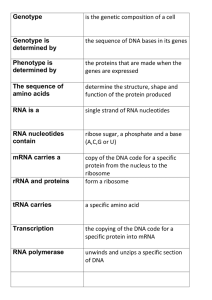
Transcription AND Translation
... regions) and exons (coding regions; the parts of a gene that are expressed). Both are transcribed from the DNA to the RNA. • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page ...
... regions) and exons (coding regions; the parts of a gene that are expressed). Both are transcribed from the DNA to the RNA. • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page ...
posted
... copy of a DNA sequence to site of protein synthesis at the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA)—carries amino acids for polypeptide assembly • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—catalyzes peptide bond formation and provides structure for the ribosome ...
... copy of a DNA sequence to site of protein synthesis at the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA)—carries amino acids for polypeptide assembly • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—catalyzes peptide bond formation and provides structure for the ribosome ...
PDF Datastream - Brown Digital Repository
... - We know that water, flour, and sugar are not alive, but what about yeast? How could we test to see if it is alive? - One characteristic of a living organism is metabolism (the ability to take “food” and convert it into energy, along with some byproducts) - To find out, we’ll give ...
... - We know that water, flour, and sugar are not alive, but what about yeast? How could we test to see if it is alive? - One characteristic of a living organism is metabolism (the ability to take “food” and convert it into energy, along with some byproducts) - To find out, we’ll give ...
Transcription and Translation
... • All 3 kinds of RNA are made by Transcription: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA • mRNA – carries the code from DNA to Ribosome • rRNA – makes up the Ribosomes (site of protein production) • tRNA – carries the amino acids to the ribosomes to be made into proteins • Most biology classes focus on the production of ...
... • All 3 kinds of RNA are made by Transcription: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA • mRNA – carries the code from DNA to Ribosome • rRNA – makes up the Ribosomes (site of protein production) • tRNA – carries the amino acids to the ribosomes to be made into proteins • Most biology classes focus on the production of ...
human biochemistry - churchillcollegebiblio
... Humans and other organisms have short sequences of bases that are repeated many times called satellite DNA. This satellite DNA varies greatly between different individuals in the number of repeats. If it is coped using a methods which is called PCR and then cut up into small fragments using restrict ...
... Humans and other organisms have short sequences of bases that are repeated many times called satellite DNA. This satellite DNA varies greatly between different individuals in the number of repeats. If it is coped using a methods which is called PCR and then cut up into small fragments using restrict ...
C - NCSU Bioinformatics Research Center
... Life depends on three critical molecules • DNAs • Hold information on how cell works ...
... Life depends on three critical molecules • DNAs • Hold information on how cell works ...
Protocol for QuickExtract™ RNA Extraction Kit
... transcriptase and a standard 20-μl protocol. Up to 50% of the reaction volume can be extracted RNA. 2. For standard and fast end-point PCR cycling profiles, use 1-5 μl of cDNA. 3. When using extracts in real-time RT-PCR with SYBR® Green I Dye, or other similar dye detection, DNase treatment of the ...
... transcriptase and a standard 20-μl protocol. Up to 50% of the reaction volume can be extracted RNA. 2. For standard and fast end-point PCR cycling profiles, use 1-5 μl of cDNA. 3. When using extracts in real-time RT-PCR with SYBR® Green I Dye, or other similar dye detection, DNase treatment of the ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-central dogma
... Translation Translation is the final step on the way from DNA to protein. - It is the synthesis of proteins directed by a mRNA template. - The information contained in the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is read as three letter words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. ...
... Translation Translation is the final step on the way from DNA to protein. - It is the synthesis of proteins directed by a mRNA template. - The information contained in the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is read as three letter words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. ...
MicroRNAs
... • Is miRNA regulated ? On which levels ? • Is there a regulation on the RISC ‘loading’ • Why is so many annotated miRNA related to differentiation ? – mRNA can be passed on during mitosis and need to cleaved ...
... • Is miRNA regulated ? On which levels ? • Is there a regulation on the RISC ‘loading’ • Why is so many annotated miRNA related to differentiation ? – mRNA can be passed on during mitosis and need to cleaved ...
Ch. 13 end of chapter review
... cause the fly to grow eyes in odd places. This happens despite the fact that mouse eyes and fly eyes are very different. In fact the only reason we describe them as “eyes” is because they make vision possible. How can the Pax6 gene perform the same role in such diverse animals? It probably began very ...
... cause the fly to grow eyes in odd places. This happens despite the fact that mouse eyes and fly eyes are very different. In fact the only reason we describe them as “eyes” is because they make vision possible. How can the Pax6 gene perform the same role in such diverse animals? It probably began very ...
Chapter 14 Guided Reading
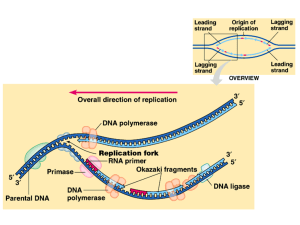
... 46. Label the diagram below showing the coupling of transcription and translation in prokaryotes. ...
... 46. Label the diagram below showing the coupling of transcription and translation in prokaryotes. ...
BIOL 112 – Principles of Zoology
... III. Post-transcriptional control A. Alternative splicing - Some messages undergo ...
... III. Post-transcriptional control A. Alternative splicing - Some messages undergo ...
12-3: RNA
... Mutations can be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external agents. Mutations in reproductive cells Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a ________ in a sperm or an egg cell. If this cell takes pa ...
... Mutations can be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external agents. Mutations in reproductive cells Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a ________ in a sperm or an egg cell. If this cell takes pa ...
Text - Enlighten - University of Glasgow
... of a set of genes controls lactose utilization. When lactose is absent a repressor binds at a site within the bacterial chromosome known as the lac operator that is proximal to the promoter sequence that drives expression of the lac operon. When present, lactose stimulates production of allolactose ...
... of a set of genes controls lactose utilization. When lactose is absent a repressor binds at a site within the bacterial chromosome known as the lac operator that is proximal to the promoter sequence that drives expression of the lac operon. When present, lactose stimulates production of allolactose ...
micro-RNAs (miRNAs) are short (22
... biosynthesis involves a number of processing steps (Fig. 1). Long primary miRNA (primiRNA) molecules are transcribed from non-coding polycistronic regions of the genome under the control of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) promoters (Zhou et al., 2007). These pri-miRNA transcripts can exceed 1 kb and may ...
... biosynthesis involves a number of processing steps (Fig. 1). Long primary miRNA (primiRNA) molecules are transcribed from non-coding polycistronic regions of the genome under the control of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) promoters (Zhou et al., 2007). These pri-miRNA transcripts can exceed 1 kb and may ...
DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated February 2013)
... polymerase III transcribes 5S rDNA, tDNA and other snDNA genes.] Other transcription factors bind the CAAT box, GC boxes or CACCC boxes if present as well as enhancer or silencer sequences which may also be found in certain upstream regulatory sequences of a given structural gene promoter. Sometimes ...
... polymerase III transcribes 5S rDNA, tDNA and other snDNA genes.] Other transcription factors bind the CAAT box, GC boxes or CACCC boxes if present as well as enhancer or silencer sequences which may also be found in certain upstream regulatory sequences of a given structural gene promoter. Sometimes ...
Prokaryotic Regulatory RNAs Cole Franks Proteins have been
... Prokaryotic regulatory proteins are particularly well understood; allosteric enzymes have been known since the 1960’s to carry out negative feedback. It seems, however, that proteins are far from the whole regulatory story. Evidence has been compiling for regulation by RNA itself. Most are familiar ...
... Prokaryotic regulatory proteins are particularly well understood; allosteric enzymes have been known since the 1960’s to carry out negative feedback. It seems, however, that proteins are far from the whole regulatory story. Evidence has been compiling for regulation by RNA itself. Most are familiar ...
Slide ()
... The transcription cycle. The transcription cycle can be described in six steps: (1) Template binding and closed RNA polymerase-promoter complex formation: RNAP binds to DNA and then locates a promoter (P), (2) Open promoter complex formation: once bound to the promoter, RNAP melts the two DNA strand ...
... The transcription cycle. The transcription cycle can be described in six steps: (1) Template binding and closed RNA polymerase-promoter complex formation: RNAP binds to DNA and then locates a promoter (P), (2) Open promoter complex formation: once bound to the promoter, RNAP melts the two DNA strand ...
From Gene to Protein The Central Dogma
... Experiments with E. Coli showed that it is capable of regulating the expression of its genes. Discovered prokaryote operons A prokaryote operon consists of the following elements ...
... Experiments with E. Coli showed that it is capable of regulating the expression of its genes. Discovered prokaryote operons A prokaryote operon consists of the following elements ...