a-Naturally acquired passive immunity Occurs when antibody are transferred from mother to fetus (IgG ) or in colostrum (Ig A). b- Artificially acquired passive immunity Short-ter ...
... I- Passive acquired immunity Ready made Ab transferred to individual giving rapid protection and short lasting immunity: a-Naturally acquired passive immunity Occurs when antibody are transferred from mother to fetus (IgG ) or in colostrum (Ig A). b- Artificially acquired passive immunity Short-ter ...
Document
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
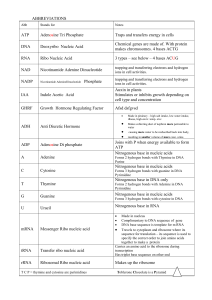
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
Immune System
... - body response when the same antigen enters the body another time - within 1-2 days after infection there are high levels of antibodies & specialized cells B Cells & Antibodies (figure 10-9) Complement system – enzymes in the blood that burst bacterial cells T Cells & Immunity (figure 10-9) ...
... - body response when the same antigen enters the body another time - within 1-2 days after infection there are high levels of antibodies & specialized cells B Cells & Antibodies (figure 10-9) Complement system – enzymes in the blood that burst bacterial cells T Cells & Immunity (figure 10-9) ...
Spring 2011 Midterm Review Answers
... cause only one amino acid to change. Mutations can be frameshift mutations in which a base is added or deleted from the sequence – this will cause all the amino acids past the change to be different. ...
... cause only one amino acid to change. Mutations can be frameshift mutations in which a base is added or deleted from the sequence – this will cause all the amino acids past the change to be different. ...
Document
... special note: the captions in the textbook for this graphic are important to review ...
... special note: the captions in the textbook for this graphic are important to review ...
Biol 207 Workshop 8 Answer Key
... plasmid purification endonucleases sometimes cut the supercoiled circular plasmid producing the relaxed circular and linear forms of the DNA molecule. e) 1. A molecular biologist needs to be able to select for transformed bacteria. A plasmid with a selectable marker gene such as one that makes the b ...
... plasmid purification endonucleases sometimes cut the supercoiled circular plasmid producing the relaxed circular and linear forms of the DNA molecule. e) 1. A molecular biologist needs to be able to select for transformed bacteria. A plasmid with a selectable marker gene such as one that makes the b ...
1. dia - immunology.unideb.hu
... Induction of CD8+ T cell responses against tumors. CD8+ T cell responses to tumors may be induced by cross-priming (also called cross-presentation), in which the tumor cells or tumor antigens (or both) are taken up by dendritic cells, processed, and presented to T cells. In some cases, B7 costimulat ...
... Induction of CD8+ T cell responses against tumors. CD8+ T cell responses to tumors may be induced by cross-priming (also called cross-presentation), in which the tumor cells or tumor antigens (or both) are taken up by dendritic cells, processed, and presented to T cells. In some cases, B7 costimulat ...
03 Anichini
... Which antigens are relevant? Antigens encoded by non mutated genes (tissue-specific TAA or cancer-testis antigens) ...
... Which antigens are relevant? Antigens encoded by non mutated genes (tissue-specific TAA or cancer-testis antigens) ...
DNA RNA structure
... • Coding regions of DNA • Hold the code or instructions to build a protein • The protein causes a chemical reaction that results in a physical trait ...
... • Coding regions of DNA • Hold the code or instructions to build a protein • The protein causes a chemical reaction that results in a physical trait ...
Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen (HBsAg), L
... Hepatitis B virus (HBV) expresses three types of surface antigens, i.e. S-, M-, and L-protein. L-protein is composed of S-, Pre-S2, and Pre-S1 region. The deletion of Pre-S1 region forms M-protein, and further deletion of Pre-S2 region results in S-protein. Most of commercially available HBsAgs is c ...
... Hepatitis B virus (HBV) expresses three types of surface antigens, i.e. S-, M-, and L-protein. L-protein is composed of S-, Pre-S2, and Pre-S1 region. The deletion of Pre-S1 region forms M-protein, and further deletion of Pre-S2 region results in S-protein. Most of commercially available HBsAgs is c ...
Gregor Mendel & DNA structure
... and seemed to apply to many traits across many different species However, in the early 1900s two geneticists discovered that some traits can be inherited together, going against Mendel’s laws of independent assortment (linkage) ...
... and seemed to apply to many traits across many different species However, in the early 1900s two geneticists discovered that some traits can be inherited together, going against Mendel’s laws of independent assortment (linkage) ...
Virus-Cell Interactions
... subgroup A viruses due to saturation of subgroup A receptor, but are still sensitive to subgroup B viruses which use a different receptor (and vice versa) ...
... subgroup A viruses due to saturation of subgroup A receptor, but are still sensitive to subgroup B viruses which use a different receptor (and vice versa) ...
4A DNA Pre-Standard ANSWER KEY DNA STRUCTURE What type
... TRANSLATION/PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 30. What is produced in translation? PROTEIN OR POLYPEPTIDE 31. Ribosomes are made up of rRNA , 2 PARTS . Know the steps of translation: 32. Identify the following structures in the diagram: A: DNA TEMPLATE B: DNA COMPLIMENTARY STRAND C: NUCLEOTIDE D: mRNA ...
... TRANSLATION/PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 30. What is produced in translation? PROTEIN OR POLYPEPTIDE 31. Ribosomes are made up of rRNA , 2 PARTS . Know the steps of translation: 32. Identify the following structures in the diagram: A: DNA TEMPLATE B: DNA COMPLIMENTARY STRAND C: NUCLEOTIDE D: mRNA ...
EOC Review 2 - Wayne County Public Schools
... abnormal shape of red blood cell that make them unable to carry oxygen is ______. People who are heterozygous are immune to the mosquito carrying disease called ______________. ...
... abnormal shape of red blood cell that make them unable to carry oxygen is ______. People who are heterozygous are immune to the mosquito carrying disease called ______________. ...
Discovery of the DNA molecule
... Results of the Hershey Chase Experiment • Results: bacterial cells infected with the radioactive label of 32P had incorporated 32P into its cells. • The bacteria infected with the 35S did not incorporate it into itself, the 35S was left in the broth. ...
... Results of the Hershey Chase Experiment • Results: bacterial cells infected with the radioactive label of 32P had incorporated 32P into its cells. • The bacteria infected with the 35S did not incorporate it into itself, the 35S was left in the broth. ...
Biosafety and recombinant DNA technology
... expression systems • Biological expression systems consist of vectors and host cells. • E.g is plasmid pUC18. • Frequently used as a cloning vector in combination with Escherichia coli K12 cells, the pUC18 plasmid has been entirely sequenced. • All genes required for expression in other bacteria hav ...
... expression systems • Biological expression systems consist of vectors and host cells. • E.g is plasmid pUC18. • Frequently used as a cloning vector in combination with Escherichia coli K12 cells, the pUC18 plasmid has been entirely sequenced. • All genes required for expression in other bacteria hav ...
Classification of Viruses
... They are not classified as living organisms because they do not have a cellular structure. They do not have any of the structures that are found in living cells. They consist of strands of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. What are They? Virus’s are little more than mobile gen ...
... They are not classified as living organisms because they do not have a cellular structure. They do not have any of the structures that are found in living cells. They consist of strands of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. What are They? Virus’s are little more than mobile gen ...
Document
... Genes Contain Instructions for Building Proteins Genes contain instructions for making proteins, one of the major types of the molecules of life, or “biomolecules” Proteins, like DNA, are polymers ...
... Genes Contain Instructions for Building Proteins Genes contain instructions for making proteins, one of the major types of the molecules of life, or “biomolecules” Proteins, like DNA, are polymers ...
BIOLOGY (Theory)
... Name the cells that are released from the above mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity. ...
... Name the cells that are released from the above mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity. ...
dna testing workshop 2005
... 3. p53 is among the most important of the tumor suppressor genes identified so far. a. Which cancers have the highest incidence of p53 mutation associated with them? b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated ...
... 3. p53 is among the most important of the tumor suppressor genes identified so far. a. Which cancers have the highest incidence of p53 mutation associated with them? b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.