Biology 12
... provide STRUCTURAL SUPPORT (e.g. elastin, collagen in cartilage and bone, muscle cells) MOVEMENT (actin and myosin etc. in muscle cells) ...
... provide STRUCTURAL SUPPORT (e.g. elastin, collagen in cartilage and bone, muscle cells) MOVEMENT (actin and myosin etc. in muscle cells) ...
Syllabus Checklist
... the structural properties of the helical DNA molecule, including double-stranded, nucleotide composition and weak bonds involved in base pairing between the complementary strands, allow for its replication. ...
... the structural properties of the helical DNA molecule, including double-stranded, nucleotide composition and weak bonds involved in base pairing between the complementary strands, allow for its replication. ...
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... • Problem: there are only 4 N-bases, and 20 amino acids to make a protein! • We need a TRANSLATION! • What’s the code? ...
... • Problem: there are only 4 N-bases, and 20 amino acids to make a protein! • We need a TRANSLATION! • What’s the code? ...
EOC Benchmark Review!
... b. If plants cannot produce enough ATP in the process of photosynthesis to meet their energy needs, they can produce it in aerobic respiration. c. Sugars are produced in chloroplasts. These sugars can be stored and used by the mitochondria to produce ATP. d. The leaves and sometimes the stems of pla ...
... b. If plants cannot produce enough ATP in the process of photosynthesis to meet their energy needs, they can produce it in aerobic respiration. c. Sugars are produced in chloroplasts. These sugars can be stored and used by the mitochondria to produce ATP. d. The leaves and sometimes the stems of pla ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... Complete the chart on the three chemical ...
... Complete the chart on the three chemical ...
Pre-AP Biology 2009
... 48. Sketch a typical eukaryotic gene and label the regions (see fig 6.1) 49. Eukaryotic genes contain a sequence called the “TATA box”. What is the function of the TATA box? 50. Eukaryotic genes also have enhancer sequences. What are some of the jobs of the many proteins that bind to these enhancer ...
... 48. Sketch a typical eukaryotic gene and label the regions (see fig 6.1) 49. Eukaryotic genes contain a sequence called the “TATA box”. What is the function of the TATA box? 50. Eukaryotic genes also have enhancer sequences. What are some of the jobs of the many proteins that bind to these enhancer ...
Chapter 11
... – A gene that is “turned on” is being transcribed to produce mRNA that is translated to make its corresponding protein – Organisms respond to environmental changes by controlling gene ...
... – A gene that is “turned on” is being transcribed to produce mRNA that is translated to make its corresponding protein – Organisms respond to environmental changes by controlling gene ...
Unit 4
... Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. As an RNA polymerase molecule moves along a gene from the initiation site to the termination site., it synthesizes an RNA molecule that consists of the nucleotide sequence determined by t ...
... Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. As an RNA polymerase molecule moves along a gene from the initiation site to the termination site., it synthesizes an RNA molecule that consists of the nucleotide sequence determined by t ...
4.1 Genetics
... Bellringer 2/23 • DNA is able to control cellular activities most directly by regulating the process of (1) meiotic division (2) protein synthesis (3) active transport (4) selective breeding ...
... Bellringer 2/23 • DNA is able to control cellular activities most directly by regulating the process of (1) meiotic division (2) protein synthesis (3) active transport (4) selective breeding ...
Genetics Unit Test
... d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a a. base. c. gene. b. prot ...
... d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a a. base. c. gene. b. prot ...
1) Genetics Vocabulary
... Gene – small section of DNA on a chromosome that carries information about a trait. Genetics – the study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring. Heredity – passing on traits from parents to offspring. Meiosis – process in which sex cells are formed in reproductive organs; involves two div ...
... Gene – small section of DNA on a chromosome that carries information about a trait. Genetics – the study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring. Heredity – passing on traits from parents to offspring. Meiosis – process in which sex cells are formed in reproductive organs; involves two div ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
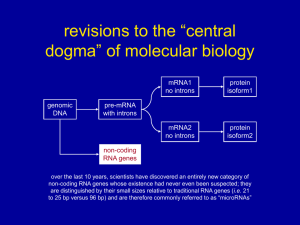
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
Fine Structure and Analysis of Eukaryotic Genes
... Fine Structure and Analysis of Eukaryotic Genes Split genes Multigene families Functional analysis of eukaryotic genes ...
... Fine Structure and Analysis of Eukaryotic Genes Split genes Multigene families Functional analysis of eukaryotic genes ...
Transcription and Processing
... Sigma factor, as part of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme, recognizes and binds to these sequences. b. The mutated (transposed) sequences would not be a binding site for sigma factor. The two regions are not in the correct orientation to each other and therefore would not be recognized as a promoter. 1 ...
... Sigma factor, as part of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme, recognizes and binds to these sequences. b. The mutated (transposed) sequences would not be a binding site for sigma factor. The two regions are not in the correct orientation to each other and therefore would not be recognized as a promoter. 1 ...
Molecular Genetics
... A molecule that binds to the repressor protein. Transcription occurs because the repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator site and prevent transcription. A gene that is not transcribed. The chart formed when photographs of chromosomes are laid out in order. Karyotypes are used to identify chro ...
... A molecule that binds to the repressor protein. Transcription occurs because the repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator site and prevent transcription. A gene that is not transcribed. The chart formed when photographs of chromosomes are laid out in order. Karyotypes are used to identify chro ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET
... Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves ...
... Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves ...
File
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.