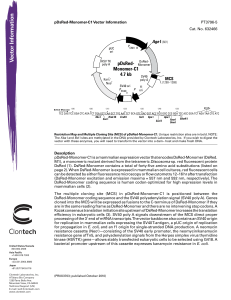
pDsRed-Monomer-C1 Vector Information
... The multiple cloning site (MCS) in pDsRed-Monomer-C1 is positioned between the DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Mon ...
... The multiple cloning site (MCS) in pDsRed-Monomer-C1 is positioned between the DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Mon ...
Effects of Protein-Deprivation on the Regeneration of Rat Liver after
... 1972), rRNA and mRNA content (Atryzek & Fausto, 1979), and ornithine decarboxylase activity (Fausto, 1969, 1971). The relationships between each of these events and the timing and magnitude of DNA synthesis during the regenerative process are still poorly understood. Because of the central role of t ...
... 1972), rRNA and mRNA content (Atryzek & Fausto, 1979), and ornithine decarboxylase activity (Fausto, 1969, 1971). The relationships between each of these events and the timing and magnitude of DNA synthesis during the regenerative process are still poorly understood. Because of the central role of t ...
Chpt13_GeneticCode.doc
... Overview for Genetic Code and Translation: Once transcription and processing of rRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs are completed, the RNAs are ready to be used in the cell - assembled into ribosomes or snRNPs and used in splicing and protein synthesis. But the mature mRNA is not yet functional to the cell. It ...
... Overview for Genetic Code and Translation: Once transcription and processing of rRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs are completed, the RNAs are ready to be used in the cell - assembled into ribosomes or snRNPs and used in splicing and protein synthesis. But the mature mRNA is not yet functional to the cell. It ...
and GvpD-mediated transcription regulation of the p
... This halophilic archaeon lacks gvp genes and offers a clean genetic background for these investigations. One of the four promoters (pA, driving the expression of the p-gvpA gene) has already been studied in Hfx. volcanii transformants with respect to the action of GvpE (Gregor & Pfeifer, 2001). The ...
... This halophilic archaeon lacks gvp genes and offers a clean genetic background for these investigations. One of the four promoters (pA, driving the expression of the p-gvpA gene) has already been studied in Hfx. volcanii transformants with respect to the action of GvpE (Gregor & Pfeifer, 2001). The ...
Consistent Errors in First Strand cDNA Due to Random Hexamer
... demonstrate that not all mispriming events have the same likelihood and RNA-DNA hexamer mispriming is the main source of error in the first seven nucleotides. Consistent mismatch patterns observed in the first seven nucleotides of first strand cDNA will affect downstream applications such as de novo ...
... demonstrate that not all mispriming events have the same likelihood and RNA-DNA hexamer mispriming is the main source of error in the first seven nucleotides. Consistent mismatch patterns observed in the first seven nucleotides of first strand cDNA will affect downstream applications such as de novo ...
Isolation and characterization of an RNA that binds with high affinity
... The expression of genes encoded by human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) is regulated by the interaction of cellular factors and a viral trans-activator protein, Tat, with specific regulatory elements in the long terminal repeat (LTR) of HIV-1 (Gaynor, 1992). The HIV1 regulatory protein Tat bi ...
... The expression of genes encoded by human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) is regulated by the interaction of cellular factors and a viral trans-activator protein, Tat, with specific regulatory elements in the long terminal repeat (LTR) of HIV-1 (Gaynor, 1992). The HIV1 regulatory protein Tat bi ...
Sequence analysis of the Marburg virus nucleoprotein gene
... The first 3000 nucleotides from the 3' end of the Marburg virus (MBG) genome were determined from cDNA clones produced from genomic RNA and mRNA. Identified in the sequence was a short putative leader sequence at the extreme 3' end, followed by the complete nucleoprotein (NP) gene. The 5' end of the ...
... The first 3000 nucleotides from the 3' end of the Marburg virus (MBG) genome were determined from cDNA clones produced from genomic RNA and mRNA. Identified in the sequence was a short putative leader sequence at the extreme 3' end, followed by the complete nucleoprotein (NP) gene. The 5' end of the ...
splicing.pdf
... This is just a preview, you will explore some of these different uses in more detail in the activity that follows. • In the example above, alternative splicing was used to include only one of several versions of an exon into a final protein product. This allows many slightly different versions of th ...
... This is just a preview, you will explore some of these different uses in more detail in the activity that follows. • In the example above, alternative splicing was used to include only one of several versions of an exon into a final protein product. This allows many slightly different versions of th ...
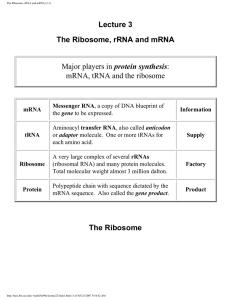
The Ribosome, rRNA and mRNA (3.1)
... determined the crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui at 2.4 angstrom resolution, and it includes 2833 of the subunit's 3045 nucleotides and 27 of its 31 proteins. The domains of its RNAs all have irregular shapes and fit together in the ribosome like the pieces ...
... determined the crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui at 2.4 angstrom resolution, and it includes 2833 of the subunit's 3045 nucleotides and 27 of its 31 proteins. The domains of its RNAs all have irregular shapes and fit together in the ribosome like the pieces ...
BMB 400 PART THREE
... Overview for Genetic Code and Translation: Once transcription and processing of rRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs are completed, the RNAs are ready to be used in the cell - assembled into ribosomes or snRNPs and used in splicing and protein synthesis. But the mature mRNA is not yet functional to the cell. It ...
... Overview for Genetic Code and Translation: Once transcription and processing of rRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs are completed, the RNAs are ready to be used in the cell - assembled into ribosomes or snRNPs and used in splicing and protein synthesis. But the mature mRNA is not yet functional to the cell. It ...
10 Day Lesson Plan - Joseph L. Anderson
... DNA. There is a slight difference in the sugar phosphate structure. RNA has one base that is different than DNA. This base replaces thymine and is called uracil. RNA also comes in two different types, messenger and transfer. Messenger RNA is made in the cell nucleus as a polymerase unwinds and copie ...
... DNA. There is a slight difference in the sugar phosphate structure. RNA has one base that is different than DNA. This base replaces thymine and is called uracil. RNA also comes in two different types, messenger and transfer. Messenger RNA is made in the cell nucleus as a polymerase unwinds and copie ...
PDF
... that initiated buds always developed the normal tubular appearance characteristic of later stages. This supports the earlier suggestion (Clarkson & Wolpert, 1967) that bud elongation must be interpreted in terms of tissue movement rather than growth. In addition, tentacles were frequently observed o ...
... that initiated buds always developed the normal tubular appearance characteristic of later stages. This supports the earlier suggestion (Clarkson & Wolpert, 1967) that bud elongation must be interpreted in terms of tissue movement rather than growth. In addition, tentacles were frequently observed o ...
Gene expression: Translation
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
Document
... to the operator. The shape of the repressor is represented as a series of connected domains as revealed by its crystal structure (see later). ...
... to the operator. The shape of the repressor is represented as a series of connected domains as revealed by its crystal structure (see later). ...
Slide 1
... A gene that codes for an enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene produces proteins that regulate patterns of tissue growth in a leaf. Yet another may trigger the female or male pattern of development in an embryo. Proteins are microscopic tools, each specifically de ...
... A gene that codes for an enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene produces proteins that regulate patterns of tissue growth in a leaf. Yet another may trigger the female or male pattern of development in an embryo. Proteins are microscopic tools, each specifically de ...
PDF - Blood Journal
... than background DNA,7 although it appears that many lncRNAs detected in one species might not even be transcribed in another species.29 Whether this implies lack of function or an ability to gain and lose function more rapidly during evolution than protein-coding genes requires further study. Suppor ...
... than background DNA,7 although it appears that many lncRNAs detected in one species might not even be transcribed in another species.29 Whether this implies lack of function or an ability to gain and lose function more rapidly during evolution than protein-coding genes requires further study. Suppor ...
CHAPTER 6 Gene Expression: Translation
... d. It is almost universal. In nearly all organisms studied, most codons have the same amino acid meaning. Examples of minor code differences include the protozoan Tetrahymena and mitochondria of some organisms. e. It is degenerate. Of 20 amino acids, 18 are encoded by more than one codon. Met (AUG) ...
... d. It is almost universal. In nearly all organisms studied, most codons have the same amino acid meaning. Examples of minor code differences include the protozoan Tetrahymena and mitochondria of some organisms. e. It is degenerate. Of 20 amino acids, 18 are encoded by more than one codon. Met (AUG) ...
Document
... precursors into mature RNAs ready for translation. For example, the splicing process removes extended stretches of the nucleotide sequences called introns from an RNA precursor such that only the remaining RNA sequence codes for a protein. Besides these normal processing events, many novel phenomena ...
... precursors into mature RNAs ready for translation. For example, the splicing process removes extended stretches of the nucleotide sequences called introns from an RNA precursor such that only the remaining RNA sequence codes for a protein. Besides these normal processing events, many novel phenomena ...
Document
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
evolution and mechanism of translation in chloroplasts
... of the large IR (112). No such IR has been observed in cyanobacterial genomes analyzed so far. The genomes of Synechococcus 6301 (49) and of Synechocystis PCC 6803 (50) contain two copies of rRNA gene clusters in the inverse orientation, but no additional genes are present in the repeats. Therefore, ...
... of the large IR (112). No such IR has been observed in cyanobacterial genomes analyzed so far. The genomes of Synechococcus 6301 (49) and of Synechocystis PCC 6803 (50) contain two copies of rRNA gene clusters in the inverse orientation, but no additional genes are present in the repeats. Therefore, ...
Toll-7
... - Toll-7 mRNA will be detected using digoxygenin labeled RNA probes - These will be synthesized as run off transcripts from the pSPT19 vector with a Toll-7 insertion - Two different fragments of Toll-7 will be used - an extracellular fragment that was inserted into pWIZ - a fragment from the TIR dom ...
... - Toll-7 mRNA will be detected using digoxygenin labeled RNA probes - These will be synthesized as run off transcripts from the pSPT19 vector with a Toll-7 insertion - Two different fragments of Toll-7 will be used - an extracellular fragment that was inserted into pWIZ - a fragment from the TIR dom ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.