Alnylam Licenses Intellectual Property from Cold Spring Harbor
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
Transition bias and substitution models
... – they are more likely synonymous in protein-coding sequences than transversions – they are less likely to disrupt RNA secondary structure than transversions. ...
... – they are more likely synonymous in protein-coding sequences than transversions – they are less likely to disrupt RNA secondary structure than transversions. ...
Differential Regulation of a-Lactalbumin and
... gland on various days of pregnancy and lactation. Chart 8 pups during lactation; casein messenger levels are dimin shows total protein synthesized as a function of the pg of ished (Chart 9A). When a-lactalbumin mRNA activity was measured at RNA added to the translation system. It is apparent from th ...
... gland on various days of pregnancy and lactation. Chart 8 pups during lactation; casein messenger levels are dimin shows total protein synthesized as a function of the pg of ished (Chart 9A). When a-lactalbumin mRNA activity was measured at RNA added to the translation system. It is apparent from th ...
Nucleic Acids
... In Chapter 18, we saw that the four levels of structural complexity in polypeptides and proteins are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. There are three levels of structural complexity in nucleic acids, and although these levels are somewhat comparable to those in polypeptides and proteins ...
... In Chapter 18, we saw that the four levels of structural complexity in polypeptides and proteins are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. There are three levels of structural complexity in nucleic acids, and although these levels are somewhat comparable to those in polypeptides and proteins ...
Inhibition of the Particle-associated RNA
... and magnesium ions but which would form very stable complexes with heavy metals such as zinc, copper and iron (SiUen & Martell, 197 0. These latter three metals are the ones commonly found in metalloenzymes and heavy metal-activated enzymes (Williams, 197I). Although some of the ligands tested would ...
... and magnesium ions but which would form very stable complexes with heavy metals such as zinc, copper and iron (SiUen & Martell, 197 0. These latter three metals are the ones commonly found in metalloenzymes and heavy metal-activated enzymes (Williams, 197I). Although some of the ligands tested would ...
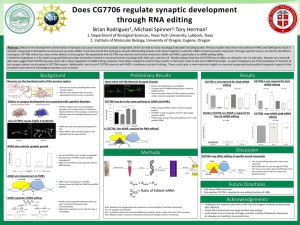
Symposium Poster - uospur
... Abstract: Defects in the development and formation of synapses can cause neuronal and synaptic overgrowth, which can lead to many neurological disorders including autism. Previous studies have shown that defective FMR1 and ADAR genes result in synaptic overgrowth in Drosophila neuromuscular junction ...
... Abstract: Defects in the development and formation of synapses can cause neuronal and synaptic overgrowth, which can lead to many neurological disorders including autism. Previous studies have shown that defective FMR1 and ADAR genes result in synaptic overgrowth in Drosophila neuromuscular junction ...
Full contents - Scion Publishing
... 9.2.2 The structure and function of the electron transport chain ����� 00 Box 9.4 The location of the electron transport chain............................ 00 9.2.3 Synthesis of ATP..................................................................... 00 Box 9.5 Why is a protein that makes A ...
... 9.2.2 The structure and function of the electron transport chain ����� 00 Box 9.4 The location of the electron transport chain............................ 00 9.2.3 Synthesis of ATP..................................................................... 00 Box 9.5 Why is a protein that makes A ...
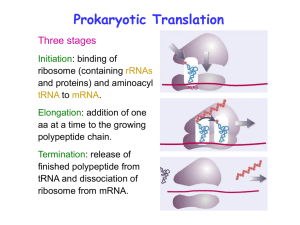
Class I tRNA
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
Synthesis of Oligonucleotides
... also vulnerable to phosphorylation by the activated deoxyribonucleoside phosphomonoester to give a trisubstituted pyrophosphate derivative. An aqueous work-up is necessary to regenerate the desired phosphodiester. Extension of the chain involves removal of the 3⬘-protecting group with alkali (for R ...
... also vulnerable to phosphorylation by the activated deoxyribonucleoside phosphomonoester to give a trisubstituted pyrophosphate derivative. An aqueous work-up is necessary to regenerate the desired phosphodiester. Extension of the chain involves removal of the 3⬘-protecting group with alkali (for R ...
HW4_final
... 2. What is the significance of the identified motif? Look at the occurrences distribution by clicking on “view occurrences distribution” or by downloading the motif occurrences file and explain how come the motif is so highly significant. 3. In a different study it has been shown that PUM2 binds RNA ...
... 2. What is the significance of the identified motif? Look at the occurrences distribution by clicking on “view occurrences distribution” or by downloading the motif occurrences file and explain how come the motif is so highly significant. 3. In a different study it has been shown that PUM2 binds RNA ...
Skeletal muscle actin mRNA. Characterization of the 3
... inserts that were sequenced are indicated by dotted lines. Restriction enzymes that were used and the position of their cleavage sites are indicated. The alignment of the cDNA inserts of plasmids p749 and pl50 with actin mRNA was made by comparing the amino acid sequences deduced from the nucleotide ...
... inserts that were sequenced are indicated by dotted lines. Restriction enzymes that were used and the position of their cleavage sites are indicated. The alignment of the cDNA inserts of plasmids p749 and pl50 with actin mRNA was made by comparing the amino acid sequences deduced from the nucleotide ...
PDF - Blood Journal
... than background DNA,7 although it appears that many lncRNAs detected in one species might not even be transcribed in another species.29 Whether this implies lack of function or an ability to gain and lose function more rapidly during evolution than protein-coding genes requires further study. Suppor ...
... than background DNA,7 although it appears that many lncRNAs detected in one species might not even be transcribed in another species.29 Whether this implies lack of function or an ability to gain and lose function more rapidly during evolution than protein-coding genes requires further study. Suppor ...
Received June 19, 1964.
... nucleotides by the pathway proposed in the Introduction. The observed greater conversion of orotic acid than either aspartic or carbamyl aspartic acids to -RNA is predicted by its position in the metabolic sequence, although comparisons are somewhat difficult because only the DL-forms of the latter ...
... nucleotides by the pathway proposed in the Introduction. The observed greater conversion of orotic acid than either aspartic or carbamyl aspartic acids to -RNA is predicted by its position in the metabolic sequence, although comparisons are somewhat difficult because only the DL-forms of the latter ...
X chromosome inactivation- Review
... X chromosome inactivation in flys and worms Distinct mechanisms to achieve dosage compensation C. elegans- Dosage compensation by reducing gene activity by two fold on each X chromosome Mechanism- if one X-, XO-lethal gene is on resulting in male determination Drosophila- Stimulate X gene t ...
... X chromosome inactivation in flys and worms Distinct mechanisms to achieve dosage compensation C. elegans- Dosage compensation by reducing gene activity by two fold on each X chromosome Mechanism- if one X-, XO-lethal gene is on resulting in male determination Drosophila- Stimulate X gene t ...
Transcripts of the MHM region on the chicken Z chromosome
... of chickens, consists of approximately 210 tandem repeats of a BamHI 2.2-kb sequence unit. Cytosines of the CpG dinucleotides of this region are extensively methylated on the two Z chromosomes in the male but much less methylated on the single Z chromosome in the female. The state of methylation of ...
... of chickens, consists of approximately 210 tandem repeats of a BamHI 2.2-kb sequence unit. Cytosines of the CpG dinucleotides of this region are extensively methylated on the two Z chromosomes in the male but much less methylated on the single Z chromosome in the female. The state of methylation of ...
Slides
... §Successful information-based system involves conservation and transfer §DNA - stable structure that maximizes storage and duplication §RNA - more reactive with numerous roles in protein synthesis and gene expression regulation ...
... §Successful information-based system involves conservation and transfer §DNA - stable structure that maximizes storage and duplication §RNA - more reactive with numerous roles in protein synthesis and gene expression regulation ...
Nucleic Acids - Lyndhurst Schools
... adenine (A) ❂ thymine (T) DNA only ❂ uracil (U) RNA only ❂ cytosine (C) ❂ guanine (G) ...
... adenine (A) ❂ thymine (T) DNA only ❂ uracil (U) RNA only ❂ cytosine (C) ❂ guanine (G) ...
Sex Chromosomes
... • In every diploid cell of the female only one X chromosomes is active. • Inactivation of X chromosome occurs randomly in somatic cells during embryogenesis. • Progeny of cells all have same inactivated X chromosome as original (clonality), creating mosaic individual. • X inactivation is irreversibl ...
... • In every diploid cell of the female only one X chromosomes is active. • Inactivation of X chromosome occurs randomly in somatic cells during embryogenesis. • Progeny of cells all have same inactivated X chromosome as original (clonality), creating mosaic individual. • X inactivation is irreversibl ...
Virp1 Is a Host Protein with a Major Role in Potato - IMBB
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that, while not coding for any protein, cause several plant diseases. Viroids rely for their infectious cycle on host proteins, most of which are likely to be involved in endogenous RNA-mediated phenomena. Therefore, characterization of host ...
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that, while not coding for any protein, cause several plant diseases. Viroids rely for their infectious cycle on host proteins, most of which are likely to be involved in endogenous RNA-mediated phenomena. Therefore, characterization of host ...
Full-Text PDF
... coenzyme Pyridoxal Phosphate, PLP, as in the transamination of Pyruvate to Alanine, Oxalacetate to Aspartate, Alpha-ketoglutarate to Glutamate, and Glyoxalate to Glycine. This implies that the coenzyme PLP may be ancient and have preceded the associated enzyme [2]. The next group of amino acids by t ...
... coenzyme Pyridoxal Phosphate, PLP, as in the transamination of Pyruvate to Alanine, Oxalacetate to Aspartate, Alpha-ketoglutarate to Glutamate, and Glyoxalate to Glycine. This implies that the coenzyme PLP may be ancient and have preceded the associated enzyme [2]. The next group of amino acids by t ...
Genome-wide RNAi Robert Barstead
... genetics to identify interacting pairs of genes. Recently, geneticists working on C. elegans have been challenged to apply genetic strategies to the study of those genes discovered by genome sequencing, which, within some small margin of error, shows us that the number of protein-coding genes in C. ...
... genetics to identify interacting pairs of genes. Recently, geneticists working on C. elegans have been challenged to apply genetic strategies to the study of those genes discovered by genome sequencing, which, within some small margin of error, shows us that the number of protein-coding genes in C. ...
A Bifunctional tRNA for In Vitro Selection
... mRNA and ribonucleases. The ribosome-bound PT fusions were then linked to their mRNAs by UV irradiation (Figure 3A), which crosslinks the wybutine base in tRNAx to the 5⬘-U of the Phe codon [16] (Figure 3B). As expected from a process that links a peptide to its mRNA, the product detected when the p ...
... mRNA and ribonucleases. The ribosome-bound PT fusions were then linked to their mRNAs by UV irradiation (Figure 3A), which crosslinks the wybutine base in tRNAx to the 5⬘-U of the Phe codon [16] (Figure 3B). As expected from a process that links a peptide to its mRNA, the product detected when the p ...
Origins and Early Evolution of the tRNA Molecule
... Abstract: Modern transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are composed of ~76 nucleotides and play an important role as “adaptor” molecules that mediate the translation of information from messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Many studies suggest that the contemporary full-length tRNA was formed by the ligation of half-sized hairp ...
... Abstract: Modern transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are composed of ~76 nucleotides and play an important role as “adaptor” molecules that mediate the translation of information from messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Many studies suggest that the contemporary full-length tRNA was formed by the ligation of half-sized hairp ...
Posttranscriptional Control of Chloroplast Gene Expression
... genome and transcribed independently. The assembly of the mature psaA mRNA depends on two transsplicing reactions that require several trans-acting factors (7). Factors involved in this process were recently characterized. One of them resembles -uridine synthases, although this enzyme activity is n ...
... genome and transcribed independently. The assembly of the mature psaA mRNA depends on two transsplicing reactions that require several trans-acting factors (7). Factors involved in this process were recently characterized. One of them resembles -uridine synthases, although this enzyme activity is n ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.