HOW ARE PROTEINS MADE?
... Introns get cut out of mRNA by proteins and the Exons are pasted together. ...
... Introns get cut out of mRNA by proteins and the Exons are pasted together. ...
國立彰化師範大學九十六學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... 8. _____: The bacterial RNA polymerase consists of a core enzyme (α2ββ’) and a sigma factor (σ). If we treated the enzyme with an antibiotic (rifamycin), the activity of a subunit β was inhibited by preventing initiation of transcription, prior to the formation of the first phospodiester bond. So th ...
... 8. _____: The bacterial RNA polymerase consists of a core enzyme (α2ββ’) and a sigma factor (σ). If we treated the enzyme with an antibiotic (rifamycin), the activity of a subunit β was inhibited by preventing initiation of transcription, prior to the formation of the first phospodiester bond. So th ...
Name__________________________ Date______ Period
... 2. Proteins are made of chains of ___________ __________ held together by ___________ bonds. 3. How many amino acids are there? 5. Each combination of three nucleotides on mRNA is called a _____________ and codes for a specific __________ __________. 7. Do some amino acids have more than one codon? ...
... 2. Proteins are made of chains of ___________ __________ held together by ___________ bonds. 3. How many amino acids are there? 5. Each combination of three nucleotides on mRNA is called a _____________ and codes for a specific __________ __________. 7. Do some amino acids have more than one codon? ...
LS1a Fall 09
... o rRNA (where “r” = “ribosomal”) associates with ribosomal proteins to form the ribosome. A nucleotide triplet (e.g., AGA) in mRNA is called a codon. Each codon encodes one amino acid (except for stop codons, which do not encode amino acids). Codons are read consecutively on mRNA from 5’ to 3’. The ...
... o rRNA (where “r” = “ribosomal”) associates with ribosomal proteins to form the ribosome. A nucleotide triplet (e.g., AGA) in mRNA is called a codon. Each codon encodes one amino acid (except for stop codons, which do not encode amino acids). Codons are read consecutively on mRNA from 5’ to 3’. The ...
Lesson 2
... information in mRNA is translated into proteins. A codon is made of three nucleotide bases (triplet) and it may translate into: ...
... information in mRNA is translated into proteins. A codon is made of three nucleotide bases (triplet) and it may translate into: ...
Name
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
RNA Viruses
... sequence but have unique AUG site and share 3’ end of genome • May be produced by jumping polymerase - 7 base sequence in various parts of genome – Get recombinant viruses with mixed infections – DI particles are common ...
... sequence but have unique AUG site and share 3’ end of genome • May be produced by jumping polymerase - 7 base sequence in various parts of genome – Get recombinant viruses with mixed infections – DI particles are common ...
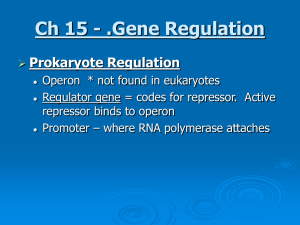
Ch 15 - .Gene Regulation
... allows differential protein expression dependent on specialized function of cell. ...
... allows differential protein expression dependent on specialized function of cell. ...
ORGANELLES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Worksheet #3
... 1. The nucleotide sequence for hemoglobin (one subunit) has 576 bases (nucleotides). How many amino acids would be in this subunit? Number of amino acids = ___________ 2. Below, copy the first 15 DNA nucleotides for the Hemoglobin gene into DNA Strand 1. Using the DNA nucleotide pairing rules, creat ...
... 1. The nucleotide sequence for hemoglobin (one subunit) has 576 bases (nucleotides). How many amino acids would be in this subunit? Number of amino acids = ___________ 2. Below, copy the first 15 DNA nucleotides for the Hemoglobin gene into DNA Strand 1. Using the DNA nucleotide pairing rules, creat ...
Gene to protein
... • GENE = sequence of DNA with a specific function (final product = polypeptide OR RNA) • RNA's = intermediates between DNA code and proteins that determine phenotype • For each gene only one of the two strands is transcribed into an RNA (template strand) • For some genes one strand may be used; for ...
... • GENE = sequence of DNA with a specific function (final product = polypeptide OR RNA) • RNA's = intermediates between DNA code and proteins that determine phenotype • For each gene only one of the two strands is transcribed into an RNA (template strand) • For some genes one strand may be used; for ...
Ch 1617 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... GENE = sequence of DNA with a specific function (final product = polypeptide OR RNA) RNA's = intermediates between DNA code and proteins that determine phenotype For each gene only one of the two strands is transcribed into an RNA (template strand) For some genes one strand may be used; for other ge ...
... GENE = sequence of DNA with a specific function (final product = polypeptide OR RNA) RNA's = intermediates between DNA code and proteins that determine phenotype For each gene only one of the two strands is transcribed into an RNA (template strand) For some genes one strand may be used; for other ge ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS STEP 1: Transcription
... you build a __________. Proteins bond together by __________ _____. ...
... you build a __________. Proteins bond together by __________ _____. ...
5 Chapter 12 DNA RNA
... There are three major differences between RNA and DNA 1. RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose 2. RNA is usually singled stranded 3. RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine ...
... There are three major differences between RNA and DNA 1. RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose 2. RNA is usually singled stranded 3. RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine ...
2.1 2 Translation - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... acid can bind. At the other end of the molecule are three unpaired nucleotide bases, known as an anticodon. Each anticodon can bind temporarily with its complementary codon. ...
... acid can bind. At the other end of the molecule are three unpaired nucleotide bases, known as an anticodon. Each anticodon can bind temporarily with its complementary codon. ...
Genetics Keywords - No Brain Too Small
... Ee Otherwise called the sense strand; has the same nucleotide sequence as the mRNA (with T replaced by U in the RNA of course). ...
... Ee Otherwise called the sense strand; has the same nucleotide sequence as the mRNA (with T replaced by U in the RNA of course). ...
Protein Synthesis
... mRNA leaves nucleus and attaches to ribosomes tRNA with the anticodon UAC attaches to the mRNA start codon AUG to begin protein chain with amino acid methionine Additional tRNA’s add other amino acids to the protein chain connecting them with peptide bonds Protein synthesis continues until it reache ...
... mRNA leaves nucleus and attaches to ribosomes tRNA with the anticodon UAC attaches to the mRNA start codon AUG to begin protein chain with amino acid methionine Additional tRNA’s add other amino acids to the protein chain connecting them with peptide bonds Protein synthesis continues until it reache ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
Proein Synthesis Note Fill-in
... 30. What enzyme aids in transcription by adding RNA nucleotides to form the mRNA molecule? 31. Do we copy both sides of the DNA molecule during transcription? Explain. 32. Transcription begins at a site called promoter DNA or ____________ box. 33. Transcription ends at a site called the terminator D ...
... 30. What enzyme aids in transcription by adding RNA nucleotides to form the mRNA molecule? 31. Do we copy both sides of the DNA molecule during transcription? Explain. 32. Transcription begins at a site called promoter DNA or ____________ box. 33. Transcription ends at a site called the terminator D ...
DNA and Translation Gene
... • Every DNA gene codes for a specific protein • Codon/anticodon match guarantees proper amino acid • Many amino acids link to make one protein ...
... • Every DNA gene codes for a specific protein • Codon/anticodon match guarantees proper amino acid • Many amino acids link to make one protein ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... The tRNA attaches itself to the mRNA. Place the complimentary tRNA anticodon on your mRNA. 9. Keep the tRNA attached to the mRNA and move the mRNA to the left 3 bases. Find tRNA for the second codon. Attach it. ...
... The tRNA attaches itself to the mRNA. Place the complimentary tRNA anticodon on your mRNA. 9. Keep the tRNA attached to the mRNA and move the mRNA to the left 3 bases. Find tRNA for the second codon. Attach it. ...
of the protein - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... keratinization. As this occurs, the hair cells die. The dead cells and keratin form the shaft of the hair. 3. Fingernails grow about three or four times as quickly as toenails 4. Each hair grows about 1/4 inch/month and grows for up to 6 years. 5. The most expressive muscles are the facial muscles. ...
... keratinization. As this occurs, the hair cells die. The dead cells and keratin form the shaft of the hair. 3. Fingernails grow about three or four times as quickly as toenails 4. Each hair grows about 1/4 inch/month and grows for up to 6 years. 5. The most expressive muscles are the facial muscles. ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
... in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.