Outline Wprowadzenie do genetyki i zastosowa statystyki w
... the proteins in any given cell, but also the set of all protein isoforms and modifications, the interactions between them, the structural description of proteins and their ...
... the proteins in any given cell, but also the set of all protein isoforms and modifications, the interactions between them, the structural description of proteins and their ...
Highlight Review – Common Assessment #4 Multiple Choice
... ____ 21. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is “rewritten” as a molecule of a. messenger RNA. c. transfer RNA. b. ribosomal RNA. d. translation RNA. ____ 22. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b.messenger RNA only c. ribos ...
... ____ 21. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is “rewritten” as a molecule of a. messenger RNA. c. transfer RNA. b. ribosomal RNA. d. translation RNA. ____ 22. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b.messenger RNA only c. ribos ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosome Quiz
... 24.) DNA is converted into RNA during the process of DNA _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ****Bonus***** 1.) What is the 3 letter sequence that codes for an amino acid called? ...
... 24.) DNA is converted into RNA during the process of DNA _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ****Bonus***** 1.) What is the 3 letter sequence that codes for an amino acid called? ...
Supplementary Methods
... plates and for the well-dependent drift caused by the instrument, we normalized all plate averages to global average, and subsequently normalized intraplate data so that a least squares fit across the plate yielded a horizontal line. Finally, the results from individual wells were normalized to thei ...
... plates and for the well-dependent drift caused by the instrument, we normalized all plate averages to global average, and subsequently normalized intraplate data so that a least squares fit across the plate yielded a horizontal line. Finally, the results from individual wells were normalized to thei ...
Molecular Genetics
... - Historical evidence and chemical models of DNA helped to discover and prove its role as the carrier of genetic information. - DNA replication ensures continuity of hereditary information. - The flow of genetic information is from a sequence of nucleic acids in a gene to a sequence of amino acids i ...
... - Historical evidence and chemical models of DNA helped to discover and prove its role as the carrier of genetic information. - DNA replication ensures continuity of hereditary information. - The flow of genetic information is from a sequence of nucleic acids in a gene to a sequence of amino acids i ...
Oxygen (O 2 ) - Mona Shores Blogs
... We used to think one gene made one protein. How is it possible to make more than one protein from a single gene? ...
... We used to think one gene made one protein. How is it possible to make more than one protein from a single gene? ...
Activation of Transcription
... a mechanism that generates protein diversity Protein diversity also generated via alternate splicing Regulates gene expression at the level of RNA processing A mechanism by which a single gene can encode two or more related proteins ...
... a mechanism that generates protein diversity Protein diversity also generated via alternate splicing Regulates gene expression at the level of RNA processing A mechanism by which a single gene can encode two or more related proteins ...
RNA
... 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unzips DNA beginning at the gene (one strand acts a template) 2. Free nucleotides pair with their complementary bases on the exposed DNA template 3. RNA polymerase continues until it reached the terminator sequence and stops 4. mRNA is released and goes to the ribo ...
... 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unzips DNA beginning at the gene (one strand acts a template) 2. Free nucleotides pair with their complementary bases on the exposed DNA template 3. RNA polymerase continues until it reached the terminator sequence and stops 4. mRNA is released and goes to the ribo ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
Clicker Review Exam #3 2013
... In which of the following actions does RNA primase differ from DNA polymerase? A) RNA polymerase uses RNA as a template, and DNA polymerase uses a DNA template. B) RNA polymerase binds to single-stranded DNA, and DNA polymerase binds to doublestranded DNA. C) RNA polymerase is much more accurate th ...
... In which of the following actions does RNA primase differ from DNA polymerase? A) RNA polymerase uses RNA as a template, and DNA polymerase uses a DNA template. B) RNA polymerase binds to single-stranded DNA, and DNA polymerase binds to doublestranded DNA. C) RNA polymerase is much more accurate th ...
2_Outline_BIO119_div..
... B. Example: Genus, Species: Escherichia coli must be Latin endings. 1. Genus is always capitalized and the species is lower case 2. Always italicize or underline. 3. Name usually has some significance. C. How do identify a new isolate and classify it to the species level? 1. There are international ...
... B. Example: Genus, Species: Escherichia coli must be Latin endings. 1. Genus is always capitalized and the species is lower case 2. Always italicize or underline. 3. Name usually has some significance. C. How do identify a new isolate and classify it to the species level? 1. There are international ...
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... Which technique was most likely used to develop this new variety of dog? ...
... Which technique was most likely used to develop this new variety of dog? ...
Ch. 5 Notes Microscopes Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: This is
... Proteins are assembled (put together) on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of part protein and part RNA. The mRNA threads through the ribosomes. The rRNA is the major material within the ribosome, with about 60% of the rRNA and 40% protein by weight. tRNA Transfer RNA molecules are very short ...
... Proteins are assembled (put together) on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of part protein and part RNA. The mRNA threads through the ribosomes. The rRNA is the major material within the ribosome, with about 60% of the rRNA and 40% protein by weight. tRNA Transfer RNA molecules are very short ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
Exam 2
... 6. Hydrogen bonding between molecules plays a critical role in information flow in all organisms. For each process listed below, provide one example of where hydrogen bonding plays a role (if applicable). There were other possible answers, but these are the main one: a. DNA replication - H bonding b ...
... 6. Hydrogen bonding between molecules plays a critical role in information flow in all organisms. For each process listed below, provide one example of where hydrogen bonding plays a role (if applicable). There were other possible answers, but these are the main one: a. DNA replication - H bonding b ...
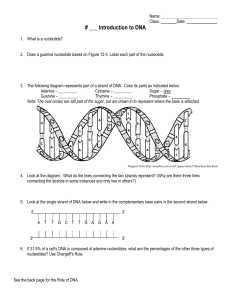
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: THE GENETIC CODE
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
Additional information
... many biological systems, including cancer and other human diseases. We use yeast as a model organism, since it provides for powerful genetics and experimental tools, and yet shares many of the basic regulatory and chromatin mechanisms with all eukaryotes. Our main tool is using genetic screens to ch ...
... many biological systems, including cancer and other human diseases. We use yeast as a model organism, since it provides for powerful genetics and experimental tools, and yet shares many of the basic regulatory and chromatin mechanisms with all eukaryotes. Our main tool is using genetic screens to ch ...
Chapter 14: Gene Transcription and RNA Modification
... Instead, following transcription, the pre-mRNA molecule is modified by a number of different processes that can drastically alter the size and function of the pre-mRNA produced by the RNA polymerase (Table 14.3). These processes can be divided into two general categories. The first form of modificat ...
... Instead, following transcription, the pre-mRNA molecule is modified by a number of different processes that can drastically alter the size and function of the pre-mRNA produced by the RNA polymerase (Table 14.3). These processes can be divided into two general categories. The first form of modificat ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.