13.3 RNA and Gene Expression
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
Ch. 17 DNA to Protein (Transcription and Translation)
... Missense mutations still code for an amino acid, but not necessarily the right amino acid Nonsense mutations change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a nonfunctional protein Missense mutations are more common *Ex – can cause some cancers, attributes to ...
... Missense mutations still code for an amino acid, but not necessarily the right amino acid Nonsense mutations change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a nonfunctional protein Missense mutations are more common *Ex – can cause some cancers, attributes to ...
Trimble County High School CP Biology Teacher: Debby Griffin Date
... Predicting Making Inferences Synthesizing Texts Determining Importance Visualization Monitoring for Meaning Summarizing Other ______________ ...
... Predicting Making Inferences Synthesizing Texts Determining Importance Visualization Monitoring for Meaning Summarizing Other ______________ ...
Translation
... Translation is the final step on the way from DNA to protein. - It is the synthesis of proteins directed by a mRNA template. - The information contained in the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is read as three letter words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. - During tra ...
... Translation is the final step on the way from DNA to protein. - It is the synthesis of proteins directed by a mRNA template. - The information contained in the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is read as three letter words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. - During tra ...
Slide 1
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
Molecular_files/Translation Transcription
... – A codon = a 3 nucleotide base sequence – Each codon codes for an amino acid – Should have 64 different codons (4 nucleotide choices, 3 bases) but only 20 amino acids- why? ...
... – A codon = a 3 nucleotide base sequence – Each codon codes for an amino acid – Should have 64 different codons (4 nucleotide choices, 3 bases) but only 20 amino acids- why? ...
doc Practice Midterm 2006
... concepts covered in class. As for the questions above, it is important that your answers are concise and unambiguous, and that they directly address the questions posed. 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? ...
... concepts covered in class. As for the questions above, it is important that your answers are concise and unambiguous, and that they directly address the questions posed. 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? ...
What is RNA splicing?
... Combinatorial selection of one exon at each of four variable regions generates more than 38,000 different mRNAs and proteins in the Drosophila cell adhesion molecule Dscam ...
... Combinatorial selection of one exon at each of four variable regions generates more than 38,000 different mRNAs and proteins in the Drosophila cell adhesion molecule Dscam ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
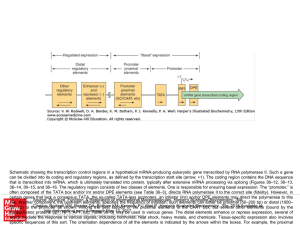
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
05_GENE_EXPRESSION
... Made as subunits in the nucleolus rRNA provides the platform from protein synthesis ...
... Made as subunits in the nucleolus rRNA provides the platform from protein synthesis ...
Sept10
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
Protein synthesis
... • Peptide bond formation - Polypeptide separates from tRNA in P site and attaches by a peptide bond to amino acid carried by tRNA in A site • Translocation - P site tRNA now leaves the ribosome, and ribosome translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. T ...
... • Peptide bond formation - Polypeptide separates from tRNA in P site and attaches by a peptide bond to amino acid carried by tRNA in A site • Translocation - P site tRNA now leaves the ribosome, and ribosome translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. T ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... RNA nucleotides form a complement to one side of the unzipped DNA The RNA complement is called mRNA and it leaves the nucleus carrying a copy of a DNA gene. The DNA zips back up, unchanged. ...
... RNA nucleotides form a complement to one side of the unzipped DNA The RNA complement is called mRNA and it leaves the nucleus carrying a copy of a DNA gene. The DNA zips back up, unchanged. ...
Review Topics for Final Part 1
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
DNA - Ellis Benjamin
... – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combines with proteins to form a ribosome – Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acid to ribosome ...
... – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combines with proteins to form a ribosome – Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acid to ribosome ...
Warm-Ups and Closures Week 18
... Monday, January 11th Warm-Up: Why does protein synthesis involve DNA making mRNA first? a. DNA is stuck in the nucleus and cannot go directly to the ribosome; it needs mRNA to deliver its message to the ribosome. b. mRNA is the building block of proteins. c. mRNA is used to transfer amino acids onto ...
... Monday, January 11th Warm-Up: Why does protein synthesis involve DNA making mRNA first? a. DNA is stuck in the nucleus and cannot go directly to the ribosome; it needs mRNA to deliver its message to the ribosome. b. mRNA is the building block of proteins. c. mRNA is used to transfer amino acids onto ...
translation
... strand of DNA. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. TRANSLATION: In the ribosome, tRNAs match up with their codons in the mRNA. The backsides of the tRNAs have specific amino acids attached to them. When the tRNAs line up, the amino acids bond to each other and let go of the t ...
... strand of DNA. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. TRANSLATION: In the ribosome, tRNAs match up with their codons in the mRNA. The backsides of the tRNAs have specific amino acids attached to them. When the tRNAs line up, the amino acids bond to each other and let go of the t ...
Transcription
... RNA that is wrapped with proteins to form ribosomes. Purpose Synthesis of primary protein structure ...
... RNA that is wrapped with proteins to form ribosomes. Purpose Synthesis of primary protein structure ...
3.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS overview
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
Slide 1
... Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
... Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.