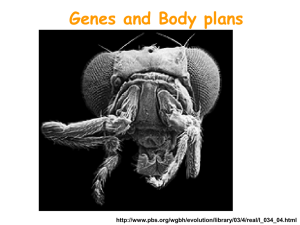
Evolution
... a. Small population that include the descendants of a small number of organisms: example – The Amish of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania one of the 30 settlers in this community carried the recessive genes that resulted in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes. Today 1 in 14 have these traits ...
... a. Small population that include the descendants of a small number of organisms: example – The Amish of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania one of the 30 settlers in this community carried the recessive genes that resulted in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes. Today 1 in 14 have these traits ...
03 EvolutionEvidence
... all vertebrate embryos have similar structures at different stages of development gill pouch in fish, frog, snake, birds, human, etc. ...
... all vertebrate embryos have similar structures at different stages of development gill pouch in fish, frog, snake, birds, human, etc. ...
Evolution Notes
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
... Evolution of Dance In order for evolution to occur variation (changes) in genes such as mutations, must exist Organism’s genes change because of mutations—which can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect. ...
PY460: Physiological Psychology
... A conscious understanding of “reasons” for behavior are not necessary to explain behavior! We act because of nervous system wiring We act because of genetic make-up could you ask someone to explain the reasons for ...
... A conscious understanding of “reasons” for behavior are not necessary to explain behavior! We act because of nervous system wiring We act because of genetic make-up could you ask someone to explain the reasons for ...
Topic Checklist
... Artificial animal cloning involves the transfer of a nucleus from an adult body cell into an unfertilised egg cell, which has had its own nucleus removed. Stem cells are unspecialised cells that can develop into different cell types. In the future, stem cells may be used to treat certain degenerativ ...
... Artificial animal cloning involves the transfer of a nucleus from an adult body cell into an unfertilised egg cell, which has had its own nucleus removed. Stem cells are unspecialised cells that can develop into different cell types. In the future, stem cells may be used to treat certain degenerativ ...
Evolution Evidence Notes
... Q: What do similarities in early development indicate? • The organisms have similar genes controlling early development. Q: What do these similar genes indicate? • These organisms have a common ancestor. Q: Why do the embryos become different as they develop? • Different genes start to contribute o ...
... Q: What do similarities in early development indicate? • The organisms have similar genes controlling early development. Q: What do these similar genes indicate? • These organisms have a common ancestor. Q: Why do the embryos become different as they develop? • Different genes start to contribute o ...
No Slide Title
... • The examples we have seen so far were genes on autosomes, so it didn’t matter which parent was mother or father • Many organisms are “monoecious” - an individual can produce both male and female gametes • Others (including humans, birds, fruit-flies) are “dioecious” so individuals are either male ...
... • The examples we have seen so far were genes on autosomes, so it didn’t matter which parent was mother or father • Many organisms are “monoecious” - an individual can produce both male and female gametes • Others (including humans, birds, fruit-flies) are “dioecious” so individuals are either male ...
evolution and natural selection
... Each living thing (organism) has a set of characteristics encoded by its genes The organism inherits its genes from its parent(s) Variations between organisms are caused by variations in the genotype ...
... Each living thing (organism) has a set of characteristics encoded by its genes The organism inherits its genes from its parent(s) Variations between organisms are caused by variations in the genotype ...
Reading: Charles Darwin and the Process of Natural Selection
... different organisms. They are “built/ put together” with the same basic parts. This shows “variation on a theme.” A similar, basic body plan has adapted to “fit” different environments. • Example: forelimbs (bat wings, whale front fins, human arms, dolphin fins, horse forelimbs, cat ...
... different organisms. They are “built/ put together” with the same basic parts. This shows “variation on a theme.” A similar, basic body plan has adapted to “fit” different environments. • Example: forelimbs (bat wings, whale front fins, human arms, dolphin fins, horse forelimbs, cat ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... Evolution by natural selection happens in populations, not individuals. A single organism cannot evolve. Populations evolve. ...
... Evolution by natural selection happens in populations, not individuals. A single organism cannot evolve. Populations evolve. ...
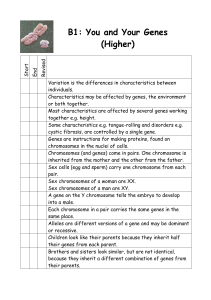
B1.7 Genetic variation and its control B1.7.1 Why organisms are
... embryo before they become specialised, then transplanting the identical embryos into host mothers adult cell cloning – the nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell. The nucleus from an adult body cell, eg a skin cell, is then inserted into the egg cell. An electric shock then causes the eg ...
... embryo before they become specialised, then transplanting the identical embryos into host mothers adult cell cloning – the nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell. The nucleus from an adult body cell, eg a skin cell, is then inserted into the egg cell. An electric shock then causes the eg ...
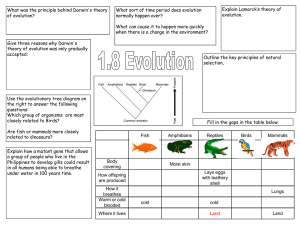
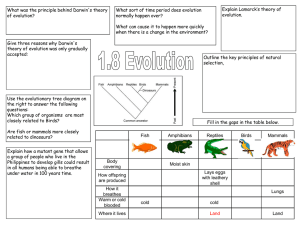
1.8_Evolution
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
File
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
Natural Selection Vocabulary - Denise Deaton 8th Grade Science
... Biodiversity - the diversity of life forms on earth or part of the earth, including diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, esp. when regarded as providing the optimal conditions for evolution Species - a group of living things that can mate with one another but not with those of other groups C ...
... Biodiversity - the diversity of life forms on earth or part of the earth, including diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, esp. when regarded as providing the optimal conditions for evolution Species - a group of living things that can mate with one another but not with those of other groups C ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters (Swarthmore
... especially Adah Leshem-Ackerman and Jonathan Wendel for the opportunity to participate in the program. We are very grateful to Lex Flagel for his mentorship, patience, and willingness to set aside his other projects to guide us through this project. Thank you, also, to the other members of the Wende ...
... especially Adah Leshem-Ackerman and Jonathan Wendel for the opportunity to participate in the program. We are very grateful to Lex Flagel for his mentorship, patience, and willingness to set aside his other projects to guide us through this project. Thank you, also, to the other members of the Wende ...
Evolutionary Development and HOX Genes
... Homeotic and Homeobox Genes • Control how an organism’s body develops as it grows from a zygote into a complete organism. • They determine the body plan including the polarity (front and back part) and positioning of organs. • Homeotic genes define a region or position in the embryo and code for tr ...
... Homeotic and Homeobox Genes • Control how an organism’s body develops as it grows from a zygote into a complete organism. • They determine the body plan including the polarity (front and back part) and positioning of organs. • Homeotic genes define a region or position in the embryo and code for tr ...
Fossil Record-Homologies-Mechanisms of Evolution
... some traits with the ancestor. – Each species in a clade has traits that have changed. ...
... some traits with the ancestor. – Each species in a clade has traits that have changed. ...
Chapter 20 - Evolution of genes and traits
... Morphological evolution-wing spots on fruit flies (regulatory sequence evolution) ...
... Morphological evolution-wing spots on fruit flies (regulatory sequence evolution) ...
Transgenics--Kayla and Sarah
... • Should scientists focus on in vitro transgenic methods rather than, or before, using live animals to alleviate animal suffering? • Will transgenic animals radically change the direction of evolution, which may result in drastic consequences for nature and humans alike? • Is human welfare the only ...
... • Should scientists focus on in vitro transgenic methods rather than, or before, using live animals to alleviate animal suffering? • Will transgenic animals radically change the direction of evolution, which may result in drastic consequences for nature and humans alike? • Is human welfare the only ...
Biology-Chapter-15
... These similar genes indicate that these various organisms have a common ancestor that passed on the similar genes o As the embryos develop their own genes become active and cause the dissimilarities to occur. These are mutations of the original genes. ...
... These similar genes indicate that these various organisms have a common ancestor that passed on the similar genes o As the embryos develop their own genes become active and cause the dissimilarities to occur. These are mutations of the original genes. ...
EVOLUTION
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and increase the o ...
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and increase the o ...
PreAP Biology
... Why did early naturalists “invent” a classification system? In a scientific name, what term is always capitalized? How many Kingdoms are there in modern classification? How many Kingdoms were there in Linnaeus’ classification system (originally)? What distinguishes one branch from another in a clado ...
... Why did early naturalists “invent” a classification system? In a scientific name, what term is always capitalized? How many Kingdoms are there in modern classification? How many Kingdoms were there in Linnaeus’ classification system (originally)? What distinguishes one branch from another in a clado ...