RNA DNA
... • Use circle or lines to help you keep track of bases. • AAT TCC CGG GGA T… The original CYP2A6 gene. ...
... • Use circle or lines to help you keep track of bases. • AAT TCC CGG GGA T… The original CYP2A6 gene. ...
(DNA, RNA, or DNA/RNA) Microinjection Service Form
... cleavage/editing. It is the responsibility of the investigator to confirm whether mutagenesis and/or genome editing has occurred successfully in the resulting mice. • SgRNA-mediated cleavage has been reported to be prone to off-target mutagenesis. These events have been observed in some CRISPR-modif ...
... cleavage/editing. It is the responsibility of the investigator to confirm whether mutagenesis and/or genome editing has occurred successfully in the resulting mice. • SgRNA-mediated cleavage has been reported to be prone to off-target mutagenesis. These events have been observed in some CRISPR-modif ...
nucleic acids
... code for the order of the amino acids in the protein. The four bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). ...
... code for the order of the amino acids in the protein. The four bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). ...
week9_DNA&geneExpression.bak
... • The genetic code is both universal and degenerate. – Universal = found in all living organisms – Degenerate = having more than one base triplet (codon) to code for one amino acid ...
... • The genetic code is both universal and degenerate. – Universal = found in all living organisms – Degenerate = having more than one base triplet (codon) to code for one amino acid ...
The Process of Transcription-2
... – Commaless, spaceless, and non-overlapping : each 3 bases is read one after the other. – Punctuated: certain codons specify “start” and “stop”. – Universal: by viruses, both prokaryotic domains, and eukaryotes (except for some protozoa, mitochondria). ...
... – Commaless, spaceless, and non-overlapping : each 3 bases is read one after the other. – Punctuated: certain codons specify “start” and “stop”. – Universal: by viruses, both prokaryotic domains, and eukaryotes (except for some protozoa, mitochondria). ...
TRANSCRIPTION – TRANSLATION
... bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, uracil and cytosine. The various components are linked up as in DNA. There are three types of RNA in every cell: messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal RNA or rRNA and transfer RNA or tRNA. The three types of RNAs are transcribed from different regions of DNA template. R ...
... bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, uracil and cytosine. The various components are linked up as in DNA. There are three types of RNA in every cell: messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal RNA or rRNA and transfer RNA or tRNA. The three types of RNAs are transcribed from different regions of DNA template. R ...
Promega Notes: Separate Isolation of Genomic DNA and Total RNA
... removal of contaminating genomic DNA from the purified RNA, RNase-Free DNase I is applied directly to the SV Total RNA Isolation System membrane. To ensure that the RNA is not contaminated with DNase I, the enzyme is inactivated by the SV DNase Stop Solution. Contaminating salts and cellular impurit ...
... removal of contaminating genomic DNA from the purified RNA, RNase-Free DNase I is applied directly to the SV Total RNA Isolation System membrane. To ensure that the RNA is not contaminated with DNase I, the enzyme is inactivated by the SV DNase Stop Solution. Contaminating salts and cellular impurit ...
Emergence and Applications of RNA Interference
... trying to deepen the purple color of these flowers, Rich Jorgensen and colleagues introduced a pigment-producing gene under the control of a powerful promoter. Instead of the expected deep purple color, many of the flowers appeared variegated or even white. This phenomenon was considered to be postt ...
... trying to deepen the purple color of these flowers, Rich Jorgensen and colleagues introduced a pigment-producing gene under the control of a powerful promoter. Instead of the expected deep purple color, many of the flowers appeared variegated or even white. This phenomenon was considered to be postt ...
Click here for powerpoint
... The code to make protein is in DNA. aa Since DNA can’t leave the nucleus a copy aa called mRNA is made, which is sent to the aa ribosome to then make protein aa ...
... The code to make protein is in DNA. aa Since DNA can’t leave the nucleus a copy aa called mRNA is made, which is sent to the aa ribosome to then make protein aa ...
Exam II Answer Key
... Once it is determined that a bacterium needs to transcribe an operon, hundreds (if not thousands) of copies of polycistronic mRNAs are generated, as is shown in the image. Further, each mRNA is translated multiple times to produce an explosive increase in the concentration of each encoded protein i ...
... Once it is determined that a bacterium needs to transcribe an operon, hundreds (if not thousands) of copies of polycistronic mRNAs are generated, as is shown in the image. Further, each mRNA is translated multiple times to produce an explosive increase in the concentration of each encoded protein i ...
SURVEY AND SUMMARY Origins of tmRNA: the
... of metabolism (4). Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) is a hybrid molecule present in all bacteria. It exhibits properties of both transfer and messenger RNA, and permits the rescue of ribosomes arrested during translation. So not only does tmRNA play a key cellular role in modern bacteria, but in a sin ...
... of metabolism (4). Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) is a hybrid molecule present in all bacteria. It exhibits properties of both transfer and messenger RNA, and permits the rescue of ribosomes arrested during translation. So not only does tmRNA play a key cellular role in modern bacteria, but in a sin ...
Recognition of an Essential Adenine at a Protein
... stabilization of protein-nucleic acid complexes is not well established.1 Stacking interactions between proteins and nucleic acid helices are uncommon because the nucleic acid bases are already involved in this interaction in the helix.2 However, bases in single-stranded regions of nucleic acids are ...
... stabilization of protein-nucleic acid complexes is not well established.1 Stacking interactions between proteins and nucleic acid helices are uncommon because the nucleic acid bases are already involved in this interaction in the helix.2 However, bases in single-stranded regions of nucleic acids are ...
Learning Objectives
... Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain ...
... Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain ...
Learning Objectives
... Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain ...
... Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain ...
protein synthesis
... nucleus and translated in the cytosol Proteins are generally equipped with targeting signals ( a signal sequence of 12-70 amino acids at the amino terminal) Protein import occurs at translocation site In most cases, protein destined for the mitochondrial inner membrane after transport through ...
... nucleus and translated in the cytosol Proteins are generally equipped with targeting signals ( a signal sequence of 12-70 amino acids at the amino terminal) Protein import occurs at translocation site In most cases, protein destined for the mitochondrial inner membrane after transport through ...
The DNA of microorganisms is made up of subunits called A
... RNA molecules differ from DNA molecules because only RNA A. has ribose. B. has uracil. C. is typically one strand of nucleotides. D. does not have thymine. E. All of the choices are correct. ...
... RNA molecules differ from DNA molecules because only RNA A. has ribose. B. has uracil. C. is typically one strand of nucleotides. D. does not have thymine. E. All of the choices are correct. ...
blank worksheet
... LIGHTCYCLER and FASTSTART are trademarks of Roche. All other product names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners. NOTICE: This product may be subject to certain use restrictions. Before using this product, please refer to the Online Technical Support page (http://technical-suppo ...
... LIGHTCYCLER and FASTSTART are trademarks of Roche. All other product names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners. NOTICE: This product may be subject to certain use restrictions. Before using this product, please refer to the Online Technical Support page (http://technical-suppo ...
Lecture #4 Translation
... Basic Genetic Mechanisms are Universal The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. It appears that all life forms have a common evolutionary ancestor w ...
... Basic Genetic Mechanisms are Universal The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. It appears that all life forms have a common evolutionary ancestor w ...
bio 15 midterm exam 2 qa 141112
... d. NaCl e. H2O 2. The following molecules are considered polymers except……Mark all that apply a. Starch b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the ...
... d. NaCl e. H2O 2. The following molecules are considered polymers except……Mark all that apply a. Starch b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation Activity
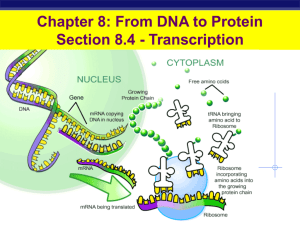
... In a process called transcription, the DNA code is transcribed (copied) into mRNA, following rules similar to DNA replication we saw earlier (see below). mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it links up with ribosomes and begins churning out proteins. Recall that DNA consists of a ...
... In a process called transcription, the DNA code is transcribed (copied) into mRNA, following rules similar to DNA replication we saw earlier (see below). mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it links up with ribosomes and begins churning out proteins. Recall that DNA consists of a ...
DNA and Protein Production
... Determine the complementary mRNA sequence from a DNA sequence. What are the steps of protein synthesis (production) for a cytosolic protein and for a protein that will be exported from the cell – starting in the nucleus, know the parts of the cell and their role in protein synthesis and protein modi ...
... Determine the complementary mRNA sequence from a DNA sequence. What are the steps of protein synthesis (production) for a cytosolic protein and for a protein that will be exported from the cell – starting in the nucleus, know the parts of the cell and their role in protein synthesis and protein modi ...
DNA - Napa Valley College
... What is the structure of proteins What are the structural differences between DNA and RNA, what are the structural similarities? Determine the complementary mRNA sequence from a DNA sequence. What are the steps of protein synthesis (production) for a cytosolic protein and for a protein that will be ...
... What is the structure of proteins What are the structural differences between DNA and RNA, what are the structural similarities? Determine the complementary mRNA sequence from a DNA sequence. What are the steps of protein synthesis (production) for a cytosolic protein and for a protein that will be ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.