Document
... Level of Gene Regulation Genes can be regulated at a number of points along the pathway: - Alteration of gene structure (DNA methylation/ changes in chromatin) - Transcription - mRNA processing - RNA stability (rate mRNA is degraded) - Translation - Posttranslational modification ...
... Level of Gene Regulation Genes can be regulated at a number of points along the pathway: - Alteration of gene structure (DNA methylation/ changes in chromatin) - Transcription - mRNA processing - RNA stability (rate mRNA is degraded) - Translation - Posttranslational modification ...
Chap 3 - Workforce3One
... • Compact structural regions of a protein are referred to as domains • Domains may contain common structuralfunctional motifs – Zinc finger – Hydrophobic pocket ...
... • Compact structural regions of a protein are referred to as domains • Domains may contain common structuralfunctional motifs – Zinc finger – Hydrophobic pocket ...
DNA Replication, RNA Molecules and Transcription
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
Transcription and Translation - Microbiology and Molecular Genetics
... Mycoplasma mycoides: Color code indicates gene clustering by function. The inner most circle shows GC content. Red , > 50% and black, < 50%. ...
... Mycoplasma mycoides: Color code indicates gene clustering by function. The inner most circle shows GC content. Red , > 50% and black, < 50%. ...
Trnascription in eucaryotes
... • The basal elements include a short sequence of pyrimidines (initiator) and the TATA box, which is at about –25 base pairs. • Upstream control elements occur between –50 and –200 base pairs. These include the CAAT box, and the GC box. All genes require at least one of these but there is no standard ...
... • The basal elements include a short sequence of pyrimidines (initiator) and the TATA box, which is at about –25 base pairs. • Upstream control elements occur between –50 and –200 base pairs. These include the CAAT box, and the GC box. All genes require at least one of these but there is no standard ...
NF1X - BioMed Central
... [9], which is involved in intermediary metabolism of xenobiotics and is also shown to be rhythmic in our study (additional file 1). NF1 proteins also exhibit a redox-sensitive regulation of CYP1A transcription in humans [10]. Since CYP1A protein levels alter the oxidative state of the cell, which in ...
... [9], which is involved in intermediary metabolism of xenobiotics and is also shown to be rhythmic in our study (additional file 1). NF1 proteins also exhibit a redox-sensitive regulation of CYP1A transcription in humans [10]. Since CYP1A protein levels alter the oxidative state of the cell, which in ...
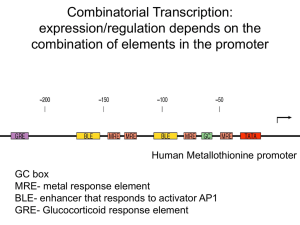
Combinatorial Transcription: expression/regulation depends on the
... defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the promoter of either gene. (b) If a boundary element such as the gypsy insulator (gyp) is inserted between the two enhancers, a new chr ...
... defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the promoter of either gene. (b) If a boundary element such as the gypsy insulator (gyp) is inserted between the two enhancers, a new chr ...
L 09 _pro gene reg
... negative control = protein binding prevents (or decreases) transcription positive control = protein binding increases transcription Regulatory proteins are trans-acting – they are encoded by genes that can be anywhere in the genome, even on a plasmid. In contrast, the sequences to which the protein ...
... negative control = protein binding prevents (or decreases) transcription positive control = protein binding increases transcription Regulatory proteins are trans-acting – they are encoded by genes that can be anywhere in the genome, even on a plasmid. In contrast, the sequences to which the protein ...
Problem Set II Answer Key
... trehalose (glucose only), the operon should be off with the repressor bound. When tre B is absent, the operon is on, so tre B must be a repressor. A is an activator because in the presence of trehalose only (no glucose), we would expect high expression of the operon due to activator activity. But ...
... trehalose (glucose only), the operon should be off with the repressor bound. When tre B is absent, the operon is on, so tre B must be a repressor. A is an activator because in the presence of trehalose only (no glucose), we would expect high expression of the operon due to activator activity. But ...
Document
... c. a repressor protein d. an inducer. _____ 3. In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs a. on parts of the DNA that are uncoiled. c. b. only on introns. d. ...
... c. a repressor protein d. an inducer. _____ 3. In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs a. on parts of the DNA that are uncoiled. c. b. only on introns. d. ...
Lecture #7 Date ______
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
1) Lecture notes: mechanisms of gene activation
... sequence, which is processed to a message (mRNA). This is called TRANSCRIPTION. •The mRNA is then read by ribosomes to make the protein. This is called TRANSLATION. ...
... sequence, which is processed to a message (mRNA). This is called TRANSCRIPTION. •The mRNA is then read by ribosomes to make the protein. This is called TRANSLATION. ...
Recombinant human RNA polymerase II CTD repeat
... CDK7 phosphorylation of POLR2A associated with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Phosphorylation also takes place at 'Ser-7' of the heptapeptide repeat, which is required for efficient transcription of snRNA genes and processing of the transcripts. The phosph ...
... CDK7 phosphorylation of POLR2A associated with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Phosphorylation also takes place at 'Ser-7' of the heptapeptide repeat, which is required for efficient transcription of snRNA genes and processing of the transcripts. The phosph ...
{alpha}-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation by Regulating
... Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors- (PPAR-) is an orphan nuclear hormone receptor that is known to control the expression of genes involved in lipid homeostasis and energy balance. PPAR- activates gene transcription in response to a variety of compounds including hypolipidemic drugs as ...
... Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors- (PPAR-) is an orphan nuclear hormone receptor that is known to control the expression of genes involved in lipid homeostasis and energy balance. PPAR- activates gene transcription in response to a variety of compounds including hypolipidemic drugs as ...
No Slide Title
... (SD/LD plants), gametophytes (pollen, egg sac), gametes, pollen tube growth, fertilization, self-incompatibility via ligand-receptor (self-self recognition) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Lecture 9 - "Genetic Mechanisms in Plant Development and ...
... (SD/LD plants), gametophytes (pollen, egg sac), gametes, pollen tube growth, fertilization, self-incompatibility via ligand-receptor (self-self recognition) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Lecture 9 - "Genetic Mechanisms in Plant Development and ...
Feb 24
... Structure of Prokaryotic promoters Three DNA sequences (core regions) 1) Pribnow box at -10 (10 bp 5’ to transcription start) 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor Other sequences also of ...
... Structure of Prokaryotic promoters Three DNA sequences (core regions) 1) Pribnow box at -10 (10 bp 5’ to transcription start) 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor Other sequences also of ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... 1. These mutants show evidence of leaf development in darkness: they have expanded cotyledons, plastids that resemble chloroplasts, and chlorophyll protein genes turned on. 2. In the dark, these genes repress photomorphogenesis –related genes in all tissues. 3. In the light, they repress them only i ...
... 1. These mutants show evidence of leaf development in darkness: they have expanded cotyledons, plastids that resemble chloroplasts, and chlorophyll protein genes turned on. 2. In the dark, these genes repress photomorphogenesis –related genes in all tissues. 3. In the light, they repress them only i ...
L15 Gene Regulation Part1 Fa08
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
Model Description Sheet
... develop breast cancer in their lifetime. Strikingly, many of these women share a significant genetic commonality. It has been shown that many breast cancer patients test positive for high levels of Estrogen Receptor (ERα), a protein that regulates the differentiation and maintenance of neural, skele ...
... develop breast cancer in their lifetime. Strikingly, many of these women share a significant genetic commonality. It has been shown that many breast cancer patients test positive for high levels of Estrogen Receptor (ERα), a protein that regulates the differentiation and maintenance of neural, skele ...
Document
... Technologies II: Array based • cDNA arrays, long oligo arrays: immobilize a piece of DNA per gene. These are (usually) 2color arrays, i.e. two samples are labeled with different dyes and hybridized • Short oligo arrays (Affymetrix): immobilize several short oligonucleotides per gene. These are 1-co ...
... Technologies II: Array based • cDNA arrays, long oligo arrays: immobilize a piece of DNA per gene. These are (usually) 2color arrays, i.e. two samples are labeled with different dyes and hybridized • Short oligo arrays (Affymetrix): immobilize several short oligonucleotides per gene. These are 1-co ...
Name
... Name: ___________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Period: ______ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Period: ______ ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.