Week 39 (2015-09-21)
... years of age at Boston Children's Hospital were randomized to the hypothetical scenario that their child was enrolled in one of four biobanks with different policies for IRRs to receive (a) "None," (b) "All," (c) "Binary"-choice to receive all or none, and (d) "Granular"-use the preference-setting t ...
... years of age at Boston Children's Hospital were randomized to the hypothetical scenario that their child was enrolled in one of four biobanks with different policies for IRRs to receive (a) "None," (b) "All," (c) "Binary"-choice to receive all or none, and (d) "Granular"-use the preference-setting t ...
Classical and Modern Genetics
... iClicker Question • The studies of Gregor Mendel in the mid 1860’s provide data in support of the theory of particulate theory of inheritance. The other notable observation of Mendel was the quantitative data showing a ratio of ____ in the offspring of pea plant flower ...
... iClicker Question • The studies of Gregor Mendel in the mid 1860’s provide data in support of the theory of particulate theory of inheritance. The other notable observation of Mendel was the quantitative data showing a ratio of ____ in the offspring of pea plant flower ...
Genetic information determines structure
... Describe the process of transcription. What is produced by this process? How does the “sense” strand (also called template or transcribed strand) of DNA differ from the “nonsense” strand? Which is the longer? If the “nonsense” strand is not transcribed what is its value? Is nature wasteful? What rol ...
... Describe the process of transcription. What is produced by this process? How does the “sense” strand (also called template or transcribed strand) of DNA differ from the “nonsense” strand? Which is the longer? If the “nonsense” strand is not transcribed what is its value? Is nature wasteful? What rol ...
DNA Transcription All#read
... including RNA and protein. Research has also shown that the instructions stored within DNA are "read" in two steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, a portion of the doublestranded DNA template gives rise to a single-stranded RNA molecule. In some cases, the RNA molecule itself is a ...
... including RNA and protein. Research has also shown that the instructions stored within DNA are "read" in two steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, a portion of the doublestranded DNA template gives rise to a single-stranded RNA molecule. In some cases, the RNA molecule itself is a ...
Genetics Notes C Molecular Genetics Vocabulary • central dogma of
... nucleus to a ribosome in the cytoplasm and then helps assemble the protein. In short: DNA → RNA → Protein Discovering this sequence of events was a major milestone in molecular biology. It is called the central dogma of molecular biology. An overview of protein synthesis can be viewed at http://www. ...
... nucleus to a ribosome in the cytoplasm and then helps assemble the protein. In short: DNA → RNA → Protein Discovering this sequence of events was a major milestone in molecular biology. It is called the central dogma of molecular biology. An overview of protein synthesis can be viewed at http://www. ...
Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology PPT
... Adenine, Thymine, Gaunine, Cytosine, Difference: Thymine G,C,A,T ...
... Adenine, Thymine, Gaunine, Cytosine, Difference: Thymine G,C,A,T ...
Ch7 microbgeneticspart1HOLrg
... As DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of one Okazaki fragment, it encounters the 5′ end of another. A different type of DNA polymerase then removes the RNA primer nucleotides and simultaneously ...
... As DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of one Okazaki fragment, it encounters the 5′ end of another. A different type of DNA polymerase then removes the RNA primer nucleotides and simultaneously ...
Quantitative RT-PCR
... templates. If there is difficulty in the amplification, it may be very helpful to test different [Mg2+]. Titrate the [Mg2+] from 0.5 mM to 5 mM and run the PCR to determine the optimal [Mg2+]. 3. Preparation of Internal Control RNA Template The aim is to make a small internal deletion in the cDNA be ...
... templates. If there is difficulty in the amplification, it may be very helpful to test different [Mg2+]. Titrate the [Mg2+] from 0.5 mM to 5 mM and run the PCR to determine the optimal [Mg2+]. 3. Preparation of Internal Control RNA Template The aim is to make a small internal deletion in the cDNA be ...
Ch_17 From Gene to Protein
... Transcription & translation are simultaneous in bacteria DNA is in cytoplasm no mRNA ...
... Transcription & translation are simultaneous in bacteria DNA is in cytoplasm no mRNA ...
Mutations are any changes in the genetic material
... Adenine, Thymine, Gaunine, Cytosine, Difference: Thymine G,C,A,T ...
... Adenine, Thymine, Gaunine, Cytosine, Difference: Thymine G,C,A,T ...
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction What exactly is a Virus?
... maintain homeostasis in any way **It’s hard to “kill” something that’s not really alive, so antibiotics that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
... maintain homeostasis in any way **It’s hard to “kill” something that’s not really alive, so antibiotics that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
gene expression - cloudfront.net
... The genetic code is transferred to an amino acid sequence in a protein through the translation process, which begins with the arrival of the mRNA molecule at the ribosome. While the mRNA was being synthesized, tRNA molecules were uniting with their specific amino acids according to the activity of s ...
... The genetic code is transferred to an amino acid sequence in a protein through the translation process, which begins with the arrival of the mRNA molecule at the ribosome. While the mRNA was being synthesized, tRNA molecules were uniting with their specific amino acids according to the activity of s ...
Molecular genetics of gene expression
... • Describe the main parts of a gene and their functions. • What role do cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors play in gene regulation? • What is responsible for the wide diversity of protein structure found in nature? • In what different ways can gene expression be regulated? ...
... • Describe the main parts of a gene and their functions. • What role do cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors play in gene regulation? • What is responsible for the wide diversity of protein structure found in nature? • In what different ways can gene expression be regulated? ...
Central Dogma of Genetics
... • Once initiation is completed, RNA synthesis begins. – After 8–9 NTPs have been joined in the growing RNA chain, – sigma factor is released and reused for other initiations. – Core enzyme completes the transcript (Figure 13.4). ...
... • Once initiation is completed, RNA synthesis begins. – After 8–9 NTPs have been joined in the growing RNA chain, – sigma factor is released and reused for other initiations. – Core enzyme completes the transcript (Figure 13.4). ...
NZY M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase
... Little or no RT-PCR/RT-qPCR amplification product RNA damage or degradation Analyse RNA on a denaturing gel to verify integrity. Use aseptic conditions while working with RNA to prevent RNase contamination. Ensure the use of NZY Ribonuclease Inhibitor; the addition of this inhibitor is essential w ...
... Little or no RT-PCR/RT-qPCR amplification product RNA damage or degradation Analyse RNA on a denaturing gel to verify integrity. Use aseptic conditions while working with RNA to prevent RNase contamination. Ensure the use of NZY Ribonuclease Inhibitor; the addition of this inhibitor is essential w ...
1 Protein Synthesis DNA protein (nucleus) (ribosome) 1
... -there 64 different possible codons -only four bases in RNA carry instructions for 20 different amino acids because they can form 64 different codons -how and why: -the nucleotides are the 4 “letters” of the DNA alphabet -the small size of this alphabet is a problem protein molecules are built fro ...
... -there 64 different possible codons -only four bases in RNA carry instructions for 20 different amino acids because they can form 64 different codons -how and why: -the nucleotides are the 4 “letters” of the DNA alphabet -the small size of this alphabet is a problem protein molecules are built fro ...
1 Protein Synthesis DNA protein (nucleus) (ribosome) 1
... -initiation determines exactly where translation will begin -starting from this point, the grouping of bases into codons is called the reading frame -if the start is shifted by one or two nucleotides in either direction, the frame changes -a different sequence of codons and amino acids will result - ...
... -initiation determines exactly where translation will begin -starting from this point, the grouping of bases into codons is called the reading frame -if the start is shifted by one or two nucleotides in either direction, the frame changes -a different sequence of codons and amino acids will result - ...
bch2ibm: molecular biology end of semester 1 exam notes 2014
... Qu. What is the Shine-‐Delgarno sequence? -‐ It’s a ribosomal binding site in mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of AUG -‐ Exists only in prokaryotes -‐ The six-‐base consensus sequence is AGGAG ...
... Qu. What is the Shine-‐Delgarno sequence? -‐ It’s a ribosomal binding site in mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of AUG -‐ Exists only in prokaryotes -‐ The six-‐base consensus sequence is AGGAG ...
DNA
... •one strand of DNA acts as a template •RNA polymerase reads the DNA bases •RNA nucleotides are placed across from the complimentary DNA bases ...
... •one strand of DNA acts as a template •RNA polymerase reads the DNA bases •RNA nucleotides are placed across from the complimentary DNA bases ...
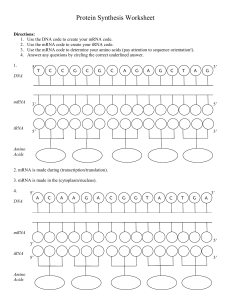
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
No Slide Title
... Sequence of the RNA is identical to that of the coding strand (with the replacements of Us for Ts). ...
... Sequence of the RNA is identical to that of the coding strand (with the replacements of Us for Ts). ...
1 Biological information flow
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) - ~15% of total RNA, 73-95 nucleotides long, carry activated amino acids to ribosomes during translation (Small RNA) - may have catalytic activity and/or associate with proteins to enhance activity, some involved with RNA processing (includes snRNA and microRNA, the latter involv ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) - ~15% of total RNA, 73-95 nucleotides long, carry activated amino acids to ribosomes during translation (Small RNA) - may have catalytic activity and/or associate with proteins to enhance activity, some involved with RNA processing (includes snRNA and microRNA, the latter involv ...
Transcription in Bacteria
... Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase. If the gene transcribed encodes a protein, the result of transcription is messenger RNA (mRNA), which then will be used to create that protein via the process of ...
... Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase. If the gene transcribed encodes a protein, the result of transcription is messenger RNA (mRNA), which then will be used to create that protein via the process of ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.