! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
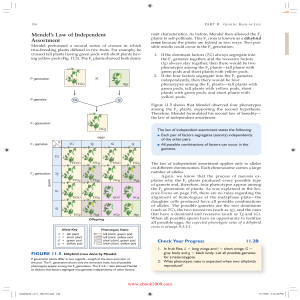
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
Chpt2_Struc_Nucleic_Acids.doc
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
The Structure and Function of the DNA from Bacteriophage Lambda
... These then are the two gene orders of normal lambda that have been established by genetic mapping procedures. They relate to two aspects of lambda DNA which will be considered here. The first concerns the position of these genes in the lambda DNA molecule as isolated from mature phage. The second co ...
... These then are the two gene orders of normal lambda that have been established by genetic mapping procedures. They relate to two aspects of lambda DNA which will be considered here. The first concerns the position of these genes in the lambda DNA molecule as isolated from mature phage. The second co ...
Large Scale SNP Scanning on Human Chromosome Y and DNA
... large numbers of SNP genotyping. Labeled with fluorescence, the oligonucliotide highthroughput genotyping methods are TaqMan (4), Hybridization probe (5), Simple probe (6), Invader assay (7) and allele-specific ligation (8) genotyping. We developed a non gel-based genotyping technique. This techniqu ...
... large numbers of SNP genotyping. Labeled with fluorescence, the oligonucliotide highthroughput genotyping methods are TaqMan (4), Hybridization probe (5), Simple probe (6), Invader assay (7) and allele-specific ligation (8) genotyping. We developed a non gel-based genotyping technique. This techniqu ...
Minireview Alpha Satellite and the Quest for the Human Centromere
... which in this case mediate chromosome movement rather than gene expression. In contrast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Drosophila melanogaster do not appear to contain such a “magic sequence” within their more complex and larger centromeres and may instead rely on higher order structure and epigenet ...
... which in this case mediate chromosome movement rather than gene expression. In contrast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Drosophila melanogaster do not appear to contain such a “magic sequence” within their more complex and larger centromeres and may instead rely on higher order structure and epigenet ...
Phenotypic and Genotypic Comparisons among Strains of the
... strains, fermentative testing does not clearly differentiate between these two groups. A prominent phenotypic characteristic of the A . viriduns G L strains was their tetrad-forming capacity, not found in other strains in the present study. Nonmarine strains of A . viriduns may also form packets of ...
... strains, fermentative testing does not clearly differentiate between these two groups. A prominent phenotypic characteristic of the A . viriduns G L strains was their tetrad-forming capacity, not found in other strains in the present study. Nonmarine strains of A . viriduns may also form packets of ...
The presence of two UvrB subunits in the UvrAB complex ensures
... the UvrB protein and this DNA wrap is dependent on ATP binding by UvrB (Verhoeven et al., 2001). DNA wrapping is expected to cause local melting of the DNA helix, thereby facilitating insertion of the b-hairpin of UvrB between the DNA strands. From mutational analysis of the b-hairpin it was propose ...
... the UvrB protein and this DNA wrap is dependent on ATP binding by UvrB (Verhoeven et al., 2001). DNA wrapping is expected to cause local melting of the DNA helix, thereby facilitating insertion of the b-hairpin of UvrB between the DNA strands. From mutational analysis of the b-hairpin it was propose ...
Slide 1
... promotor (pBAD) – site at which RNA polymerase binds to DNA to initiate transcription (an RNA copy of the genes are made which then moves to the ribosomes which use them to build the proteins) From the plasmid pARA ampicillin resistance gene (ampR) – enables us to selectively grow only bacteria ...
... promotor (pBAD) – site at which RNA polymerase binds to DNA to initiate transcription (an RNA copy of the genes are made which then moves to the ribosomes which use them to build the proteins) From the plasmid pARA ampicillin resistance gene (ampR) – enables us to selectively grow only bacteria ...
Biology Ch. 13
... These fragments were combined with vectors to create recombinant DNA, cloned to make many copies, and sequenced using automated sequencing machines. Computers analyzed the overlapping regions to generate one continuous sequence. ...
... These fragments were combined with vectors to create recombinant DNA, cloned to make many copies, and sequenced using automated sequencing machines. Computers analyzed the overlapping regions to generate one continuous sequence. ...
Chapter Seventeen: Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... Chapter Seventeen: Gene Mutations and DNA Repair 211 may also occur at two different locations within the same protein. If two regions of a protein interact, a mutation in one of these regions could disrupt that interaction. The suppressor mutation in the other region would restore the interaction. ...
... Chapter Seventeen: Gene Mutations and DNA Repair 211 may also occur at two different locations within the same protein. If two regions of a protein interact, a mutation in one of these regions could disrupt that interaction. The suppressor mutation in the other region would restore the interaction. ...
The Study of Genetics: A Historical Perspective Ross Edwards
... Despite the atrocities that occurred when combining scientific notions with politics, scientists continued to objectively determine the material inside the cells that passed hereditary information. Earlier in the 20th century, prior to the predominance of Lysenkoism, Russian biochemist Phoebus Leven ...
... Despite the atrocities that occurred when combining scientific notions with politics, scientists continued to objectively determine the material inside the cells that passed hereditary information. Earlier in the 20th century, prior to the predominance of Lysenkoism, Russian biochemist Phoebus Leven ...
Slides
... many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. • The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children 20-30 years later with the same problems despite being conceived and born during a normal dietary state. ...
... many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. • The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children 20-30 years later with the same problems despite being conceived and born during a normal dietary state. ...
CpG methylation analysis from targeted
... Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have enabled the analysis of differential methylation patterns at a genome-wide scale. These genome-wide approaches have enabled the discovery of epigenetic variations associated with disease progression, including cancer. To validate these ...
... Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have enabled the analysis of differential methylation patterns at a genome-wide scale. These genome-wide approaches have enabled the discovery of epigenetic variations associated with disease progression, including cancer. To validate these ...
pdf
... periods, labeled nucleotides can be incorporated during initiation of the short nascent chain as well as the during the elongation and termination. Since the 5’ end was labeled only during longer pulses, it must be the part synthesized first. Thus the direction of chain growth is 5’ to 3. Answer 5.1 ...
... periods, labeled nucleotides can be incorporated during initiation of the short nascent chain as well as the during the elongation and termination. Since the 5’ end was labeled only during longer pulses, it must be the part synthesized first. Thus the direction of chain growth is 5’ to 3. Answer 5.1 ...
DNA Replication Origin Function Is Promoted by H3K4 Di
... cycle. Individual origins vary both in the likelihood that they will initiate replication, or “fire,” in any given S phase and in the firing time within the S phase (Weinreich et al. 2004). Highly efficient origins fire in most cell cycles, whereas inefficient origins fire in only some cycles and are usua ...
... cycle. Individual origins vary both in the likelihood that they will initiate replication, or “fire,” in any given S phase and in the firing time within the S phase (Weinreich et al. 2004). Highly efficient origins fire in most cell cycles, whereas inefficient origins fire in only some cycles and are usua ...
PartTwoAnswers.doc
... periods, labeled nucleotides can be incorporated during initiation of the short nascent chain as well as the during the elongation and termination. Since the 5’ end was labeled only during longer pulses, it must be the part synthesized first. Thus the direction of chain growth is 5’ to 3. Answer 5.1 ...
... periods, labeled nucleotides can be incorporated during initiation of the short nascent chain as well as the during the elongation and termination. Since the 5’ end was labeled only during longer pulses, it must be the part synthesized first. Thus the direction of chain growth is 5’ to 3. Answer 5.1 ...
Genetics Heredity and Variation: *Heredity is the branch of science
... Gene mapping meaning relative positions of genes on chromosomes Calculating (CoV) crossing over value help us to produce maps for gene position on the chromosomes, by converting CoV this value into hypothetical distances along the chromosome. Ex: a (CoV) of 4% between genes A and B means that those ...
... Gene mapping meaning relative positions of genes on chromosomes Calculating (CoV) crossing over value help us to produce maps for gene position on the chromosomes, by converting CoV this value into hypothetical distances along the chromosome. Ex: a (CoV) of 4% between genes A and B means that those ...
Fractals are observed in nature
... reference). This image is remarkably similar to the ones reported in the literature. Chaos game of human globin region (73,357bp) (Jeffrey, 1990), human intron sequences (Solovyev, 1993), and randomly selected human DNA sequence of 100Kbp long (Deschavanne et al., 1999) resemble the image shown in ...
... reference). This image is remarkably similar to the ones reported in the literature. Chaos game of human globin region (73,357bp) (Jeffrey, 1990), human intron sequences (Solovyev, 1993), and randomly selected human DNA sequence of 100Kbp long (Deschavanne et al., 1999) resemble the image shown in ...
Nitrosation of aspartic acid, aspartame, and glycine ethylester
... unlikely target. However, methylamine has been shown to produce 7-methylguanine in DNA isolated from the stomach of rats after administration of radiolabelled methylamine together with high Ievels of nitrite (Huber and Lutz, 1984). It was therefore considered worth while to investigate in more detai ...
... unlikely target. However, methylamine has been shown to produce 7-methylguanine in DNA isolated from the stomach of rats after administration of radiolabelled methylamine together with high Ievels of nitrite (Huber and Lutz, 1984). It was therefore considered worth while to investigate in more detai ...
A Mathematical Formulation of DNA Computation
... results in a zero vector, then the hybridization by mixing the test tubes should be complete. A complete hybridization means all single-stranded DNA sequences find their complementaries. Proposition 2.3: Under the definition (1), if the inner product of two equal-lengthed sequences is not a real num ...
... results in a zero vector, then the hybridization by mixing the test tubes should be complete. A complete hybridization means all single-stranded DNA sequences find their complementaries. Proposition 2.3: Under the definition (1), if the inner product of two equal-lengthed sequences is not a real num ...
Enhancers reside in a unique epigenetic environment during early
... expression are characterized by relatively low levels of DNA methylation (hypo-methylation), while inactive enhancers display hyper-methylation of the underlying DNA. The direct functional significance of the DNA methylation state of enhancers is, however, unclear for most loci. Results: In contrast ...
... expression are characterized by relatively low levels of DNA methylation (hypo-methylation), while inactive enhancers display hyper-methylation of the underlying DNA. The direct functional significance of the DNA methylation state of enhancers is, however, unclear for most loci. Results: In contrast ...
Chapter 2. Structures of Nucleic Acids
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
A novel environment-sensitive biodegradable polydisulfide with
... disulfide-containing polycations were prepared from low molecular weight cationic peptides, which showed low cytotoxicity but poor gene transferring capability [23,24]. Reducible polycations with improved transfection efficiency were then prepared by linking histidine-rich or PEI segments with disul ...
... disulfide-containing polycations were prepared from low molecular weight cationic peptides, which showed low cytotoxicity but poor gene transferring capability [23,24]. Reducible polycations with improved transfection efficiency were then prepared by linking histidine-rich or PEI segments with disul ...
Micronuclei and the Cytoplasm of Growing Tetrahymena Contain a
... interested to see whether purified micronuclei contain any extractable activity that could acetylate macronuclear histones. Macronuclear histone (both DNA free and chromatin) was chosen as an initial substrate for these experiments (as opposed to micronuclear histone) since it is easier to prepare l ...
... interested to see whether purified micronuclei contain any extractable activity that could acetylate macronuclear histones. Macronuclear histone (both DNA free and chromatin) was chosen as an initial substrate for these experiments (as opposed to micronuclear histone) since it is easier to prepare l ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.