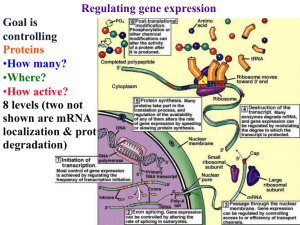
Chapter 10: Control of Gene Expression What Is Gene Control? A
... mRNA for destruction, no translation occurs and no protein is produced _____________________is also a factor in control over translation in prokaryotes Bacteria can shut off translation of a particular mRNA by expressing an ____________ (complementary) RNA strand With double-stranded RNA, __________ ...
... mRNA for destruction, no translation occurs and no protein is produced _____________________is also a factor in control over translation in prokaryotes Bacteria can shut off translation of a particular mRNA by expressing an ____________ (complementary) RNA strand With double-stranded RNA, __________ ...
First week lectures
... A self-replicating molecule that uses material and energy from the environment ...
... A self-replicating molecule that uses material and energy from the environment ...
Jeopardy!!
... free floating in the cytoplasm In Eukaryotes, the DNA is safely contained within the nucleus ...
... free floating in the cytoplasm In Eukaryotes, the DNA is safely contained within the nucleus ...
RNA PROCESSING AND RNPs
... Self-cleaving RNA encoded by viral genome to resolve the concatameric molecules of the viral genomic RNA produced. These molecules are able to fold up in such a way as to selfcleave themselves into monomeric. ...
... Self-cleaving RNA encoded by viral genome to resolve the concatameric molecules of the viral genomic RNA produced. These molecules are able to fold up in such a way as to selfcleave themselves into monomeric. ...
Microbial Genetics
... Amino acids are coded for by more than one codon Genetic Code is Degenerative Genetic Code is Universal ...
... Amino acids are coded for by more than one codon Genetic Code is Degenerative Genetic Code is Universal ...
Bio 121: Chapter 17 Protein Synthesis Assignment Objective
... Objective: Students explore the process of protein synthesis and demonstrate an understanding of the various steps involved through the completion of one of the following activities. Introduction Protein synthesis is an essential process that occurs constantly within our cells. As you sit reading th ...
... Objective: Students explore the process of protein synthesis and demonstrate an understanding of the various steps involved through the completion of one of the following activities. Introduction Protein synthesis is an essential process that occurs constantly within our cells. As you sit reading th ...
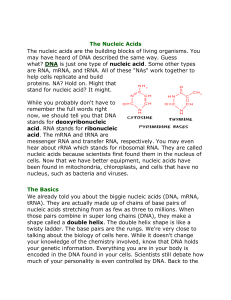
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cells that have no nucleus, such as bacteria and viruses. The Basics We already told you about the biggie nucleic acids (DNA, mRNA, tRNA). They are actually made up of chains of base pairs of n ...
... cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cells that have no nucleus, such as bacteria and viruses. The Basics We already told you about the biggie nucleic acids (DNA, mRNA, tRNA). They are actually made up of chains of base pairs of n ...
chapter12
... They remove two phosphates as the subunits are covalently linked to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule. These reactions are strongly exergonic. Messenger RNA contains the base sequence that codes for proteins. ...
... They remove two phosphates as the subunits are covalently linked to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule. These reactions are strongly exergonic. Messenger RNA contains the base sequence that codes for proteins. ...
Novel way plants pass traits to next generation found: Inheritance
... Pol IV has puzzled scientists because despite its this way. An investigation of the affected alleles strong conservation in all plants, it appears to have revealed the nearby presence of a transposon, or no discernible impact on the development of transposable element: a tiny piece of DNA that has A ...
... Pol IV has puzzled scientists because despite its this way. An investigation of the affected alleles strong conservation in all plants, it appears to have revealed the nearby presence of a transposon, or no discernible impact on the development of transposable element: a tiny piece of DNA that has A ...
AP_Gene to Protein
... These results showed that each mutant had a mutation in a SINGLE gene & that each gene affected only ONE enzyme. ...
... These results showed that each mutant had a mutation in a SINGLE gene & that each gene affected only ONE enzyme. ...
Slide 1
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition TRANSCRIPTION
... mRNAs for destruction Group 2: the miRNAs – generally regulate protein translation from mRNAs Group 3: the short siRNAs which target chromatin for modification ...
... mRNAs for destruction Group 2: the miRNAs – generally regulate protein translation from mRNAs Group 3: the short siRNAs which target chromatin for modification ...
NEW revision booklt - Eduspace
... 7.4.6 Explain the process of translation, including ribosomes, polysomes, start codons and stop codons. 3 ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... 7.4.6 Explain the process of translation, including ribosomes, polysomes, start codons and stop codons. 3 ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
3.5 Transcription and translation – summary of
... DNA is split into two strands; mRNA is made by transcription; promoter region (by start of gene) causes RNA polymerase to bind; anti-sense / template strand of DNA is transcribed; direction of transcription is 5’ 3’; free nucleotide triphosphates used; complementary base pairing between template s ...
... DNA is split into two strands; mRNA is made by transcription; promoter region (by start of gene) causes RNA polymerase to bind; anti-sense / template strand of DNA is transcribed; direction of transcription is 5’ 3’; free nucleotide triphosphates used; complementary base pairing between template s ...
Minireview: Global Regulation and Dynamics of Ribonucleic Acid
... level of RNA stability provide an advantage to multicellular systems (48). An important feature of RNA networks is that a significant proportion of cellular proteins encode RBPs that in turn regulate the mRNAs encoding other RBPs. This property of the ribonome forms a “regulators of regulators” feat ...
... level of RNA stability provide an advantage to multicellular systems (48). An important feature of RNA networks is that a significant proportion of cellular proteins encode RBPs that in turn regulate the mRNAs encoding other RBPs. This property of the ribonome forms a “regulators of regulators” feat ...
answers
... Each CODON in an m-RNA message is made of __3__ nucleotides. Each CODON in an m-RNA message represents __1____ amino acid. Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Whic ...
... Each CODON in an m-RNA message is made of __3__ nucleotides. Each CODON in an m-RNA message represents __1____ amino acid. Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Whic ...
Microarray_module_lecture_(both_courses)
... Look up p-value for the calculated t-statistic. Here: 9.21% are in the red shaded area. p= 0.09 Accept null hypothesis: Treatment and control are NOT different, M = 0 ...
... Look up p-value for the calculated t-statistic. Here: 9.21% are in the red shaded area. p= 0.09 Accept null hypothesis: Treatment and control are NOT different, M = 0 ...