KEY TERMS FOR Characteristics of Life
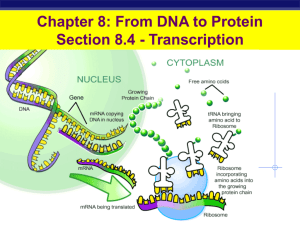
... Name: ___________________________________ Date: ____________ Class: ______ Page 5/19 Types of RNA Involved • There are three types of RNA involved in making proteins: – mRNA (messenger RNA): brings the DNA message into the cytoplasm – tRNA (transfer RNA): transfers amino acids to the growing protei ...
... Name: ___________________________________ Date: ____________ Class: ______ Page 5/19 Types of RNA Involved • There are three types of RNA involved in making proteins: – mRNA (messenger RNA): brings the DNA message into the cytoplasm – tRNA (transfer RNA): transfers amino acids to the growing protei ...
2014
... 16. [6 points] In the initiation of transcription in E. coli, the catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase first combines with the ________________ subunit to form the RNA polymerase holoenzyme complex which then binds to the DNA promoter to form the __________________ complex. Melting of the DNA duplex ...
... 16. [6 points] In the initiation of transcription in E. coli, the catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase first combines with the ________________ subunit to form the RNA polymerase holoenzyme complex which then binds to the DNA promoter to form the __________________ complex. Melting of the DNA duplex ...
Chapter 11 Nucleic Acids Nucleotides
... binding for the negatively charged ribose-phosphate chain of DNA. ...
... binding for the negatively charged ribose-phosphate chain of DNA. ...
Translation
... tRNA • tRNA first hypothesized by Francis Crick. • Small RNA chain that transfers a specific amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain in the ribosome • Has a 3' terminal site for amino acids (whose linkage depends on aminoacyl tRNA synthetase). • Contains a three base region called the anticodon t ...
... tRNA • tRNA first hypothesized by Francis Crick. • Small RNA chain that transfers a specific amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain in the ribosome • Has a 3' terminal site for amino acids (whose linkage depends on aminoacyl tRNA synthetase). • Contains a three base region called the anticodon t ...
BiochemReview
... • Breaking Val 98 – Tyr 145 bond has two effects: – 1) An H-bond between His 146 – Asp 94 is broken. – 2) An H-bond between His 146 and a Lysine on the alpha chain is broken. ...
... • Breaking Val 98 – Tyr 145 bond has two effects: – 1) An H-bond between His 146 – Asp 94 is broken. – 2) An H-bond between His 146 and a Lysine on the alpha chain is broken. ...
Press Release
... EMBL is Europe’s flagship laboratory for the life sciences, with more than 80 independent groups covering the spectrum of molecular biology. EMBL is international, innovative and interdisciplinary – its 1800 employees, from many nations, operate across five sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, ...
... EMBL is Europe’s flagship laboratory for the life sciences, with more than 80 independent groups covering the spectrum of molecular biology. EMBL is international, innovative and interdisciplinary – its 1800 employees, from many nations, operate across five sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, ...
1 Introduction 2 Central Dogma of molecular biology 3 DNA
... the sense that it is also a polymer made up of repeated nucleotides. However, it is single stranded. It is made up of also a different sugar. Its nucleotides are A, U, G, and C, where U is the analog of T in DNA. While most of the RNA gets translated into proteins there are some other types of RNA t ...
... the sense that it is also a polymer made up of repeated nucleotides. However, it is single stranded. It is made up of also a different sugar. Its nucleotides are A, U, G, and C, where U is the analog of T in DNA. While most of the RNA gets translated into proteins there are some other types of RNA t ...
Learning Objectives
... 15. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 16. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can prod ...
... 15. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 16. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can prod ...
set 3
... The table below represents the DNA sequence of a short region within a gene, the sequence of the RNA transcript, the anticodon sequences of the tRNA’s that decode the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of the protein product. The identities of some nucleotides and amino acid/s are given, but most boxe ...
... The table below represents the DNA sequence of a short region within a gene, the sequence of the RNA transcript, the anticodon sequences of the tRNA’s that decode the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of the protein product. The identities of some nucleotides and amino acid/s are given, but most boxe ...
university of oslo
... UAG, UGA) is in the A site. Only release factors (RF-1 or RF-2) that enter the A site can interact with translation stop codons and release the newly synthesized peptide in an energy-requiring reaction. Dissociation of the ribosome into separate large and small subunits is mediated by a ribosome rec ...
... UAG, UGA) is in the A site. Only release factors (RF-1 or RF-2) that enter the A site can interact with translation stop codons and release the newly synthesized peptide in an energy-requiring reaction. Dissociation of the ribosome into separate large and small subunits is mediated by a ribosome rec ...
Eukaryotic Transcription
... factors, and elongation is allowed to proceed as it does in prokaryotes with the polymerase synthesizing premRNA in the 5' to 3' direction. As discussed previously, RNA polymerase II transcribes the major share of eukaryotic genes, so this section will focus on how this polymerase accomplishes elong ...
... factors, and elongation is allowed to proceed as it does in prokaryotes with the polymerase synthesizing premRNA in the 5' to 3' direction. As discussed previously, RNA polymerase II transcribes the major share of eukaryotic genes, so this section will focus on how this polymerase accomplishes elong ...
Unraveling the mechanisms of RNA
... specifically in neurons and are believed to be involved in neuron-specific post-transcriptional gene regulation. These functions may involve the effects of Hu proteins on mRNA stability. The AU-rich sequences to which these proteins bind are frequently found in the 3´ untranslated regions of labile mR ...
... specifically in neurons and are believed to be involved in neuron-specific post-transcriptional gene regulation. These functions may involve the effects of Hu proteins on mRNA stability. The AU-rich sequences to which these proteins bind are frequently found in the 3´ untranslated regions of labile mR ...
AIBSTCT Nucleic Acids Research - Walter Lab
... in primary sequence, the secondary structure is nevertheless highly conserved (7-11), suggesting that these RNAs are parts of SRP analogues. 7SL RNA forms a central double stranded rod which is flanked at one end by two small stem loop structures comprising the 3 and 5 terminal nucleotides and at th ...
... in primary sequence, the secondary structure is nevertheless highly conserved (7-11), suggesting that these RNAs are parts of SRP analogues. 7SL RNA forms a central double stranded rod which is flanked at one end by two small stem loop structures comprising the 3 and 5 terminal nucleotides and at th ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
... 1. Why is transcription necessary? Transcription makes messenger RNA (MRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble MRNA. 3. Why ...
... 1. Why is transcription necessary? Transcription makes messenger RNA (MRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble MRNA. 3. Why ...
DNA - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... 2. Insertions or deletions of large pieces of DNA. 3. Combining parts of 2 different genes together. Mutations are very common: every cell contains multiple mutations. Also, everyone is genetically different from every other person due to the accumulation of mutations. Genetic load: on average, each ...
... 2. Insertions or deletions of large pieces of DNA. 3. Combining parts of 2 different genes together. Mutations are very common: every cell contains multiple mutations. Also, everyone is genetically different from every other person due to the accumulation of mutations. Genetic load: on average, each ...
Ch7 Enzymes II: Coenzymes, Regulation, Abzymes, and Ribozymes
... – M and H are made from two separate genes, are similar in amino acid sequence but can be separated by electrophoresis. – M4 in skeletal muscle – H4 in heart muscle – Mixture of five possible forms (M4, M3H, M2H2, MH3, H4) in ...
... – M and H are made from two separate genes, are similar in amino acid sequence but can be separated by electrophoresis. – M4 in skeletal muscle – H4 in heart muscle – Mixture of five possible forms (M4, M3H, M2H2, MH3, H4) in ...
HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
Molecular Genetics
... 4. There is at least one tRNA molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer tRNAs than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called the wobble hypothesis. ...
... 4. There is at least one tRNA molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer tRNAs than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called the wobble hypothesis. ...
Biochemistry
... Ribosomal RNAs-exist outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm of a cell in structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes are small, granular structures where protein synthesis takes place.Each ribosome is a complex consisting of about 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 40% protein. Messenger RNAs-are the nucleic aci ...
... Ribosomal RNAs-exist outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm of a cell in structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes are small, granular structures where protein synthesis takes place.Each ribosome is a complex consisting of about 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 40% protein. Messenger RNAs-are the nucleic aci ...
Personalized medicine - Pitt Department of Biomedical Informatics
... efforts that can be disseminated to a variety of stakeholders, including biomedical scientists, clinicians, and patients.” • Translational = benchside to bedside Atul Butte, JAMIA 2008;15:709-714 doi:10.1197 ...
... efforts that can be disseminated to a variety of stakeholders, including biomedical scientists, clinicians, and patients.” • Translational = benchside to bedside Atul Butte, JAMIA 2008;15:709-714 doi:10.1197 ...
Protein Synthesis and Sorting
... Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2016 ...
... Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2016 ...
group_presentation
... Massachusetts realized they could prevent a gene from being expressed by injecting or feeding the animal (nematode worms in this case) a double stranded RNA that corresponds to the worm’s DNA gene they are trying to silence ...
... Massachusetts realized they could prevent a gene from being expressed by injecting or feeding the animal (nematode worms in this case) a double stranded RNA that corresponds to the worm’s DNA gene they are trying to silence ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.