ap-biology-big-idea-3-review-answers
... After inserting their RNA into the cell – the enzyme uses the viral RNA to transcript itself into the DNA of the cell – after which it will be translated and produced. 5. List four types of RNA and how they differ from one another in function. mRNA carries information from DNA to ribosome tRNA bond ...
... After inserting their RNA into the cell – the enzyme uses the viral RNA to transcript itself into the DNA of the cell – after which it will be translated and produced. 5. List four types of RNA and how they differ from one another in function. mRNA carries information from DNA to ribosome tRNA bond ...
DNA Strand 1 - Duncanville ISD
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
Transcription/Translation
... Recombinant DNA Technology • A set of methods used to locate, analyze, alter, study, and recombine DNA sequences • Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources (even different species) are combined in the laboratory to produce a new combination of genes ...
... Recombinant DNA Technology • A set of methods used to locate, analyze, alter, study, and recombine DNA sequences • Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources (even different species) are combined in the laboratory to produce a new combination of genes ...
DNA - Valhalla High School
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
Capsid Virus Lysogenic Infection B acteriophage Prophage Lytic
... Directions: Cut out the cards along the lines, mix the cards then put the square back together. ...
... Directions: Cut out the cards along the lines, mix the cards then put the square back together. ...
Jumping Genes - University of South Alabama
... leading to speculation that they share a common ancestor. • Since excessive transposon activity can destroy a genome, many organisms seem to have developed mechanisms to reduce transposition to a manageable level (genetic deletion). • Transposons may have been co-opted by the vertebrate immune syste ...
... leading to speculation that they share a common ancestor. • Since excessive transposon activity can destroy a genome, many organisms seem to have developed mechanisms to reduce transposition to a manageable level (genetic deletion). • Transposons may have been co-opted by the vertebrate immune syste ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
LINEs
... 3 related LINE families in humans – LINE-1, LINE-2, LINE-3. LINE-1 still active (~17% of human genme) Believed to be responsible for retrotransposition of SINEs and creation of processed pseudogenes ...
... 3 related LINE families in humans – LINE-1, LINE-2, LINE-3. LINE-1 still active (~17% of human genme) Believed to be responsible for retrotransposition of SINEs and creation of processed pseudogenes ...
Bio1100Ch19W
... response to signals from the environment. • 2. Regulate expression of genes common for cell function and specialized functions (liver vs kidney function) ...
... response to signals from the environment. • 2. Regulate expression of genes common for cell function and specialized functions (liver vs kidney function) ...
Chapter 21 - dewhozitz.net
... 4. Barbara McClintock http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/barbara-mcclintock-and-the-discovery-of-jumping-34083 5. transposable elements can a. promote b. change c. modify d. change 6. retrotransposons include ERVs 7. other repetitive DNA a. large-segment duplication b. simple sequence http://w ...
... 4. Barbara McClintock http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/barbara-mcclintock-and-the-discovery-of-jumping-34083 5. transposable elements can a. promote b. change c. modify d. change 6. retrotransposons include ERVs 7. other repetitive DNA a. large-segment duplication b. simple sequence http://w ...
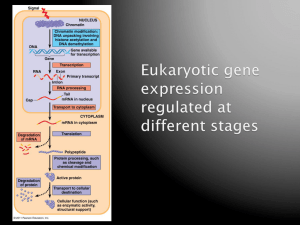
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
Gene expression and DNA microarrays
... – Comparison of E. coli O157:H7 with E. coli K-12 (common lab strain) found that the O157:H7 genome is ~ 1Mb larger than K-12 and contains 1,387 genes specific for O157:H7. – Genomes share a 4.1 Mb backbone with species specific DNA interspersed throughout the genome • K-islands - specific to K-12 ( ...
... – Comparison of E. coli O157:H7 with E. coli K-12 (common lab strain) found that the O157:H7 genome is ~ 1Mb larger than K-12 and contains 1,387 genes specific for O157:H7. – Genomes share a 4.1 Mb backbone with species specific DNA interspersed throughout the genome • K-islands - specific to K-12 ( ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... o Enzymes involved in DNA Replication: helicase, DNA polymerase (particularly directionality), replication forks, primase, primers, DNA Ligase, telomerase/telomers Protein Synthesis o Transcription - Initiation, Elongations, Termination (differences in Pro and Eukaryotes), codons, RNA modification, ...
... o Enzymes involved in DNA Replication: helicase, DNA polymerase (particularly directionality), replication forks, primase, primers, DNA Ligase, telomerase/telomers Protein Synthesis o Transcription - Initiation, Elongations, Termination (differences in Pro and Eukaryotes), codons, RNA modification, ...
16. Nuclear gene organization
... Location on many chromosomes means individuals have many different DNA regions that hybridize to mini-satellite probes. Microsatellite DNA: SSRs (simple sequence repeats)=small arrays of tandem repeats of simple sequence Interspersed throughout the genome Make up 2% of genome CA/TG repeats a ...
... Location on many chromosomes means individuals have many different DNA regions that hybridize to mini-satellite probes. Microsatellite DNA: SSRs (simple sequence repeats)=small arrays of tandem repeats of simple sequence Interspersed throughout the genome Make up 2% of genome CA/TG repeats a ...
Document
... behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic material. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein - the ...
... behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic material. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein - the ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... 13. Translation is the second step of protein synthesis. How does the translation of RNA into protein begin? a) A G cap is added to the RNA b) The promoter sequence is recognized c) A release factor binds to the RNA d) Transcription Factors bind to the RNA e) The start codon is recognized by the rib ...
... 13. Translation is the second step of protein synthesis. How does the translation of RNA into protein begin? a) A G cap is added to the RNA b) The promoter sequence is recognized c) A release factor binds to the RNA d) Transcription Factors bind to the RNA e) The start codon is recognized by the rib ...
Answers11.february
... are characteristic for eukaryotic genomes contain more than one gene contain more than one promoter contain always similar genes contain almost no intergenic sequences Telomers are located ...
... are characteristic for eukaryotic genomes contain more than one gene contain more than one promoter contain always similar genes contain almost no intergenic sequences Telomers are located ...
Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... Why does the percent of non-coding DNA vary wildly among organisms with similar levels of cellular and developmental complexity? Hypotheses: 1)Selfish DNA – most non-coding DNA consists for selfish elements capable of proliferating until the cost to host fitness becomes prohibitive. 2)Bulk DNA – gen ...
... Why does the percent of non-coding DNA vary wildly among organisms with similar levels of cellular and developmental complexity? Hypotheses: 1)Selfish DNA – most non-coding DNA consists for selfish elements capable of proliferating until the cost to host fitness becomes prohibitive. 2)Bulk DNA – gen ...
Word Definition 1 non-Mendelian genetics rules for inheritance that
... mucus in their lungs, which makes it difficult for them to breathe an international effort to sequence all 3 billion bases that make up our DNA 10 Human Genome Project and to identify within this code more than 20,000 human genes 11 genome all the DNA in one cell 12 pedigree a family tree that track ...
... mucus in their lungs, which makes it difficult for them to breathe an international effort to sequence all 3 billion bases that make up our DNA 10 Human Genome Project and to identify within this code more than 20,000 human genes 11 genome all the DNA in one cell 12 pedigree a family tree that track ...
Biology Chapter 11-1
... - The 4.5 Billion years are divided into ERAS and then PERIODS and the EPCOHS. - The fossil record shows the change the followed change on Earth but is incomplete due to lack of data. - When embryos are small they all closely resemble each other. Chapter 14 VOCAB Evolution- a theory – a collection o ...
... - The 4.5 Billion years are divided into ERAS and then PERIODS and the EPCOHS. - The fossil record shows the change the followed change on Earth but is incomplete due to lack of data. - When embryos are small they all closely resemble each other. Chapter 14 VOCAB Evolution- a theory – a collection o ...
Complementary base pairing Hydrogen bonding between purines
... Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought t ...
... Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought t ...
PERSONAL GENOMICS
... “They fully sequenced the genes of both his cancer cells and healthy cells for comparison, and at the same time analyzed his RNA, a close chemical cousin to DNA, for clues to what his genes were doing.” “And they found a culprit - a normal gene that was in overdrive, churning out huge amounts of a p ...
... “They fully sequenced the genes of both his cancer cells and healthy cells for comparison, and at the same time analyzed his RNA, a close chemical cousin to DNA, for clues to what his genes were doing.” “And they found a culprit - a normal gene that was in overdrive, churning out huge amounts of a p ...
Questions11.february
... are characteristic for eukaryotic genomes contain more than one gene contain more than one promoter contain similar genes contain almost no intergenic sequences Telomers are located ...
... are characteristic for eukaryotic genomes contain more than one gene contain more than one promoter contain similar genes contain almost no intergenic sequences Telomers are located ...