On Evolution…
... Small changes in the DNA of living organisms (which occurs through genetic mutations when cells make copies of themselves) is the main driving force behind the large changes seen over billions of years of life on Earth. This is evolution! ...
... Small changes in the DNA of living organisms (which occurs through genetic mutations when cells make copies of themselves) is the main driving force behind the large changes seen over billions of years of life on Earth. This is evolution! ...
A1983RC02000002
... and the most rapidly evolving proteins change at a rate ten times greater than average proteins; thus at least 90 percent of mutations resulting in amino acid changes are eliminated by natural selection. Genes and portions of genes most important to function are evolutionarily conserved. (The Sd® in ...
... and the most rapidly evolving proteins change at a rate ten times greater than average proteins; thus at least 90 percent of mutations resulting in amino acid changes are eliminated by natural selection. Genes and portions of genes most important to function are evolutionarily conserved. (The Sd® in ...
The Modern Synthesis: Evolution and Genetics
... • A mutation to a gene can often be harmful, even fatal • But having an extra copy means that if that gene mutates, there is still another copy to make sure the cell functions properly • New and novel mutations may now occur – Eg: rod and cone cells in eyes ...
... • A mutation to a gene can often be harmful, even fatal • But having an extra copy means that if that gene mutates, there is still another copy to make sure the cell functions properly • New and novel mutations may now occur – Eg: rod and cone cells in eyes ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence ...
... caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence ...
Emerging Methods in Molecular Biology and Genetics
... was founded in the mid-1950s, molecular biology and genetics were in their infancy and had little to offer neuropsychopharmacology. By 1967, when the first volume in this series was published, it still had not become apparent how greatly our field would be influenced by research on genes and on DNA. ...
... was founded in the mid-1950s, molecular biology and genetics were in their infancy and had little to offer neuropsychopharmacology. By 1967, when the first volume in this series was published, it still had not become apparent how greatly our field would be influenced by research on genes and on DNA. ...
What Darwin Never Knew--KEY
... 9. The Galapagos finches have different beaks because the finches used their beaks as TOOLS. 10. Darwin realized that VARIATION was the start of change in nature. 11. Over many generations, tiny variations allow the fit to get fitter and the unfit to vanish. This is evolution by NATURAL SELECTION. 1 ...
... 9. The Galapagos finches have different beaks because the finches used their beaks as TOOLS. 10. Darwin realized that VARIATION was the start of change in nature. 11. Over many generations, tiny variations allow the fit to get fitter and the unfit to vanish. This is evolution by NATURAL SELECTION. 1 ...
01 - Homework Now
... 1. A molecular system that controls the expression of a specific gene is called a genetic ______________________. 2. A group of related genes that lie close together and that work together as a unit is called a(n) ______________________. 3. To break down lactose, Escherichia coli need three differen ...
... 1. A molecular system that controls the expression of a specific gene is called a genetic ______________________. 2. A group of related genes that lie close together and that work together as a unit is called a(n) ______________________. 3. To break down lactose, Escherichia coli need three differen ...
Chapter 9
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
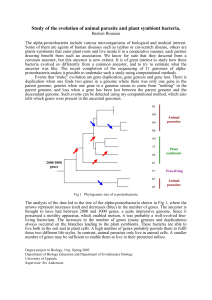
Study of the evolution of animal parasite bacteria and plant symbionts
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
Agents of Evolutionary Change
... population will mate is not the same for all possible pairs of individuals. ...
... population will mate is not the same for all possible pairs of individuals. ...
Evolutuion II
... 4. Genes are regulated by other proteins (and other genes). a. Feedback loops are common result of genetic regulation mechanisms. b. Lactose in E. coli only metabolized if gene is turned on when repressor ...
... 4. Genes are regulated by other proteins (and other genes). a. Feedback loops are common result of genetic regulation mechanisms. b. Lactose in E. coli only metabolized if gene is turned on when repressor ...
01 - HomeworkNOW.com
... In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term. ...
... In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term. ...
Coevolution (read and know!)
... 3. Small changes in the timing of this genetic control during development can affect the body type of the organism (long legs vs. short legs) THUS contributing to the variation involved in natural selection. ...
... 3. Small changes in the timing of this genetic control during development can affect the body type of the organism (long legs vs. short legs) THUS contributing to the variation involved in natural selection. ...