Translation Notes
... Translation converts an mRNA transcript into a polypeptide. The process consists of three repeating steps. (Figure on board) ...
... Translation converts an mRNA transcript into a polypeptide. The process consists of three repeating steps. (Figure on board) ...
PowerPoint
... 11.1 Proteins interacting with DNA turn prokaryotic genes on or off in response to environmental changes • Early understanding of gene control ...
... 11.1 Proteins interacting with DNA turn prokaryotic genes on or off in response to environmental changes • Early understanding of gene control ...
Chapter 7 Genes and Protein Synthesis
... One or more nucleotides are inserted/deleted from a DNA sequence Reading frame of codons shifts resulting in multiple missense and/or nonsense effects Any deletion or insertion of base pairs in multiples of ...
... One or more nucleotides are inserted/deleted from a DNA sequence Reading frame of codons shifts resulting in multiple missense and/or nonsense effects Any deletion or insertion of base pairs in multiples of ...
Document
... information from a section of DNA into mRNA. Transcription is like copying down a recipe. In this case it’s a recipe for a specific protein. ...
... information from a section of DNA into mRNA. Transcription is like copying down a recipe. In this case it’s a recipe for a specific protein. ...
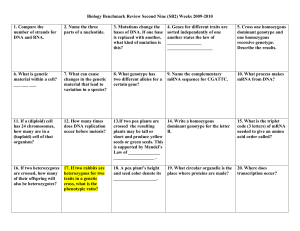
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
DiscBio_C10 Cell division PwrPnt
... Cell splits into 2 identical cells, each with 1 DNA molecule New cells are clones to self and to the parent ...
... Cell splits into 2 identical cells, each with 1 DNA molecule New cells are clones to self and to the parent ...
study guide - cloudfront.net
... What is the order of protein synthesis? (p.302-306) include translation, assembly line, completing the Polypeptide, & transcription) ...
... What is the order of protein synthesis? (p.302-306) include translation, assembly line, completing the Polypeptide, & transcription) ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons because they are “expressed” in the synthesis of proteins. When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the ex ...
... The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons because they are “expressed” in the synthesis of proteins. When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the ex ...
8.4 Transcription
... DNA stores an organism’s genetic information in sections called “genes”, the info to make one protein, in a three step process: Replication, Transcription, and Translation. There are two categories of proteins: 1)enzymes (proteins that catalyze reactions) 2)structural proteins that form parts – stru ...
... DNA stores an organism’s genetic information in sections called “genes”, the info to make one protein, in a three step process: Replication, Transcription, and Translation. There are two categories of proteins: 1)enzymes (proteins that catalyze reactions) 2)structural proteins that form parts – stru ...
DNA - morescience
... Lactose digestion in E.coli begins with its hydrolysis by the enzyme ß-galactosidase. The gene encoding ß-galactosidase, lacZ, is part of a coordinately regulated operon containing other genes ...
... Lactose digestion in E.coli begins with its hydrolysis by the enzyme ß-galactosidase. The gene encoding ß-galactosidase, lacZ, is part of a coordinately regulated operon containing other genes ...
Secondary structure of RNA
... • What is a similarity of DNA and RNA? – G binds with C in both DNA and RNA – Both have sugar and phosphate backbone ...
... • What is a similarity of DNA and RNA? – G binds with C in both DNA and RNA – Both have sugar and phosphate backbone ...
Bio 139 Exam Review Outline: Exam #3
... How can it produce a truncated (short) protein? (by introducing a stop codon) Insertion or deletion of nucleotide(s) not in a multiple of 3 causes frameshift. Why is a frameshift mutation usually more trouble than a point mutation? (changes entire subsequent protein sequence, not just one amino acid ...
... How can it produce a truncated (short) protein? (by introducing a stop codon) Insertion or deletion of nucleotide(s) not in a multiple of 3 causes frameshift. Why is a frameshift mutation usually more trouble than a point mutation? (changes entire subsequent protein sequence, not just one amino acid ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
protein processing
... • variable processing of exons creates a family of proteins, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns ...
... • variable processing of exons creates a family of proteins, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns ...
Gene to Protein
... translation of bacterial genes while not affecting the eukaryotic cell the two parts of the ribosome a. the smaller subunit keeps the mRNA in a linear sequence allowing docking of the ...
... translation of bacterial genes while not affecting the eukaryotic cell the two parts of the ribosome a. the smaller subunit keeps the mRNA in a linear sequence allowing docking of the ...
Semiconservative
... • Normally in OFF position. Operon is controlled by the binding of the repressor to the operator • Lactose binding to repressor causes conformation changes in the repressor • Repressor dislodges from the operator • RNAP binds and transcribes structural genes ...
... • Normally in OFF position. Operon is controlled by the binding of the repressor to the operator • Lactose binding to repressor causes conformation changes in the repressor • Repressor dislodges from the operator • RNAP binds and transcribes structural genes ...
RG 11 - Regulation of Gene Expression
... 3. What are viruses? Explain why they do not qualify as organisms. 4. Listed below are the steps in the lytic cycle of viruses. Put the steps in the correct order. _____ Phage genome directs host cell to produce phage components (DNA and capsids) _____ Self assembly of phage _____ Bacteriophage atta ...
... 3. What are viruses? Explain why they do not qualify as organisms. 4. Listed below are the steps in the lytic cycle of viruses. Put the steps in the correct order. _____ Phage genome directs host cell to produce phage components (DNA and capsids) _____ Self assembly of phage _____ Bacteriophage atta ...
1. A 6-frame translation map of a segment of DNA is shown, with
... transcribed at the time that the electron microscopy was done. [That's plausible... any given gene may be transcribed only some of the time, so it's quite possible that this gene was not being transcribed at the time the sample was collected.] 3. This question concerns a mutation in a gene that crea ...
... transcribed at the time that the electron microscopy was done. [That's plausible... any given gene may be transcribed only some of the time, so it's quite possible that this gene was not being transcribed at the time the sample was collected.] 3. This question concerns a mutation in a gene that crea ...
Lecture 21-23
... ii. transcription factors: in eukaryotes, these are proteins that cluster at the promoter. Without them, RNA polymerase won’t bind. More on this in lecture 23. b. RNA polymerase attaches to promoter and separates the two strands of DNA c. begins synthesizing a new strand of RNA complementary to the ...
... ii. transcription factors: in eukaryotes, these are proteins that cluster at the promoter. Without them, RNA polymerase won’t bind. More on this in lecture 23. b. RNA polymerase attaches to promoter and separates the two strands of DNA c. begins synthesizing a new strand of RNA complementary to the ...
Nucleic Acids Test Topics
... - Transcription is the process of copying DNA into mRNA (messenger RNA); This means the instructions to make a protein encoded in a gene are copied into mRNA - Transcription occurs in the nucleus - mRNA carries the information contained in DNA to the ribosome for translation Translation - Translatio ...
... - Transcription is the process of copying DNA into mRNA (messenger RNA); This means the instructions to make a protein encoded in a gene are copied into mRNA - Transcription occurs in the nucleus - mRNA carries the information contained in DNA to the ribosome for translation Translation - Translatio ...
No Slide Title
... – in an anti-sense experiment, a gene is constructed so that it produces a complementary strand to an expressed transcript, • the goal is to complement, thus inactivate the mRNA. ...
... – in an anti-sense experiment, a gene is constructed so that it produces a complementary strand to an expressed transcript, • the goal is to complement, thus inactivate the mRNA. ...
The Human Genome Project CH 13 Sec 3 notes
... •Discover structure and function of proteins •Compare similar proteins from different organisms –Group protein sequences into families ...
... •Discover structure and function of proteins •Compare similar proteins from different organisms –Group protein sequences into families ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.