Transcription and Translation Made Easy
... 1. Randomly distribute the mRNA circles and the tRNA squares throughout the room. Tell the students that the circles are the free-floating RNA nucleotides inside the nucleus and the squares are the available amino acids outside of the nucleus. 2. Explain why the DNA must transcribe to RNA to leave t ...
... 1. Randomly distribute the mRNA circles and the tRNA squares throughout the room. Tell the students that the circles are the free-floating RNA nucleotides inside the nucleus and the squares are the available amino acids outside of the nucleus. 2. Explain why the DNA must transcribe to RNA to leave t ...
Figure 5.x3 James Watson and Francis Crick
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries information from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where the proteins are assembled. It is a partial copy of ONLY the information needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries information from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where the proteins are assembled. It is a partial copy of ONLY the information needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment ...
Ch27 PowerPoint LN
... whereas the archaea RNA polymerase cannot when in vitro (transcription factors are needed.) • Archaea promoter regions are rich in A’s and T’s like the TATA box of eukaryotes. ...
... whereas the archaea RNA polymerase cannot when in vitro (transcription factors are needed.) • Archaea promoter regions are rich in A’s and T’s like the TATA box of eukaryotes. ...
The Long Non-coding RNA ELENA1 Functions in
... Once seen as potential sequencing artifacts, long-noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs; >200 nucleotides) have gained recognition as important regulatory factors. lncRNAs are transcribed from a variety of genomic locations (introns, intergenic spaces, and coding regions) from the sense or antisense strand (revie ...
... Once seen as potential sequencing artifacts, long-noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs; >200 nucleotides) have gained recognition as important regulatory factors. lncRNAs are transcribed from a variety of genomic locations (introns, intergenic spaces, and coding regions) from the sense or antisense strand (revie ...
RNA and DNA and protein PLUS mciro info sheet2.pub
... rapid method for the isolation and purification of total RNA, genomic DNA and proteins sequentially from a single sample of cultured animal cells, small tissue samples, microdissected samples including laser-capture microdissection (LCM), blood, fungi or plants. The total RNA, genomic DNA and protei ...
... rapid method for the isolation and purification of total RNA, genomic DNA and proteins sequentially from a single sample of cultured animal cells, small tissue samples, microdissected samples including laser-capture microdissection (LCM), blood, fungi or plants. The total RNA, genomic DNA and protei ...
2 - chrisbonline.com
... and, under some relatively mild conditions, can be completely degraded to smaller molecules. • The chemistry of these reactions is complex and is made ...
... and, under some relatively mild conditions, can be completely degraded to smaller molecules. • The chemistry of these reactions is complex and is made ...
Written Transcript of this video lesson in English (PDF
... to amino acids which reach the cell through blood stream where they are combined again to form the proteins essential for our body structure & growth. But, first let's talk about the cell structure: ...
... to amino acids which reach the cell through blood stream where they are combined again to form the proteins essential for our body structure & growth. But, first let's talk about the cell structure: ...
Written Transcript of this video lesson in English
... the nucleus and cytoplasm, each nucleotide is composed of ribose sugar, and nitrogen base, a phosphate group. The nitrogen bases are adenine A, guanine G, cytosine C, and uracil U, and there are three types of nucleic acids RNA: First: mRNA which carries DNA genetic code instructions, from the nucle ...
... the nucleus and cytoplasm, each nucleotide is composed of ribose sugar, and nitrogen base, a phosphate group. The nitrogen bases are adenine A, guanine G, cytosine C, and uracil U, and there are three types of nucleic acids RNA: First: mRNA which carries DNA genetic code instructions, from the nucle ...
The Origin of Life - Frederick H. Willeboordse
... components of the current atmosphere and was likely very similar to the gasses still escaping from volcanoes nowadays. H2O, CO, CO2, CH4, NH3, N2, H2S, H2 Most of the early earth’s water was probably in vaporous form leading to intense rains while the oceans were slowly forming. ...
... components of the current atmosphere and was likely very similar to the gasses still escaping from volcanoes nowadays. H2O, CO, CO2, CH4, NH3, N2, H2S, H2 Most of the early earth’s water was probably in vaporous form leading to intense rains while the oceans were slowly forming. ...
Lec 16 - RNA and IT`s Structure
... nucleotide units. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DN ...
... nucleotide units. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the cell, RNA is usually single-stranded, while DNA is usually double-stranded; RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DN ...
RNAi, Penetrance and Expressivity Genetics 322, Fall 2008
... produce petunias with dark purple flowers by introducing a purple pigment gene into the flower. They reasoned that extra copies of a purple pigment gene would produce extra pigment and help produce a darker colored flower. However, they were surprised to produce flowers that appeared variegated, spo ...
... produce petunias with dark purple flowers by introducing a purple pigment gene into the flower. They reasoned that extra copies of a purple pigment gene would produce extra pigment and help produce a darker colored flower. However, they were surprised to produce flowers that appeared variegated, spo ...
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... Bases: A,U,C,G • uracil replaces thymine Single strand ...
... Bases: A,U,C,G • uracil replaces thymine Single strand ...
Handout
... RNA Transcription RNA polymerase transcribes mRNA using the DNA template (the "coding" strand of the double-stranded DNA) the new RNA strand has ribonucleotides instead of deoxyribonucleotides & uracil (U) is used in place of thymine (T) to base pair with adenine (A) RNA polymerase binds to a promot ...
... RNA Transcription RNA polymerase transcribes mRNA using the DNA template (the "coding" strand of the double-stranded DNA) the new RNA strand has ribonucleotides instead of deoxyribonucleotides & uracil (U) is used in place of thymine (T) to base pair with adenine (A) RNA polymerase binds to a promot ...
Document
... The start codon is the one that makes the tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop ...
... The start codon is the one that makes the tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop ...
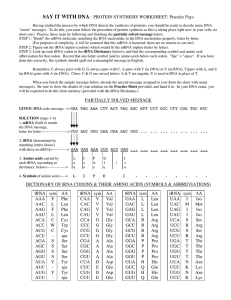
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
DNA notes - Chapel Hill
... Because viruses are protein and DNA only, they figured out that viral DNA (not viral protein) could force the bacteria to make new viruses. This was evidence that DNA can determine cell activity. ...
... Because viruses are protein and DNA only, they figured out that viral DNA (not viral protein) could force the bacteria to make new viruses. This was evidence that DNA can determine cell activity. ...
INTRODUCTION: - the BIOTECH Project
... of rRNA with genomic DNA to measure the similarity of rRNAs in various species. These experiments demonstrated that rRNA-based methods are applicable to directly comparing a broader range of organisms (i.e., spanning greater phylogenetic distances) than is whole genome DNA-DNA hybridization. However ...
... of rRNA with genomic DNA to measure the similarity of rRNAs in various species. These experiments demonstrated that rRNA-based methods are applicable to directly comparing a broader range of organisms (i.e., spanning greater phylogenetic distances) than is whole genome DNA-DNA hybridization. However ...
Poster in PDF format - Central Connecticut State University
... conclusion was drawn from the 8 positive lanes. Another conclusion drawn from this data was ...
... conclusion was drawn from the 8 positive lanes. Another conclusion drawn from this data was ...
Document
... series of three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA called codons The genetic code of mRNA is the amino acids and “start” and “stop” signals that are coded for by each of the possible 64 mRNA codons ...
... series of three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA called codons The genetic code of mRNA is the amino acids and “start” and “stop” signals that are coded for by each of the possible 64 mRNA codons ...
Gene Expression
... consequences for the polypeptide specified by the mutated DNA. 10. Be able to relate gene expression to an organism’s phenotype. Terms N-base adenine (A) guanine (G) thymine (T) cytosine (C) uracil (U) pentose deoxyribose ribose phosphate nucleotide complementary bases DNA RNA ...
... consequences for the polypeptide specified by the mutated DNA. 10. Be able to relate gene expression to an organism’s phenotype. Terms N-base adenine (A) guanine (G) thymine (T) cytosine (C) uracil (U) pentose deoxyribose ribose phosphate nucleotide complementary bases DNA RNA ...
2013
... A) a guanine nucleoside or nucleotide. B) endoribonucleases. C) polynucleotide phosphorylase. D) RNA polymerase II. E) small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). Circle the correct answer. ...
... A) a guanine nucleoside or nucleotide. B) endoribonucleases. C) polynucleotide phosphorylase. D) RNA polymerase II. E) small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). Circle the correct answer. ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... This raises the probability that a crossover will switch one version of an exon for another version found on the homologous chromosome. ° There may also be occasional mixing and matching of exons between completely different genes. ° Either way, exon shuffling can lead to new proteins through nove ...
... This raises the probability that a crossover will switch one version of an exon for another version found on the homologous chromosome. ° There may also be occasional mixing and matching of exons between completely different genes. ° Either way, exon shuffling can lead to new proteins through nove ...
Chapter 13 – RNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... Codons are the nitrogen bases on mRNA grouped into clusters of three. 2. How many codons are there? With 4 different nitrogen bases grouped into groups of three, there are 64 different combinations; therefore, there are 64 different codons. 3. What is the start codon? The start codon is the codon th ...
... Codons are the nitrogen bases on mRNA grouped into clusters of three. 2. How many codons are there? With 4 different nitrogen bases grouped into groups of three, there are 64 different combinations; therefore, there are 64 different codons. 3. What is the start codon? The start codon is the codon th ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.