Transcription & Translation
... carry a specific amino acid at one end and an anticodon region that recognizes and binds mRNA at the other end. The tRNA that binds to that mRNA codon determines what amino acid is added to a protein chain. The Three RNAs (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) all work together to turn the information in DNA into a ...
... carry a specific amino acid at one end and an anticodon region that recognizes and binds mRNA at the other end. The tRNA that binds to that mRNA codon determines what amino acid is added to a protein chain. The Three RNAs (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) all work together to turn the information in DNA into a ...
Chapter 18 notes
... 2) however only one or two proteins may bind enhancer 3) combination of control elements controls transcription. ...
... 2) however only one or two proteins may bind enhancer 3) combination of control elements controls transcription. ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
... another tRNA binds to next codon; continues until polypeptide / protein formed to stop codon; stop codon has no corresponding tRNA/amino acid / causes release of polypeptide; [8 max] ...
... another tRNA binds to next codon; continues until polypeptide / protein formed to stop codon; stop codon has no corresponding tRNA/amino acid / causes release of polypeptide; [8 max] ...
Chapter 10.2
... more DNA than prokaryotes Must continually turn genes on and off Operons are not common in eukaryotes Instead, genes with related functions are often scattered on different chromosomes ...
... more DNA than prokaryotes Must continually turn genes on and off Operons are not common in eukaryotes Instead, genes with related functions are often scattered on different chromosomes ...
Exam 3
... Explain the basic principle of natural transformation that occurs in some taxa of bacteria. How did Griffith demonstrate this experimentally? What utility is artificial transformation in biotechnology? Describe the structure and function of plasmid types. By what two ways may a plasmid replicate. De ...
... Explain the basic principle of natural transformation that occurs in some taxa of bacteria. How did Griffith demonstrate this experimentally? What utility is artificial transformation in biotechnology? Describe the structure and function of plasmid types. By what two ways may a plasmid replicate. De ...
Transcription Networks
... The timescales at which reactions happen in transcription network are quite interesting to note. Table 1 explain timescales of reactions taking place in E. coli. We can observe that the input signals such as biochemical stimuli or temperature change the activity of transcription factors on sub secon ...
... The timescales at which reactions happen in transcription network are quite interesting to note. Table 1 explain timescales of reactions taking place in E. coli. We can observe that the input signals such as biochemical stimuli or temperature change the activity of transcription factors on sub secon ...
(eg, cleft lip, polydactyly).
... formed body part by mechanical forces. It usually occurs in the fetal period, not in embryogenesis. It is a secondary alteration. It can be extrinsic, as in oligohydramnios羊水过少 (reduced amniotic fluid), or intrinsic, as in ...
... formed body part by mechanical forces. It usually occurs in the fetal period, not in embryogenesis. It is a secondary alteration. It can be extrinsic, as in oligohydramnios羊水过少 (reduced amniotic fluid), or intrinsic, as in ...
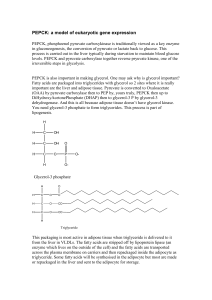
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... Starvation/fasting also stimulates the release of glucagon which binds to its receptor, stimulates adenylyl cyclise which increases cAMP PKA activated and this directly or through a cell signal pathway phosphorylates a transcription factor, CREB which enters the nucleus and binds to the CRE site. ...
... Starvation/fasting also stimulates the release of glucagon which binds to its receptor, stimulates adenylyl cyclise which increases cAMP PKA activated and this directly or through a cell signal pathway phosphorylates a transcription factor, CREB which enters the nucleus and binds to the CRE site. ...
No Slide Title
... The expression of different genes can be coordinated by a single protein in eucaryotic cells. This can result in rapid switching on or off of whole groups of genes. ...
... The expression of different genes can be coordinated by a single protein in eucaryotic cells. This can result in rapid switching on or off of whole groups of genes. ...
wanted - Copenhagen Plant Science Centre
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
Slides - Department of Computer Science
... • However, a real pattern should not differ too much from its instances in S • Start from the space of all words in S, extend to the space with real patterns ...
... • However, a real pattern should not differ too much from its instances in S • Start from the space of all words in S, extend to the space with real patterns ...
REVIEW for EXAM4-May 12th
... Furthermore, there is some control over the initiation, elongation, and termination of the polypeptide chain on the ribosome itself. IV. Post translational control are the final modifications to proteins that determine their folding. As proteins are folded, additional functional groups can be added ...
... Furthermore, there is some control over the initiation, elongation, and termination of the polypeptide chain on the ribosome itself. IV. Post translational control are the final modifications to proteins that determine their folding. As proteins are folded, additional functional groups can be added ...
divergent transcription
... dynamic model exhibiting not only stability issues but also oscilliatory effects. 5. Methylation and Epigenetic Factors: Clearly the CpG islands play an important factor. Methylation has become a significant area of study over the past decade and the processes described herein rely on many of these ...
... dynamic model exhibiting not only stability issues but also oscilliatory effects. 5. Methylation and Epigenetic Factors: Clearly the CpG islands play an important factor. Methylation has become a significant area of study over the past decade and the processes described herein rely on many of these ...
Leukaemia Section t(19;21)(q13.4;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
... expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
Everything you wanted to know about ENCODE
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
Tibor Readings - Molecular Neuroscience Part I.
... Main points: Amino acids, general classes and properties (details not needed), peptide bond, protein structure, folding, motifs (i.e.: helixes, sheets, domains). A very important issue is to realize the versatility of protein function from molecular recognition (receptors), chemical transport, enzym ...
... Main points: Amino acids, general classes and properties (details not needed), peptide bond, protein structure, folding, motifs (i.e.: helixes, sheets, domains). A very important issue is to realize the versatility of protein function from molecular recognition (receptors), chemical transport, enzym ...
医学分子生物学
... downstream and as far away as 50 kb from the transcription start site. In some cases, promoter-proximal elements occur downstream from the start site as well. (b) Most yeast genes contain only one regulatory region, called an upstream activating sequence (UAS), and a TATA box, which is ≈90 base pair ...
... downstream and as far away as 50 kb from the transcription start site. In some cases, promoter-proximal elements occur downstream from the start site as well. (b) Most yeast genes contain only one regulatory region, called an upstream activating sequence (UAS), and a TATA box, which is ≈90 base pair ...
Protein Synthesis
... The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a gene. – Replication ...
... The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a gene. – Replication ...
Office Hours
... Besides replacing hair, the discovery could lead to better skin grafts for burn victims, since grafts now can't grow hair or sebaceous glands. The next step is to try implanting human stem cells, taken from hair follicles, into the hairless mice. If the stem cells grow hair and skin like the mouse ...
... Besides replacing hair, the discovery could lead to better skin grafts for burn victims, since grafts now can't grow hair or sebaceous glands. The next step is to try implanting human stem cells, taken from hair follicles, into the hairless mice. If the stem cells grow hair and skin like the mouse ...
Transcription_12_Teacher
... Transcribed mRNA is too long and is shortened before it leaves the nucleus by a special cutting process ...
... Transcribed mRNA is too long and is shortened before it leaves the nucleus by a special cutting process ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... can influence this process, one being the environmental conditions inside and outside the cell. It can also occur during the process of translation, the conversion of mRNA information into a polypeptide. The process of translation can be influenced by the cells’ internal environment and whether inhi ...
... can influence this process, one being the environmental conditions inside and outside the cell. It can also occur during the process of translation, the conversion of mRNA information into a polypeptide. The process of translation can be influenced by the cells’ internal environment and whether inhi ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... Basic domain A basic domain is found in a number of DNAbinding proteins and is generally associated with: • the leucine zipper (ZIP) motif or • the helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif ...
... Basic domain A basic domain is found in a number of DNAbinding proteins and is generally associated with: • the leucine zipper (ZIP) motif or • the helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif ...
Capacity Matrix Name: Date Started: Date Completed: Class/Course
... Name: __________________________________________Date Started: __________________Date Completed: ______________ ...
... Name: __________________________________________Date Started: __________________Date Completed: ______________ ...
Gene Expression - Biology Department | Western Washington
... …the synthesis of a polypeptide. This occurs on ribosomes using the information encoded on mRNA, – tRNA molecules mediate the transfer of information between mRNA and the growing ...
... …the synthesis of a polypeptide. This occurs on ribosomes using the information encoded on mRNA, – tRNA molecules mediate the transfer of information between mRNA and the growing ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.