Sequence Alignment - Bilkent University
... spliced internal exons from chromosome 22 (Hide et al. 2001), which occur in the proteincoding region, are presented as reference (darker shaded bars). Exons were considered as domain adding if their length was a multiple of three, and there was no in-frame stop codon within them. Exons were conside ...
... spliced internal exons from chromosome 22 (Hide et al. 2001), which occur in the proteincoding region, are presented as reference (darker shaded bars). Exons were considered as domain adding if their length was a multiple of three, and there was no in-frame stop codon within them. Exons were conside ...
GENETICS TEST IV - Daytona State College
... • The TATA box is a core promoter element that binds the TATAbinding protein (TBP) of transcription factor TFIID and determines the start site of transcription ...
... • The TATA box is a core promoter element that binds the TATAbinding protein (TBP) of transcription factor TFIID and determines the start site of transcription ...
- Wiley Online Library
... effective condensing agent among polyphosphates, particularly because it can serve as a phosphorylating reagent in aqueous and strongly alkaline solution (pH 12) (Etaix & Orgel, 1978; Yamagata et al., 1995; Ozawa et al., 2004). The prebiotic synthesis proceeds by the thermolysis of phosphate to yiel ...
... effective condensing agent among polyphosphates, particularly because it can serve as a phosphorylating reagent in aqueous and strongly alkaline solution (pH 12) (Etaix & Orgel, 1978; Yamagata et al., 1995; Ozawa et al., 2004). The prebiotic synthesis proceeds by the thermolysis of phosphate to yiel ...
Gene Regulation Notes
... – Initiation of translation – Protein processing and degradation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... – Initiation of translation – Protein processing and degradation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
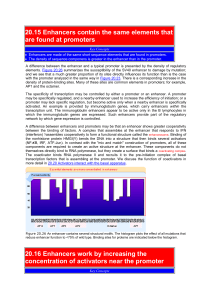
20.15 Enhancers contain the same elements that are
... An authentic GAL4 protein can activate a target gene only if it has a UAS. The LexA repressor by itself of course lacks the ability to activate either sort of target. The LexA-GAL4 hybrid can no longer activate a gene with a UAS, but it can now activate a gene that has a LexA operator! This result f ...
... An authentic GAL4 protein can activate a target gene only if it has a UAS. The LexA repressor by itself of course lacks the ability to activate either sort of target. The LexA-GAL4 hybrid can no longer activate a gene with a UAS, but it can now activate a gene that has a LexA operator! This result f ...
Messenger RNA reprogramming by spliceosome-mediated
... number of splice sites. A quick (and likely conservative) calculation suggests that if 10% of all intron-containing genes (∼30,000 genes) are actively transcribing (∼3,000 genes), and each on average is producing three transcripts, then there will be at least 70,000 introns in need of splicing (14, ...
... number of splice sites. A quick (and likely conservative) calculation suggests that if 10% of all intron-containing genes (∼30,000 genes) are actively transcribing (∼3,000 genes), and each on average is producing three transcripts, then there will be at least 70,000 introns in need of splicing (14, ...
Translation - Advanced
... into secondary and then tertiary structures. These levels of organization were discussed in the Organic Compounds: Proteins (Advanced) concept. Briefly, the primary structure of the protein is the sequence of amino acids determined by the gene and mRNA. The secondary and tertiary structures are dete ...
... into secondary and then tertiary structures. These levels of organization were discussed in the Organic Compounds: Proteins (Advanced) concept. Briefly, the primary structure of the protein is the sequence of amino acids determined by the gene and mRNA. The secondary and tertiary structures are dete ...
NIH Public Access
... Since biochemical analysis of such a large, tightly chromatin bound RNA has been difficult by standard extraction-based approaches, we pursued a different approach to manipulate the binding or release of XIST RNA directly within living cells. This strategy built upon a significant clue from our earl ...
... Since biochemical analysis of such a large, tightly chromatin bound RNA has been difficult by standard extraction-based approaches, we pursued a different approach to manipulate the binding or release of XIST RNA directly within living cells. This strategy built upon a significant clue from our earl ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... host-specific nod gene products, resulting in effective nodules on a limited range of host plants (1, 16, 38, 48). Other nod genes identified in R. leguminosarum bv. viciae are nodlJ, nodMNT (6, 54, 55), and nodO (11, 15). Mutations in these genes have more or less severe effects on nodulation, depe ...
... host-specific nod gene products, resulting in effective nodules on a limited range of host plants (1, 16, 38, 48). Other nod genes identified in R. leguminosarum bv. viciae are nodlJ, nodMNT (6, 54, 55), and nodO (11, 15). Mutations in these genes have more or less severe effects on nodulation, depe ...
An Arabidopsis Mutant with a Reduced Leve1 of cabl40 RNA 1s a
... 2 Current address: Departmentof Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114. 3 To whom correspondence should be addressed. ...
... 2 Current address: Departmentof Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114. 3 To whom correspondence should be addressed. ...
Hyper-eccentric structural genes in the mitochondrial genome of the
... Diplonemid mitochondria are considered to have very eccentric structural genes. Coding regions of individual diplonemid mitochondrial genes are fragmented into small pieces and found on different circular DNAs. Short RNAs transcribed from each DNA molecule mature through a unique RNA maturation proc ...
... Diplonemid mitochondria are considered to have very eccentric structural genes. Coding regions of individual diplonemid mitochondrial genes are fragmented into small pieces and found on different circular DNAs. Short RNAs transcribed from each DNA molecule mature through a unique RNA maturation proc ...
Fulltext PDF
... E. coli tRNA was found to be resistant to ribonuclease, an enzyme that can hydrolyse RNA. This work was carried out by Susumu Nishimura who was earlier at the National Cancer Centre Research Institute, Tokyo and presently at the University of Tsukuba, Japan. Subsequently, in collaboration with Har G ...
... E. coli tRNA was found to be resistant to ribonuclease, an enzyme that can hydrolyse RNA. This work was carried out by Susumu Nishimura who was earlier at the National Cancer Centre Research Institute, Tokyo and presently at the University of Tsukuba, Japan. Subsequently, in collaboration with Har G ...
Ribosome Profiling
... functional proteins [1]. Unlike DNA inside the cell, transcriptome varies according to the requirement of the cell. Therefore, the study of gene expression by analyzing entire transcripts can provide important insights into the spatial and temporal gene regulation inside a cell. Microarray and RNA s ...
... functional proteins [1]. Unlike DNA inside the cell, transcriptome varies according to the requirement of the cell. Therefore, the study of gene expression by analyzing entire transcripts can provide important insights into the spatial and temporal gene regulation inside a cell. Microarray and RNA s ...
Adenylate Energy Charge
... Starvation of organisms. Bacteria were harvested late in the period of arithmetic growth and just before the onset of stationary phase. They were washed with 67 mM-KNa phosphate buffer, pH 6.8, and then resuspended in the same buffer at approx. 0.8 mg dry wt,"ml.The suspension was placed in a starva ...
... Starvation of organisms. Bacteria were harvested late in the period of arithmetic growth and just before the onset of stationary phase. They were washed with 67 mM-KNa phosphate buffer, pH 6.8, and then resuspended in the same buffer at approx. 0.8 mg dry wt,"ml.The suspension was placed in a starva ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu helps the correct aa-tRNA insert into site A • An EF-Tu-GTP complex binds to all aa-tRNA molecules except fMet-tRNAfMet (initiator) • A ternary complex of EF-Tu-GTP-aa-tRNA binds in the ribosomal A site • If the anticodon of the aa-tRNA correctly base pairs with t ...
... • Bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu helps the correct aa-tRNA insert into site A • An EF-Tu-GTP complex binds to all aa-tRNA molecules except fMet-tRNAfMet (initiator) • A ternary complex of EF-Tu-GTP-aa-tRNA binds in the ribosomal A site • If the anticodon of the aa-tRNA correctly base pairs with t ...
Untitled
... entities in the cytosol. They only come together when translation is initiated (usually close to the 5’ end of the mRNA). The small subunit facilitates base pairing between the codon and anticodon sequences while the large subunit catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. The RNA ...
... entities in the cytosol. They only come together when translation is initiated (usually close to the 5’ end of the mRNA). The small subunit facilitates base pairing between the codon and anticodon sequences while the large subunit catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. The RNA ...
Untitled
... entities in the cytosol. They only come together when translation is initiated (usually close to the 5’ end of the mRNA). The small subunit facilitates base pairing between the codon and anticodon sequences while the large subunit catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. The RNA ...
... entities in the cytosol. They only come together when translation is initiated (usually close to the 5’ end of the mRNA). The small subunit facilitates base pairing between the codon and anticodon sequences while the large subunit catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. The RNA ...
Chapter 24 Translation
... 24.15 Termination Codons Are Recognized by Protein Factors • Termination codons are recognized by protein release factors, not by aminoacyltRNAs. • RF1 – The bacterial release factor that recognizes UAA and UAG as signals to terminate polypeptide translation. • RF2 – The bacterial release factor th ...
... 24.15 Termination Codons Are Recognized by Protein Factors • Termination codons are recognized by protein release factors, not by aminoacyltRNAs. • RF1 – The bacterial release factor that recognizes UAA and UAG as signals to terminate polypeptide translation. • RF2 – The bacterial release factor th ...
pdf
... a. tRNAs are short, being only 73 to 93 nts long. b. All tRNAs have the trinucleotide CCA at the 3' end. (1) The amino acid is attached to the terminal A of the CCA. (2) In most prokaryotic tRNA genes, the CCA is encoded at the 3' end of the gene. No known eukaryotic tRNA gene encodes the CCA, but r ...
... a. tRNAs are short, being only 73 to 93 nts long. b. All tRNAs have the trinucleotide CCA at the 3' end. (1) The amino acid is attached to the terminal A of the CCA. (2) In most prokaryotic tRNA genes, the CCA is encoded at the 3' end of the gene. No known eukaryotic tRNA gene encodes the CCA, but r ...
Application of Bruchin B to pea pods results in
... 1999). Bruchin B application also led to the biosynthesis of pisatin, an isoflavone phytoalexin of pea (Cruickshank and Perrin, 1962; Perrin and Bottomley, 1962). It has been hypothesized that phytoalexins play a role in disease resistance, but despite considerable study such a role has not been def ...
... 1999). Bruchin B application also led to the biosynthesis of pisatin, an isoflavone phytoalexin of pea (Cruickshank and Perrin, 1962; Perrin and Bottomley, 1962). It has been hypothesized that phytoalexins play a role in disease resistance, but despite considerable study such a role has not been def ...
XIST
... Models of Tsix-mediated repression of Xist. (A) Tsix DNA sequence itself could function as a long-range silencer to repress or block the transcription of the Xist gene. (B) Transcription of Xist may be prohibited by the processivity of RNA polymerase in the antisense orientation. As RNA polymerase ...
... Models of Tsix-mediated repression of Xist. (A) Tsix DNA sequence itself could function as a long-range silencer to repress or block the transcription of the Xist gene. (B) Transcription of Xist may be prohibited by the processivity of RNA polymerase in the antisense orientation. As RNA polymerase ...
O - IS MU
... Unfortunately, uric acid and its urate salts have a low solubility in water. The average serum concentrations in humans (normal range 100-400 µmol/l) is close to the solubility limit, above which the precipitation of needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals may begin. Excessive accumulation of urate ...
... Unfortunately, uric acid and its urate salts have a low solubility in water. The average serum concentrations in humans (normal range 100-400 µmol/l) is close to the solubility limit, above which the precipitation of needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals may begin. Excessive accumulation of urate ...
Molecular Determinants of Alphavirus Neurovirulence: Nucleotide
... signal peptide, also was found to be a G in both viruses. The m R N A sequences encoding the 6K signal proteins of TC-83 and T R D viruses were therefore identical (see Kinney et al., 1986). Nucleotide number 2822 was a C in both viral RNAs so that clone pTC-5, which contains a U at position 2822, d ...
... signal peptide, also was found to be a G in both viruses. The m R N A sequences encoding the 6K signal proteins of TC-83 and T R D viruses were therefore identical (see Kinney et al., 1986). Nucleotide number 2822 was a C in both viral RNAs so that clone pTC-5, which contains a U at position 2822, d ...
Translation | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... The genetic code is nearly universal to all known species on Earth. There are a few exceptions such as mitochondria, chloroplasts and some prokaryotes. However, it is clear that the exceptions are very few and affect very few codons. Furthermore, all known genetic codes are more similar than differe ...
... The genetic code is nearly universal to all known species on Earth. There are a few exceptions such as mitochondria, chloroplasts and some prokaryotes. However, it is clear that the exceptions are very few and affect very few codons. Furthermore, all known genetic codes are more similar than differe ...
Transcription regulation of the Escherichia coli pcnB gene coding for
... understanding these crucial cellular processes and possibly employing them in genetic engineering and biotechnology. In this light, perhaps surprisingly, regulation of expression of the pcnB gene in E. coli is relatively poorly understood. Liu and Parkinson (1989), on the basis of nucleotide sequenc ...
... understanding these crucial cellular processes and possibly employing them in genetic engineering and biotechnology. In this light, perhaps surprisingly, regulation of expression of the pcnB gene in E. coli is relatively poorly understood. Liu and Parkinson (1989), on the basis of nucleotide sequenc ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.