Chapter 18 – 17 pts total - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 3. Expression of Green Fluorescent Protein in the bacteria transformation lab was triggered by the presence of Arabanose. Describe how this system worked. (hint – take a look at the last handout from that lab) 4. Discuss if histone tail deacetylation increases or decreases the transcription of a gen ...
... 3. Expression of Green Fluorescent Protein in the bacteria transformation lab was triggered by the presence of Arabanose. Describe how this system worked. (hint – take a look at the last handout from that lab) 4. Discuss if histone tail deacetylation increases or decreases the transcription of a gen ...
Quiz 2 - Delmar
... Quiz 2 Multiple Choice 1. A neoplasm a. is always malignant b. is also known as a tumor c. may be benign d. b or c 2. A structure that digests worn-out cells and bacteria is called: a. ribosome b. lysosome c. perioxisome d. mitochondria 3. The most important organelle within the cell is the a. cytop ...
... Quiz 2 Multiple Choice 1. A neoplasm a. is always malignant b. is also known as a tumor c. may be benign d. b or c 2. A structure that digests worn-out cells and bacteria is called: a. ribosome b. lysosome c. perioxisome d. mitochondria 3. The most important organelle within the cell is the a. cytop ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organisms. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. A gene in a eukaryotic cell is tra ...
... 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organisms. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. A gene in a eukaryotic cell is tra ...
Study Guide: Chapter 10
... 4. Are the cells in an adult human the same size as an infant? Explain. 5. True or false? Volume increases more rapidly than surface area, causing the surface area to volume ratio to decrease. (p.242) 6. True or false? More surface area than volume, or a greater surface area to volume ratio, leads t ...
... 4. Are the cells in an adult human the same size as an infant? Explain. 5. True or false? Volume increases more rapidly than surface area, causing the surface area to volume ratio to decrease. (p.242) 6. True or false? More surface area than volume, or a greater surface area to volume ratio, leads t ...
Genes, Chromosomes and DNA
... _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood cells, which have no nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million base ...
... _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood cells, which have no nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million base ...
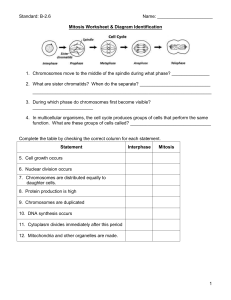
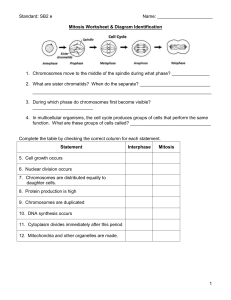
Mitosis Phase Review Sheet
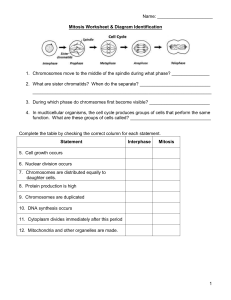
... function. What are these groups of cells called? ________________________________ ...
... function. What are these groups of cells called? ________________________________ ...
Mitosis: Cell Cycle Control
... Checkpoint = a critical control point where stop and go signals regulate the cycle Signals from within the cell tell it whether crucial cellular processes have been completed correctly and whether or not the cell should proceed with division. Signals from outside the cell are also registered at chec ...
... Checkpoint = a critical control point where stop and go signals regulate the cycle Signals from within the cell tell it whether crucial cellular processes have been completed correctly and whether or not the cell should proceed with division. Signals from outside the cell are also registered at chec ...
Mitosis Diagram Worksheet
... Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement. Statement ...
... Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement. Statement ...
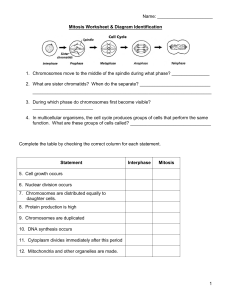
Mitosis Worksheet
... daughter cells. 8. Protein production is high 9. Chromosomes are duplicated 10. DNA synthesis occurs 11. Cytoplasm divides immediately after this period 12. Mitochondria and other organelles are made. ...
... daughter cells. 8. Protein production is high 9. Chromosomes are duplicated 10. DNA synthesis occurs 11. Cytoplasm divides immediately after this period 12. Mitochondria and other organelles are made. ...
Biology Name____________________ 10.2 wks Period ______ De
... Complete the following paragraph… Although the cell cycle usually results in the production of normal cells, sometimes ______________, or cancerous, cells are produced. Because almost any ________________ can become malignant, there are many forms of cancer. _________________ changes cause normal ce ...
... Complete the following paragraph… Although the cell cycle usually results in the production of normal cells, sometimes ______________, or cancerous, cells are produced. Because almost any ________________ can become malignant, there are many forms of cancer. _________________ changes cause normal ce ...
Gene Regulation
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
Cell Division
... 4. Series of events a cell goes through as it grows & divides; the cell ___ 6. The phase in which DNA copies itself 8. Holds sister chromatids together 9. When a cell divides, it forms two _____ cells 10. Cells that can become any other cell type; ___ cells 11. Division of the cell nucleus 13. The p ...
... 4. Series of events a cell goes through as it grows & divides; the cell ___ 6. The phase in which DNA copies itself 8. Holds sister chromatids together 9. When a cell divides, it forms two _____ cells 10. Cells that can become any other cell type; ___ cells 11. Division of the cell nucleus 13. The p ...
cell Communicaiton and Division Review
... 4. Explain the rolls of cyclin, MFP protein complex, protein kinases in cell division. 5. Describe the events that occur during the phases of mitosis. 6. How does plant cell mitosis differ from animal cell mitosis and cytokinesis 7. Describe the cell cycle, including a description of interphase. Be ...
... 4. Explain the rolls of cyclin, MFP protein complex, protein kinases in cell division. 5. Describe the events that occur during the phases of mitosis. 6. How does plant cell mitosis differ from animal cell mitosis and cytokinesis 7. Describe the cell cycle, including a description of interphase. Be ...
Cell cycle reading guide
... 9. Write down a four step (1 sentence per step) procedure for doing cell culture to test whether a specific growth factor would affect fibroblasts. ...
... 9. Write down a four step (1 sentence per step) procedure for doing cell culture to test whether a specific growth factor would affect fibroblasts. ...
Biol 212 Worksheet: Cell Specialization
... 5. What are stem cells? How is their population maintained? What are the different types? 6. What are the 6 basic cell processes involved in development? Apply these to limb development in humans. 7. Why is are cells different from one another? Is their DNA different? What factors can signal gene ex ...
... 5. What are stem cells? How is their population maintained? What are the different types? 6. What are the 6 basic cell processes involved in development? Apply these to limb development in humans. 7. Why is are cells different from one another? Is their DNA different? What factors can signal gene ex ...
The Biology of Cancer
... _________________________: normal, healthy genes that regulate cell growth, cell division, and the ability of the cell to adhere (“stick”) to other cells. A mutation in a _________________________may cause it to become an oncogene (cancer causing) ...
... _________________________: normal, healthy genes that regulate cell growth, cell division, and the ability of the cell to adhere (“stick”) to other cells. A mutation in a _________________________may cause it to become an oncogene (cancer causing) ...
Achilles` Heel of Brain Cancer Identified in Tumor Stem Cells
... the team showed these three proteins create a self amplifying signal. In the tumor stem cells, EGFRvIII comes in direct physical contact with OSMR and together these two proteins act as co-receptors to activate STAT3 which, in ...
... the team showed these three proteins create a self amplifying signal. In the tumor stem cells, EGFRvIII comes in direct physical contact with OSMR and together these two proteins act as co-receptors to activate STAT3 which, in ...
Name: Date: Aim 36: Mitosis vs. Meiosis Compare and Contrast
... How many functioning cells are produced by the end of the process? How many cell divisions are there (how many times did the cell/s split)? Does crossing over occur between chromosome pairs (exchanging of genes)? How is the genetic makeup of the cells produced, compared to the original cell? (identi ...
... How many functioning cells are produced by the end of the process? How many cell divisions are there (how many times did the cell/s split)? Does crossing over occur between chromosome pairs (exchanging of genes)? How is the genetic makeup of the cells produced, compared to the original cell? (identi ...
The Cell Cycle and Cancer - Clark Pleasant Community
... What causes cancer? • Oncogenes may be altered by mutagens such as UV light, chemicals, radiation, viruses, or a genetic predisposition • Typically dominant, meaning only one of your two genes must be mutated to cause the altered cell functions ...
... What causes cancer? • Oncogenes may be altered by mutagens such as UV light, chemicals, radiation, viruses, or a genetic predisposition • Typically dominant, meaning only one of your two genes must be mutated to cause the altered cell functions ...
Mitosis Vocab Review
... daughter cells. 8. Protein production is high 9. Chromosomes are duplicated 10. DNA synthesis occurs 11. Cytoplasm divides immediately after this period 12. Mitochondria and other organelles are made. ...
... daughter cells. 8. Protein production is high 9. Chromosomes are duplicated 10. DNA synthesis occurs 11. Cytoplasm divides immediately after this period 12. Mitochondria and other organelles are made. ...
1406-guide-Ch 11-15
... Define Non-disjunction, Aneuploidy, Trisomy Monosomic Define Deletion, Insertion, Inversion: Translocation Down syndrome is a result of ? DNA contains four possible nitrogen bases? What is the human genome project DNA vs RNA Genes code for protein How many amino acids What’s codon and anticodan Tran ...
... Define Non-disjunction, Aneuploidy, Trisomy Monosomic Define Deletion, Insertion, Inversion: Translocation Down syndrome is a result of ? DNA contains four possible nitrogen bases? What is the human genome project DNA vs RNA Genes code for protein How many amino acids What’s codon and anticodan Tran ...