Algorithms in Computational Biology
... Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino-acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. ...
... Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino-acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. ...
Theories of Evolution - BioGeoWiki-4ESO
... These are the individuals that will pass on their genes to the next generation. This can change the GENE POOL: ...
... These are the individuals that will pass on their genes to the next generation. This can change the GENE POOL: ...
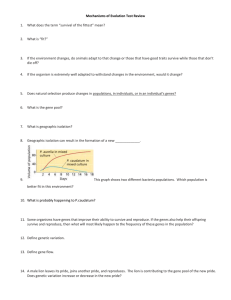
Practice Evolution Questions The last common ancestor of squid
... 2. the early stage embryo of fish, birds, rabbits and humans all have two chambered hearts and tails. This is evidence that a. all organisms have the same evolutionary history b. genes needed later in the development are not yet present in early stage embryos c. not all genes are inherited from an o ...
... 2. the early stage embryo of fish, birds, rabbits and humans all have two chambered hearts and tails. This is evidence that a. all organisms have the same evolutionary history b. genes needed later in the development are not yet present in early stage embryos c. not all genes are inherited from an o ...
MODS 14-15 NOTES Part 1
... What is the promise of molecular genetics research? Studies molecular structure and the function of genes “bottom up” research: what specific genes influence a behavior? The micro level of understanding (similar to Unit 5 and sensation/perception) What mechanisms control gene expression? ...
... What is the promise of molecular genetics research? Studies molecular structure and the function of genes “bottom up” research: what specific genes influence a behavior? The micro level of understanding (similar to Unit 5 and sensation/perception) What mechanisms control gene expression? ...
Evolution: How Change Occurs
... suited to survive, birds can’t spot the moths • Relative frequency of alleles for color changed in the gene pool for the population • H.B.D. Kettlewell tested the theory ...
... suited to survive, birds can’t spot the moths • Relative frequency of alleles for color changed in the gene pool for the population • H.B.D. Kettlewell tested the theory ...
Patterns In Evolution
... • Loss of complete huge number of species and ecological systems • Causes could be: – large asteroid during the Cretaceous period l throwing huge amonts of dust and vapor altering global climate affects organisms…like dinosaurs – Volcanic eruptions, continental shifts, changing sea levels, other m ...
... • Loss of complete huge number of species and ecological systems • Causes could be: – large asteroid during the Cretaceous period l throwing huge amonts of dust and vapor altering global climate affects organisms…like dinosaurs – Volcanic eruptions, continental shifts, changing sea levels, other m ...
Unit 7 Test with answers
... 19. How does camouflage help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If organisms can blend in with their environment to hide from predators they are more likely to survive and reproduce. 20. How does mimicry help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If an organism can mimic another organis ...
... 19. How does camouflage help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If organisms can blend in with their environment to hide from predators they are more likely to survive and reproduce. 20. How does mimicry help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If an organism can mimic another organis ...
What Darwin Never Knew Example Answers
... 5. How was Darwin’s view of nature different from the standard view of nature from Victorian times? How did this tie into his idea of natural selection? In Victorian times, the standard view of nature was sentimental. Darwin found the view of nature to be savage. Darwin saw that species were constan ...
... 5. How was Darwin’s view of nature different from the standard view of nature from Victorian times? How did this tie into his idea of natural selection? In Victorian times, the standard view of nature was sentimental. Darwin found the view of nature to be savage. Darwin saw that species were constan ...
WLHS / Biology / Monson Name Date Per READING GUIDE: 17.3
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
StudyGuideBioEvolution
... Comparative embryology - compares the embryos of different organisms. The embryos of many animals, from fish to humans, show similarities that suggest a common ancestor. Review the vertebrate chart in your science notebook ...
... Comparative embryology - compares the embryos of different organisms. The embryos of many animals, from fish to humans, show similarities that suggest a common ancestor. Review the vertebrate chart in your science notebook ...
I-4 Statistical genetics, disease biology, and drug discovery
... Department of Statistical Genetics, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine Statistical genetics is a research field that evaluates causality of human genetic variations on diseases, using statistical and bioinformatics approaches. Recent development of high-throughput genome sequencing and gen ...
... Department of Statistical Genetics, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine Statistical genetics is a research field that evaluates causality of human genetic variations on diseases, using statistical and bioinformatics approaches. Recent development of high-throughput genome sequencing and gen ...
4.2 Test Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 11. Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then what will most likely happen to the frequency of these genes in the population? ...
... 11. Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then what will most likely happen to the frequency of these genes in the population? ...
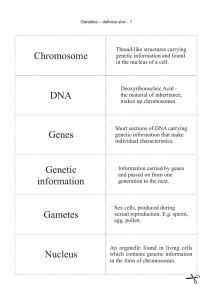
Chromosome DNA Genes Genetic information
... only one parent. The offspring have the same genes as each other and as their parent. ...
... only one parent. The offspring have the same genes as each other and as their parent. ...
1. What is epigenesis?
... 1. What is epigenesis? 2. Explain the relationship between development and evolution. 3. How are gene duplication and segmentation similar in terms of introducing evolutionary novelty? 4. What are homeotic genes, and what type of protein do they code for? 5. Explain homologous structures in terms of ...
... 1. What is epigenesis? 2. Explain the relationship between development and evolution. 3. How are gene duplication and segmentation similar in terms of introducing evolutionary novelty? 4. What are homeotic genes, and what type of protein do they code for? 5. Explain homologous structures in terms of ...
CHAPTER 11: Gene Expression
... Turing Operons on & off depends on presence of lactose. • Inducer- molecule that (if lactose is present) – turns on the gene with its 3 structural proteins – to start translating which makes 3 enzymes needed to break up lactose ...
... Turing Operons on & off depends on presence of lactose. • Inducer- molecule that (if lactose is present) – turns on the gene with its 3 structural proteins – to start translating which makes 3 enzymes needed to break up lactose ...
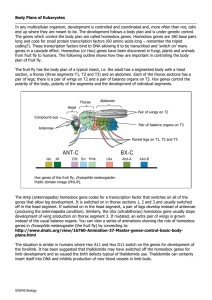
Development and Apoptosis
... In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Homeobox genes are 180 base p ...
... In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Homeobox genes are 180 base p ...
Document
... front, rear, top, or bottom – Some determine size and shape of legs or wings • Changes in expression of developmental genes may explain how differences evolved in animals. ...
... front, rear, top, or bottom – Some determine size and shape of legs or wings • Changes in expression of developmental genes may explain how differences evolved in animals. ...
分子演化 - 東華大學
... It is assumed that a gene tree (molecular data), will be a more accurate than that obtainable by morphological comparisons ...
... It is assumed that a gene tree (molecular data), will be a more accurate than that obtainable by morphological comparisons ...
File - Elko Science
... 7. Determine the age of rocks and fossils using radioactive dating. 8. Describe an example of homologous structures and vestigial structures. Explain how they provide evidence of evolution. 9. Explain how development and molecules provide evidence of evolution. 10. Interpret and develop a cladogram. ...
... 7. Determine the age of rocks and fossils using radioactive dating. 8. Describe an example of homologous structures and vestigial structures. Explain how they provide evidence of evolution. 9. Explain how development and molecules provide evidence of evolution. 10. Interpret and develop a cladogram. ...
Evolution Is Not Mainly A Matter of Genes
... hypotheses about how matter arrived at the point of being subject to natural selection (now encompassed under the still unsolved problem of the origin of life), nor did it depend on any knowledge of the source of variation, either inherited or non-inherited, in organismal form and function. The fact ...
... hypotheses about how matter arrived at the point of being subject to natural selection (now encompassed under the still unsolved problem of the origin of life), nor did it depend on any knowledge of the source of variation, either inherited or non-inherited, in organismal form and function. The fact ...
Paedomorphosis
... Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance: no blending of characters Random mutations and recombinations are the sources of variation (the raw material for natural selection). Natural populations are gene pools that contain variation ...
... Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance: no blending of characters Random mutations and recombinations are the sources of variation (the raw material for natural selection). Natural populations are gene pools that contain variation ...
Evolution Concepts
... Concept – Organisms with a given adaptation are more likely to survive and reproduce, their genes will be passed on to the next generation. -- This increases the frequency of the gene that caused the adaptation. In this way, species change over time or evolve. -- ORGANISMS THEMSELVES DO NOT EVOLVE ...
... Concept – Organisms with a given adaptation are more likely to survive and reproduce, their genes will be passed on to the next generation. -- This increases the frequency of the gene that caused the adaptation. In this way, species change over time or evolve. -- ORGANISMS THEMSELVES DO NOT EVOLVE ...
Molecular Biologists
... • All living things are generally the same in the way that they are built • They all begin as single cells that reproduce • They come to a certain life span and get old and die • All plants and animals inherit genes from their parents • Hemoglobin and Myoglobin are found in almost every multi-celle ...
... • All living things are generally the same in the way that they are built • They all begin as single cells that reproduce • They come to a certain life span and get old and die • All plants and animals inherit genes from their parents • Hemoglobin and Myoglobin are found in almost every multi-celle ...
Chapter 16: Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
... Hutton/Lyell argued Earth was old – but how old? Modern geologists use radioactive dating to determine age of rocks/fossils Earth is about 4.5 billion years old Darwin’s study of fossils convinced him, but paleontologists had not yet found enough fossils of intermediate species Since then, m ...
... Hutton/Lyell argued Earth was old – but how old? Modern geologists use radioactive dating to determine age of rocks/fossils Earth is about 4.5 billion years old Darwin’s study of fossils convinced him, but paleontologists had not yet found enough fossils of intermediate species Since then, m ...