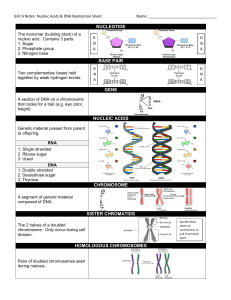
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... PURPOSE: To make an extra copy of DNA during S-Phase of the cell cycle for cellular reproduction (mitosis or meiosis). This ensures each new daughter cell has an exact copy of DNA as the original parent cell. Too much change (mutation) in the DNA sequence may result in cancer. ...
... PURPOSE: To make an extra copy of DNA during S-Phase of the cell cycle for cellular reproduction (mitosis or meiosis). This ensures each new daughter cell has an exact copy of DNA as the original parent cell. Too much change (mutation) in the DNA sequence may result in cancer. ...
11_Lecture_Presentation
... – Transcription factors promote RNA polymerase binding to the promoter – Activator proteins bind to DNA enhancers and interact with other transcription factors – Silencers are repressors that inhibit transcription ...
... – Transcription factors promote RNA polymerase binding to the promoter – Activator proteins bind to DNA enhancers and interact with other transcription factors – Silencers are repressors that inhibit transcription ...
DOC
... 2. Why is it important to maintain DNA replication fidelity? Is it acceptable to have a one in a million error rate? DNA replication fidelity protects us from spontaneous mutations due to replication errors. In each cell division, 1.2x10^10 base pairing decisions must be made. A 1 in a million error ...
... 2. Why is it important to maintain DNA replication fidelity? Is it acceptable to have a one in a million error rate? DNA replication fidelity protects us from spontaneous mutations due to replication errors. In each cell division, 1.2x10^10 base pairing decisions must be made. A 1 in a million error ...
Methods to analyze RNA expression - RNA
... RNA sequencing analysis The newest technology for RNA expression analysis • Provides data for all the genes expressed in a particular sample (tissues, conditions, stages, etc.) • Coupled with high throughput sequencing ...
... RNA sequencing analysis The newest technology for RNA expression analysis • Provides data for all the genes expressed in a particular sample (tissues, conditions, stages, etc.) • Coupled with high throughput sequencing ...
Science TAKS - Midland ISD
... F Carrying instructions for protein synthesis G Transforming into a protein H Replacing damaged DNA J Passing traits to offspring ...
... F Carrying instructions for protein synthesis G Transforming into a protein H Replacing damaged DNA J Passing traits to offspring ...
Integrated Science 3/4 Course Map Biology_EOC_FAQ_2016
... happen without these processes. Remember that plants can do both but animals only cellular respiration. 7. Cell membrane structure: (check out the Fluid Mosaic Model)the outer boundary layer of all cells is made of lipid mostly (taken in the form of phospholipids arranged in a double (“bilayer”) wit ...
... happen without these processes. Remember that plants can do both but animals only cellular respiration. 7. Cell membrane structure: (check out the Fluid Mosaic Model)the outer boundary layer of all cells is made of lipid mostly (taken in the form of phospholipids arranged in a double (“bilayer”) wit ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
Trans - Wiley
... • Dynamic remodeling of the spliceosome requires DEXH/D box RNA helicases. • SC35 and ASF/SF2, members of the highly conserved serine/arginine (SR)rich family of splicing factors have a dual role in stimulating constitutive and regulated splicing. ...
... • Dynamic remodeling of the spliceosome requires DEXH/D box RNA helicases. • SC35 and ASF/SF2, members of the highly conserved serine/arginine (SR)rich family of splicing factors have a dual role in stimulating constitutive and regulated splicing. ...
Key
... Homologous sequences required for homologous recombination. The small boxes flanking the NeoR gene correspond to parts of an exon of gene X we wish to replace. NeoR: neomycin-resistance gene confers resistance to G418 TK: thymidylate kinase (from Herpes simplex) confers sensitivity to gancyclovir, b ...
... Homologous sequences required for homologous recombination. The small boxes flanking the NeoR gene correspond to parts of an exon of gene X we wish to replace. NeoR: neomycin-resistance gene confers resistance to G418 TK: thymidylate kinase (from Herpes simplex) confers sensitivity to gancyclovir, b ...
DNA for Dummies Notes - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... • Occurs continually throughout the cell cycle with the exception of mitosis • Occurs in the nucleus as messenger RNA copies DNA ...
... • Occurs continually throughout the cell cycle with the exception of mitosis • Occurs in the nucleus as messenger RNA copies DNA ...
bch224 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 1. Describe the process by which plasmids serve as important tools in DNA technology. A plasmid is an independent, circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that carries only a few genes. Plasmids serve as vectors (vehicle/carrier) in DNA manipulation. They are cut open at specific sites (genes that c ...
... 1. Describe the process by which plasmids serve as important tools in DNA technology. A plasmid is an independent, circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that carries only a few genes. Plasmids serve as vectors (vehicle/carrier) in DNA manipulation. They are cut open at specific sites (genes that c ...
Station #3: DNA structure, replication, protein synthesis, mutation
... 5. What is the relationship between genes and chromosomes? a. Genes are the proteins encoded by chromosomes b. Genes are the proteins around which DNA chromosomes are packaged c. A chromosome is a DNA molecule with many genes d. Chromosomes are proteins that carry genes made of DNA 6. Which of the f ...
... 5. What is the relationship between genes and chromosomes? a. Genes are the proteins encoded by chromosomes b. Genes are the proteins around which DNA chromosomes are packaged c. A chromosome is a DNA molecule with many genes d. Chromosomes are proteins that carry genes made of DNA 6. Which of the f ...
DNA and RNA - Xavier High School
... – Most eukaryotic genes are controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex than those of the lac operon ...
... – Most eukaryotic genes are controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex than those of the lac operon ...
GenTech Unit 2 DNA
... polymerase binds to DNA. 2. RNA polymerase separates portion of DNA into two separate strands. 3. Free floating nucleotides in nucleus match their nitrogen bases with bases of “unzipped” DNA. DNA base code = C-G-A-T-A Complimentary RNA = G-C-U-A-U ...
... polymerase binds to DNA. 2. RNA polymerase separates portion of DNA into two separate strands. 3. Free floating nucleotides in nucleus match their nitrogen bases with bases of “unzipped” DNA. DNA base code = C-G-A-T-A Complimentary RNA = G-C-U-A-U ...
Transformation and Transduction File
... live nonpathogenic cell takes up a piece of DNA carry the ...
... live nonpathogenic cell takes up a piece of DNA carry the ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome or gene. 21. ____________________ ...
... 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome or gene. 21. ____________________ ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
BIO120 LAB --DNA + PROTEIN SYN-
... • RNA Polymerase unzips gene and moves down DNA – Complimentary RNA nucleotides bind DNA – RNA nucleotides bind together (via RNA poly) – at end of gene mRNA detaches and RNA poly detaches • DNA zips up when transcription is done • mRNA is made and leaves nucleus and enters cytoplasm ...
... • RNA Polymerase unzips gene and moves down DNA – Complimentary RNA nucleotides bind DNA – RNA nucleotides bind together (via RNA poly) – at end of gene mRNA detaches and RNA poly detaches • DNA zips up when transcription is done • mRNA is made and leaves nucleus and enters cytoplasm ...
Biology 3A Exam 3 Study Guide The exam will consist of multiple
... only have one?), replication fork, parent strand, leading strand, lagging strand (Okazaki’s fragments) - what joins the fragments together. proofreading, DNA repair, repair enzymes and excision repair, nucleases (endo vs. exo), know the types of DNA damage • Protein synthesis - where, when & why doe ...
... only have one?), replication fork, parent strand, leading strand, lagging strand (Okazaki’s fragments) - what joins the fragments together. proofreading, DNA repair, repair enzymes and excision repair, nucleases (endo vs. exo), know the types of DNA damage • Protein synthesis - where, when & why doe ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.