Document
... 2. Compare and contrast bacterial,eukaryal, and archaeal lipids, especially the molecular components and the bonds. More details later. 3. What are nucleic acids? Understand that nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine), a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one to three ...
... 2. Compare and contrast bacterial,eukaryal, and archaeal lipids, especially the molecular components and the bonds. More details later. 3. What are nucleic acids? Understand that nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine), a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one to three ...
Antisense derivatives of U7 small nuclear RNA as
... well as the therapeutic time window, it may be desirable to induce and repress the expression of a U7 cassette at will or to express it specifically in certain tissues or cell types. In this respect it is important to note that the transcription of U snRNA genes is fundamentally different from that ...
... well as the therapeutic time window, it may be desirable to induce and repress the expression of a U7 cassette at will or to express it specifically in certain tissues or cell types. In this respect it is important to note that the transcription of U snRNA genes is fundamentally different from that ...
The Genetic Code: Francis Crick`s Legacy and Beyond
... proposed the “frozen accident hypothesis” and conjectured that the genetic code evolved from the last universal common ancestor and was frozen once established. However, he explicitly left room for stereochemical interactions between amino acids and their coding nucleotides, stating that “It is ther ...
... proposed the “frozen accident hypothesis” and conjectured that the genetic code evolved from the last universal common ancestor and was frozen once established. However, he explicitly left room for stereochemical interactions between amino acids and their coding nucleotides, stating that “It is ther ...
biomass composition
... N-acetylmuramate and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine are arranged alternately to form the backbone of the peptidoglycan molecule. N-acetylmuramate molecules are cross-linked with a tail of four aminoacids (L-Ala, D-Glu, L-Lys, D-Ala). Some of those tails are linked together through an interbridge of D-aspart ...
... N-acetylmuramate and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine are arranged alternately to form the backbone of the peptidoglycan molecule. N-acetylmuramate molecules are cross-linked with a tail of four aminoacids (L-Ala, D-Glu, L-Lys, D-Ala). Some of those tails are linked together through an interbridge of D-aspart ...
The novel genome organization of the insect picorna
... The complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA from the insect picorna-like virus Drosophila C virus (DCV) was determined. The DCV sequence predicts a genome organization different to that of other RNA virus families whose sequences are known. The single-stranded positive-sense genomic RNA is 9 ...
... The complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA from the insect picorna-like virus Drosophila C virus (DCV) was determined. The DCV sequence predicts a genome organization different to that of other RNA virus families whose sequences are known. The single-stranded positive-sense genomic RNA is 9 ...
RNAi in Plants: An Argonaute-Centered View
... sRNAs, as both AGO1 and AGO4 clade proteins have comparable binding affinities for 21- and 24-nucleotide sRNAs (Wu et al., 2010). These observations suggest that the enzymatic machinery underlying the biogenesis of cmiRNAs and lmiRNAs could dominate over the 59 terminal nucleotide to funnel their res ...
... sRNAs, as both AGO1 and AGO4 clade proteins have comparable binding affinities for 21- and 24-nucleotide sRNAs (Wu et al., 2010). These observations suggest that the enzymatic machinery underlying the biogenesis of cmiRNAs and lmiRNAs could dominate over the 59 terminal nucleotide to funnel their res ...
poster_CSHL_2007
... FIRE (for Finding Informative Regulatory Elements) is a highly sensitive approach for motif discovery from expression data, based on mutual information. It has the following characteristics: ...
... FIRE (for Finding Informative Regulatory Elements) is a highly sensitive approach for motif discovery from expression data, based on mutual information. It has the following characteristics: ...
Document
... From the growth patterns of the mutants, Beadle and Tatum deduced that each mutant was unable to carry out one step in the pathway for synthesizing arginine, presumably because it lacked the necessary enzyme. Because each of their mutants was mutated in a single gene, they concluded that each mutate ...
... From the growth patterns of the mutants, Beadle and Tatum deduced that each mutant was unable to carry out one step in the pathway for synthesizing arginine, presumably because it lacked the necessary enzyme. Because each of their mutants was mutated in a single gene, they concluded that each mutate ...
Antisense derivatives of U7 small nuclear RNA as
... To be effective, splicing-modulating antisense RNAs must accumulate in the nucleoplasm where splicing occurs. This is why derivatives of U small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and in particular of U7 snRNA, have been widely used for this purpose [1]. Apart from the advantage that the antisense RNA accumulat ...
... To be effective, splicing-modulating antisense RNAs must accumulate in the nucleoplasm where splicing occurs. This is why derivatives of U small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and in particular of U7 snRNA, have been widely used for this purpose [1]. Apart from the advantage that the antisense RNA accumulat ...
Combination of Reverse Transcription and Multienzyme Restriction
... were tested. The most reproducible results were obtained when cells were extracted from food suspensions in a chaotropic buffer with the High Pure RNA Isolation kit (Roche). Since the TRIzol reagent did not extract any RNA from food samples, the spectroscopic data were not obtained. The quantity and ...
... were tested. The most reproducible results were obtained when cells were extracted from food suspensions in a chaotropic buffer with the High Pure RNA Isolation kit (Roche). Since the TRIzol reagent did not extract any RNA from food samples, the spectroscopic data were not obtained. The quantity and ...
Statistical analysis of atomic contacts at RNA– protein
... conclusions are the following: (i) in all three groups of complexes, the most preferred amino acids (Arg, Asn, Ser, Lys) and the less preferred ones (Ala, Ile, Leu, Val) are the same; Trp and Cys are rarely observed (respectively 15 and 5 amino acids in the ensemble of interfaces); (ii) of the total ...
... conclusions are the following: (i) in all three groups of complexes, the most preferred amino acids (Arg, Asn, Ser, Lys) and the less preferred ones (Ala, Ile, Leu, Val) are the same; Trp and Cys are rarely observed (respectively 15 and 5 amino acids in the ensemble of interfaces); (ii) of the total ...
TRIzol Reagent
... organic phase. TRIzol was developed by Piotr Chomczynski. The red dye allows easy detection of the organic phase and is noninteractive with nucleic acids. The TRI in TRIzol stands for Total RNA Isolation. It also signifies the fact that this reagent can be used in the purification of RNA, DNA and pr ...
... organic phase. TRIzol was developed by Piotr Chomczynski. The red dye allows easy detection of the organic phase and is noninteractive with nucleic acids. The TRI in TRIzol stands for Total RNA Isolation. It also signifies the fact that this reagent can be used in the purification of RNA, DNA and pr ...
D-Isonucleotide (isoNA) incorporation around cleavage site of
... Human herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV2) belongs to the alpha herpesvirus subfamily and infection with HSV2 produces high morbidity and exhibits broad prevalence, long latency, and difficult curability. To date, no preventive vaccines or effective therapeutic drugs for recurrent infections are availabl ...
... Human herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV2) belongs to the alpha herpesvirus subfamily and infection with HSV2 produces high morbidity and exhibits broad prevalence, long latency, and difficult curability. To date, no preventive vaccines or effective therapeutic drugs for recurrent infections are availabl ...
handout
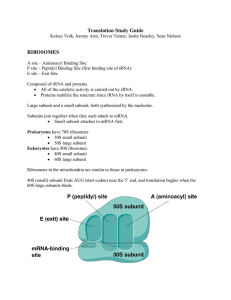
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
The DNA sequence of the fragment Hind.30, 378 bases lcng, fran
... ill vitro transcriptianal terminator sites and a sequence of 171 bases which probably codes for the N terminus of the T7 RNA polymerase. The sequence also codes for the RNase III cleavage site before gene 1. This overlaps with the transcriptianal terminators. The RNA transcript of the sequence about ...
... ill vitro transcriptianal terminator sites and a sequence of 171 bases which probably codes for the N terminus of the T7 RNA polymerase. The sequence also codes for the RNase III cleavage site before gene 1. This overlaps with the transcriptianal terminators. The RNA transcript of the sequence about ...
Translation tRNA is a link between the mRNA and the polypeptide
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) tRNA)– is an interpreter between the two forms of information – base sequence in mRNA and aminoacid sequence in polypeptides tRNA aligns appropriate aminoacids to form a new polypeptide. To perform this action tRNA must: •Transfer amino acids from the cytoplasm’s amino acid pool ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) tRNA)– is an interpreter between the two forms of information – base sequence in mRNA and aminoacid sequence in polypeptides tRNA aligns appropriate aminoacids to form a new polypeptide. To perform this action tRNA must: •Transfer amino acids from the cytoplasm’s amino acid pool ...
Chpt14_Translation.doc
... brief time (short relative to the time required to complete synthesis). 2. Completed polypeptides were collected, digested with trypsin, and the amount of radioactivity in tryptic fragments was determined. 3. Tryptic fragments from the C-terminal end of the polypeptide had radioactivity at the earli ...
... brief time (short relative to the time required to complete synthesis). 2. Completed polypeptides were collected, digested with trypsin, and the amount of radioactivity in tryptic fragments was determined. 3. Tryptic fragments from the C-terminal end of the polypeptide had radioactivity at the earli ...
Host Factors in the Replication of Positive
... proteins, (+)RNA viruses adopt a relatively conserved process for completing the RNA replication cycle in host cells. Studies of the mechanisms of (+)RNA virus replication have suggested that this process usually involves the following steps: 1) selecting and recruiting viral (+)RNA templates; 2) ta ...
... proteins, (+)RNA viruses adopt a relatively conserved process for completing the RNA replication cycle in host cells. Studies of the mechanisms of (+)RNA virus replication have suggested that this process usually involves the following steps: 1) selecting and recruiting viral (+)RNA templates; 2) ta ...
VIRUS STRUCTURE
... The capsid protects nucleic acid from inactivation by the outer physical conditions. ...
... The capsid protects nucleic acid from inactivation by the outer physical conditions. ...
Construction of an infectious cDNA clone for Omsk hemorrhagic
... the NS5 mutations, and OHF-IC-NS2A46 has the NS2A mutation. Recombinant viruses were recovered from these infectious cDNAs, and the growth curves were generated as described above. No significant differences were observed between the growth curves of OHF-IC-pt and OHF-IC-NS565 (Fig 4), indicating th ...
... the NS5 mutations, and OHF-IC-NS2A46 has the NS2A mutation. Recombinant viruses were recovered from these infectious cDNAs, and the growth curves were generated as described above. No significant differences were observed between the growth curves of OHF-IC-pt and OHF-IC-NS565 (Fig 4), indicating th ...
19-6-SA-V1-S1__mcq_a..
... 56. RNAase degrade RNA molecules of every kind irrespective of their type. Tell the type of specificity. 1. The proteins which yields aminoacids or their derivatives on hydrolysis are called __________ proteins. 23. 3D structure formed by amino acids which are being positioned far apart in the polyp ...
... 56. RNAase degrade RNA molecules of every kind irrespective of their type. Tell the type of specificity. 1. The proteins which yields aminoacids or their derivatives on hydrolysis are called __________ proteins. 23. 3D structure formed by amino acids which are being positioned far apart in the polyp ...
Chapter 17
... Let’s put this into some realistic context. Let’s imagine we are in the nucleus of a beta cell of your pancreas, which are the ones that secrete insulin when your blood glucose levels get too high (>140mg/dl). They need to be ready at any moment in case you drink a soda… and thus the gene is typical ...
... Let’s put this into some realistic context. Let’s imagine we are in the nucleus of a beta cell of your pancreas, which are the ones that secrete insulin when your blood glucose levels get too high (>140mg/dl). They need to be ready at any moment in case you drink a soda… and thus the gene is typical ...
Stages of Translation (Biol 200 Sp2015): KEY Initiation
... ii. __ The large and small ribosomal subunits separate and fall off the mRNA___ 3. What is the sequence of the codon that indicates the end of this protein? ___UAG________ (This is called a "STOP codon". This is one of 3 possible STOP codons.) 4. The release factor binds to the A-site relatively wea ...
... ii. __ The large and small ribosomal subunits separate and fall off the mRNA___ 3. What is the sequence of the codon that indicates the end of this protein? ___UAG________ (This is called a "STOP codon". This is one of 3 possible STOP codons.) 4. The release factor binds to the A-site relatively wea ...
What are enzymes and how do they work
... termination and 2) how the structure of the release factor impacts its function. Key concepts: The release factor’s role is to catalyze the hydrolysis of the bond between the last tRNA and the completed protein. The release factor does not have an anticodon or carry an amino acid, but it is the same ...
... termination and 2) how the structure of the release factor impacts its function. Key concepts: The release factor’s role is to catalyze the hydrolysis of the bond between the last tRNA and the completed protein. The release factor does not have an anticodon or carry an amino acid, but it is the same ...
Comparative day/night metatranscriptomic analysis of microbial
... sequences, Proteobacteria were most abundant (41%; Fig. 3) and were dominated by a-Proteobacteria (22%), b-Proteobacteria (8%) and g-Proteobacteria (8%). Bacteroidetes (8%) and Firmicutes (12%, biased towards the day sample) were also well represented. Taxonomically binned mRNA sequences were compar ...
... sequences, Proteobacteria were most abundant (41%; Fig. 3) and were dominated by a-Proteobacteria (22%), b-Proteobacteria (8%) and g-Proteobacteria (8%). Bacteroidetes (8%) and Firmicutes (12%, biased towards the day sample) were also well represented. Taxonomically binned mRNA sequences were compar ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.