DNAstructureandReplication
... • mRNA joins with a rRNA and tRNA – first tRNA is released from the ribosome – Amino acids bond creating a polypeptide chain – This process is repeated until one of three stop codons is reached ...
... • mRNA joins with a rRNA and tRNA – first tRNA is released from the ribosome – Amino acids bond creating a polypeptide chain – This process is repeated until one of three stop codons is reached ...
Answers
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
RNA interference (RNAi)
... • Short regulatory RNA molecules are transcribed from a cell’s DNA • There are two types of this RNA – microRNA (miRNA) – small interfering RNA (siRNA) • A single-strand of miRNA or siRNA can bind to a protein in the cytoplasm to form a complex, called an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) ...
... • Short regulatory RNA molecules are transcribed from a cell’s DNA • There are two types of this RNA – microRNA (miRNA) – small interfering RNA (siRNA) • A single-strand of miRNA or siRNA can bind to a protein in the cytoplasm to form a complex, called an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) ...
Transcription Translation Notes
... Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine The DNA bases complimentary to each other: A-T & C-G Three nitrogenous bases code for one amino acid (triplet = codon, or a 3-base code) Gene is a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein (sequence of amino acids). ...
... Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine The DNA bases complimentary to each other: A-T & C-G Three nitrogenous bases code for one amino acid (triplet = codon, or a 3-base code) Gene is a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein (sequence of amino acids). ...
Control of Gene Expression
... • mRNA degradation: without a 5’ cap and poly-A tail an mRNA will be destroyed ...
... • mRNA degradation: without a 5’ cap and poly-A tail an mRNA will be destroyed ...
bomb squad and movie mania 2012
... words (some are used twice as indicated with a “x 2”): DNA, nucleus x 2, tRNA x 2, mRNA, transcription, nuclear pore, codon x 2, anticodon, stop codon, amino acid(s) x 2, protein, cytoplasm x2, ribosome, & translation ...
... words (some are used twice as indicated with a “x 2”): DNA, nucleus x 2, tRNA x 2, mRNA, transcription, nuclear pore, codon x 2, anticodon, stop codon, amino acid(s) x 2, protein, cytoplasm x2, ribosome, & translation ...
Protein Synthesis: Translation
... 2) A special protein binds to the stop codon at the A site. 3) The newly-formed polypeptide is released. The tRNAs are released. The two ribosome subunits separate. ...
... 2) A special protein binds to the stop codon at the A site. 3) The newly-formed polypeptide is released. The tRNAs are released. The two ribosome subunits separate. ...
Protein Synthesis Digital Guide
... 4B Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6B Recognize that components ...
... 4B Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6B Recognize that components ...
DNA to Protein - byrdistheword
... made of protein and rRNA) 3. tRNA molecules bring amino acids (building blocks of protein) to the ribosome 4. Every 3 letters in the mRNA code for a single amino acid – 3 bases form a “codon” The tRNA has a 3 letter message that matches the codon on the mRNA, called the ANTICODON 5. Amino acids ge ...
... made of protein and rRNA) 3. tRNA molecules bring amino acids (building blocks of protein) to the ribosome 4. Every 3 letters in the mRNA code for a single amino acid – 3 bases form a “codon” The tRNA has a 3 letter message that matches the codon on the mRNA, called the ANTICODON 5. Amino acids ge ...
DNA Functions
... assembled in exactly the same way as in DNA except that……. ! 1. RNA is mostly single stranded and not a helix. ! 2. the sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose. ! 3. the base thymine is replaced by uracil. ...
... assembled in exactly the same way as in DNA except that……. ! 1. RNA is mostly single stranded and not a helix. ! 2. the sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose. ! 3. the base thymine is replaced by uracil. ...
In the nucleus
... The codon of mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein. Step 1- Processed mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm and joins with 2 ribosome subunits. The mRNA start codon (AUG) signals a tRNA molecule carrying methionine and attaches at the anticodon at the P site. St ...
... The codon of mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein. Step 1- Processed mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm and joins with 2 ribosome subunits. The mRNA start codon (AUG) signals a tRNA molecule carrying methionine and attaches at the anticodon at the P site. St ...
Protein Synthesis A gene is a segment of DNA that is located on a
... a. mRNA enters the ribosome. b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one en ...
... a. mRNA enters the ribosome. b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one en ...
U - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... Initiation RNA Polymerase finds the Promotor site on DNA and begins transcription Elongation RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to growing RNA. Termination Sequences in the DNA prompt the RNA polymerase to fall off ending the transcript. ...
... Initiation RNA Polymerase finds the Promotor site on DNA and begins transcription Elongation RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to growing RNA. Termination Sequences in the DNA prompt the RNA polymerase to fall off ending the transcript. ...
U - Helena High School
... Before making proteins, Your cell must first make RNA • Question: • How does RNA (ribonucleic acid) differ from DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? ...
... Before making proteins, Your cell must first make RNA • Question: • How does RNA (ribonucleic acid) differ from DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? ...
From Gene to Protein
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
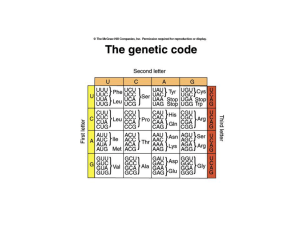
Features of the genetic code
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
AA G
... be encoding hundreds aof muscle kb. On protein, average, has translation The and DNA stability. strand that acts splicing as10-20 being the synthesis and template synthesized. poly-adenylation begins. strand varies are from known gene asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human th ...
... be encoding hundreds aof muscle kb. On protein, average, has translation The and DNA stability. strand that acts splicing as10-20 being the synthesis and template synthesized. poly-adenylation begins. strand varies are from known gene asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human th ...
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 6
... b) It would be much longer than it actually is. 8275 amino acids (1 remaining nucleotide). c) 2664 nucleotides not including the stop codon. If they include the stop codon (2667) it is fine. It is also okay if they add three for the start codon (2670) and say this methionine is sometimes cleaved off ...
... b) It would be much longer than it actually is. 8275 amino acids (1 remaining nucleotide). c) 2664 nucleotides not including the stop codon. If they include the stop codon (2667) it is fine. It is also okay if they add three for the start codon (2670) and say this methionine is sometimes cleaved off ...
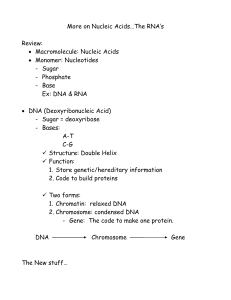
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... o C–G o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides ...
... o C–G o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides ...
Transcription PPT
... • Some proteins are hormones and carry chemical messages; for example insulin, regulates blood sugar • Transport substances such as hemoglobin in RBC that carries O2 ...
... • Some proteins are hormones and carry chemical messages; for example insulin, regulates blood sugar • Transport substances such as hemoglobin in RBC that carries O2 ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS- A small part of the DNA molecule unzips and RNA nucleotides bind to the complimentary bases on the exposed DNA strand. It is important to note that when there is an exposed ADENINE base on the DNA molecule, a URACIL base of RNA will bind with the ADENINE (U binds with A- refer ...
... DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS- A small part of the DNA molecule unzips and RNA nucleotides bind to the complimentary bases on the exposed DNA strand. It is important to note that when there is an exposed ADENINE base on the DNA molecule, a URACIL base of RNA will bind with the ADENINE (U binds with A- refer ...
From Gene to Protein
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
protein synthesis
... The steps in this part of the process are: 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA strand and unwinds a short section (about 12 base pairs long) 2. This then travels along the DNA strand building an RNA molecule from the TEMPLATE STRAND ...
... The steps in this part of the process are: 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA strand and unwinds a short section (about 12 base pairs long) 2. This then travels along the DNA strand building an RNA molecule from the TEMPLATE STRAND ...
Document
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
gene to protein 1
... a. substitutions are corrected before transcription begins. b. substitutions are restricted to introns. c. the base-pairing rules are less strict for the third base of codons and anticodons. d. a signal-recognition particle corrects coding errors. e. transcribed errors attract snRNPs, which then sti ...
... a. substitutions are corrected before transcription begins. b. substitutions are restricted to introns. c. the base-pairing rules are less strict for the third base of codons and anticodons. d. a signal-recognition particle corrects coding errors. e. transcribed errors attract snRNPs, which then sti ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.