Slide 1 - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... • A variety of cellular components play important roles in translation – These include proteins, RNAs and small molecules ...
... • A variety of cellular components play important roles in translation – These include proteins, RNAs and small molecules ...
101 -- 2006
... a) small proteins that function in translation. b) proteins and small RNAs that function in translation. c) proteins and tRNAs that function in transcription. d) proteins and mRNAs that function in translation. e) mRNAs and tRNAs that function in translation. __ 33. Which of the following is/are tru ...
... a) small proteins that function in translation. b) proteins and small RNAs that function in translation. c) proteins and tRNAs that function in transcription. d) proteins and mRNAs that function in translation. e) mRNAs and tRNAs that function in translation. __ 33. Which of the following is/are tru ...
Review #2
... Mechanisms of transcription What is the subunit structure of bacterial RNA polymerases? What is the 3D shape? What are the three phases of the process of making RNA, and what, in general, happens in each phase? What is the basic structure of the promoter, and what is the structure of the RNA polymer ...
... Mechanisms of transcription What is the subunit structure of bacterial RNA polymerases? What is the 3D shape? What are the three phases of the process of making RNA, and what, in general, happens in each phase? What is the basic structure of the promoter, and what is the structure of the RNA polymer ...
8-Cell and Molecular Biology (Transcription)
... In contrast, most RNAs are more than a few thousand nucleotide long and many are considerably shorter • The enzyme that perform transcription are called RNA polymerase • Like DNA polymerase that catalyzes DNA replication, RNA polymerases catalyze the formation of the phosphodiester bonds that li ...
... In contrast, most RNAs are more than a few thousand nucleotide long and many are considerably shorter • The enzyme that perform transcription are called RNA polymerase • Like DNA polymerase that catalyzes DNA replication, RNA polymerases catalyze the formation of the phosphodiester bonds that li ...
Biology II (Block III)
... from the mRNA, the tRNA that are being called bring specific AAs depending on the information of the mRNA and the ribosomes start making chains of these. Step 3: The polypeptide chain continues growing until the ribosome reaches a “stop” codon on the mRNA molecule. After this the ribosome releases b ...
... from the mRNA, the tRNA that are being called bring specific AAs depending on the information of the mRNA and the ribosomes start making chains of these. Step 3: The polypeptide chain continues growing until the ribosome reaches a “stop” codon on the mRNA molecule. After this the ribosome releases b ...
Origins of Life PDF
... Part II – Gaining Knowledge of One Hypothesis: Jigsaw Instructions (1) The class will separate into working groups of four members. Within the working groups, assign two members to Team 1 and two members to Team 2. For this first section, Team 1 and Team 2 separate. Team 1 will be given an informati ...
... Part II – Gaining Knowledge of One Hypothesis: Jigsaw Instructions (1) The class will separate into working groups of four members. Within the working groups, assign two members to Team 1 and two members to Team 2. For this first section, Team 1 and Team 2 separate. Team 1 will be given an informati ...
lec39_2013 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... tRNA: Although it varies, there are generally 25-45 different tRNAs/organism. This complex single chain RNA molecule structure is stabilized by W-C H-bonds, non-W-C H-bonds, and phosphate-metal interactions. Acceptor stem: amino acids are attached to the 3' terminus of the tRNA by enzymes called a ...
... tRNA: Although it varies, there are generally 25-45 different tRNAs/organism. This complex single chain RNA molecule structure is stabilized by W-C H-bonds, non-W-C H-bonds, and phosphate-metal interactions. Acceptor stem: amino acids are attached to the 3' terminus of the tRNA by enzymes called a ...
From Gene to Protein—Transcription and Translation
... of four types of nucleotides, G, C, A and T, and RNA is a polymer of four corresponding types of nucleotides, G, C, A and U (instead of T). During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase separates the two strands of DNA. One side of DNA is used as a template to assemble a strand of mRNA by adding R ...
... of four types of nucleotides, G, C, A and T, and RNA is a polymer of four corresponding types of nucleotides, G, C, A and U (instead of T). During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase separates the two strands of DNA. One side of DNA is used as a template to assemble a strand of mRNA by adding R ...
RNA base–amino acid interaction strengths derived
... (4), it appears that the strengths of individual interacting pairs are not so critical. DNA binding sequence frequencies indicate that some interacting bases can be replaced. In part, this may reflect the replacement of one hydrogen bond acceptor or donor by a similar one from another base. However, ...
... (4), it appears that the strengths of individual interacting pairs are not so critical. DNA binding sequence frequencies indicate that some interacting bases can be replaced. In part, this may reflect the replacement of one hydrogen bond acceptor or donor by a similar one from another base. However, ...
No Slide Title
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
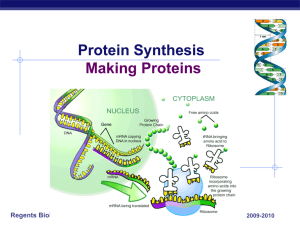
Protein Synthesis
... Fill It In … Three DNA nucleotides makes a ______. One codon controls the placement of one ...
... Fill It In … Three DNA nucleotides makes a ______. One codon controls the placement of one ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM msc
... Following are the steps involved in the processing of pre-mRNA. 1. The addition of the 5’ cap: Almost all eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are modified at their 5’ends by the addition of a structure called a 5’cap. This capping consists of the addition of an extra nucleotide at the 5’end of the mRNA and met ...
... Following are the steps involved in the processing of pre-mRNA. 1. The addition of the 5’ cap: Almost all eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are modified at their 5’ends by the addition of a structure called a 5’cap. This capping consists of the addition of an extra nucleotide at the 5’end of the mRNA and met ...
CHAPTER 12
... C15. In the context of translation, an activated amino acid has had AMP attached to it. This provides necessary energy so that the amino acid can be attached to the correct tRNA. C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significan ...
... C15. In the context of translation, an activated amino acid has had AMP attached to it. This provides necessary energy so that the amino acid can be attached to the correct tRNA. C16. Bases that have been chemically modified can occur at various locations throughout the tRNA molecule. The significan ...
Multiple Choice. ______1. Which of the following molecules
... c. genetic information is used to make proteins. d. sunlight energy is converted into chemical energy. ______39. Transcription of eukaryotic genes requires a. binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. b. binding of several transcription factors. c. capping of mRNA. d. Both a and b ______40. The exp ...
... c. genetic information is used to make proteins. d. sunlight energy is converted into chemical energy. ______39. Transcription of eukaryotic genes requires a. binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. b. binding of several transcription factors. c. capping of mRNA. d. Both a and b ______40. The exp ...
Nucleic Acids-Structure, Central Dogma
... -disrupts H-bonding of the two strands SSB (single-stranded DNA-binding proteins) – binds to the unwound strands, preventing re-annealing ...
... -disrupts H-bonding of the two strands SSB (single-stranded DNA-binding proteins) – binds to the unwound strands, preventing re-annealing ...
FROM GENE TO PROTEIN - Scranton Prep Biology
... Triplets of nucleotidesare the smallest units of uniform length to allow translation into all 20 amino acids with plenty to spare. ...
... Triplets of nucleotidesare the smallest units of uniform length to allow translation into all 20 amino acids with plenty to spare. ...
Unit 5 Molecular Genetics Objectives
... 2 The basic structural differences include: i DNA contains deoxyribose (RNA contains ribose). ii RNA contains uracil in lieu of thymine in DNA. iii DNA is usually double stranded, RNA is usually single stranded. iv The two DNA strands in double-stranded DNA are antiparallel in directionality. 3 Both ...
... 2 The basic structural differences include: i DNA contains deoxyribose (RNA contains ribose). ii RNA contains uracil in lieu of thymine in DNA. iii DNA is usually double stranded, RNA is usually single stranded. iv The two DNA strands in double-stranded DNA are antiparallel in directionality. 3 Both ...
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
... probe is about 50nt long and contains five modified T (aminoallyl-T), distanced by about 10 nt each (Sequence of the probes are in the Table SIV). The probes were labeled with ...
... probe is about 50nt long and contains five modified T (aminoallyl-T), distanced by about 10 nt each (Sequence of the probes are in the Table SIV). The probes were labeled with ...
12.1 Components of Nucleic Acids
... The secondary structure of DNA was proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. This was perhaps the greatest discovery of modern biology and one of the most remarkable and profound events in the history of science. Watson and Crick concluded that DNA is a double helix containing two polynucl ...
... The secondary structure of DNA was proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. This was perhaps the greatest discovery of modern biology and one of the most remarkable and profound events in the history of science. Watson and Crick concluded that DNA is a double helix containing two polynucl ...
12_ Nucleic Acids
... The secondary structure of DNA was proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. This was perhaps the greatest discovery of modern biology and one of the most remarkable and profound events in the history of science. Watson and Crick concluded that DNA is a double helix containing two polynucl ...
... The secondary structure of DNA was proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. This was perhaps the greatest discovery of modern biology and one of the most remarkable and profound events in the history of science. Watson and Crick concluded that DNA is a double helix containing two polynucl ...
Encoding Amino Acids • mRNA codes for amino acids
... o That would be 43, or 64, possible combinations o This is more than enough to represent all 20 amino acids ...
... o That would be 43, or 64, possible combinations o This is more than enough to represent all 20 amino acids ...
P1 The genetic code
... • Despite the fact that they all carry out the same reaction of joining an amino acid to a tRNA, the various synthetase enzymes can be quite different. • They fall into one of four classes of subunit structure, being either a, a2, a4, a2b2. • The polypeptide chains range from 334 to over 1000 amino ...
... • Despite the fact that they all carry out the same reaction of joining an amino acid to a tRNA, the various synthetase enzymes can be quite different. • They fall into one of four classes of subunit structure, being either a, a2, a4, a2b2. • The polypeptide chains range from 334 to over 1000 amino ...
An Artist in Gene Editing - Max-Planck
... transcribed CRISPR-RNA and an additional RNA molecule to identify the viral genome if it attacks again. They can cut through it, incapacitating the pathogens. In this way, the CRISPR-Cas9 system provides the bacterial immune system with a kind of memory. RNA: The DNA molecule contains the assembly i ...
... transcribed CRISPR-RNA and an additional RNA molecule to identify the viral genome if it attacks again. They can cut through it, incapacitating the pathogens. In this way, the CRISPR-Cas9 system provides the bacterial immune system with a kind of memory. RNA: The DNA molecule contains the assembly i ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.