Lesson 3 | DNA and Genetics
... Key Concept What is the role of RNA in protein production? Directions: The diagram below shows one strand of a DNA molecule with six bases shown. A strand of mRNA has just been created from those bases that will be used to make part of a protein. Write the letters of the corresponding RNA bases on e ...
... Key Concept What is the role of RNA in protein production? Directions: The diagram below shows one strand of a DNA molecule with six bases shown. A strand of mRNA has just been created from those bases that will be used to make part of a protein. Write the letters of the corresponding RNA bases on e ...
Document
... 39- Chromosomes are paired and arranged by…………… a. Banding. b. Size. c. Shape. d. All of the above are correct. 40- The relation between the sequence of DNA and the sequence of corresponding protein is called…………….. a. mutation. b. Genetic code. c. nucleosome. d. Chromatin. 41- MRNA carry the same s ...
... 39- Chromosomes are paired and arranged by…………… a. Banding. b. Size. c. Shape. d. All of the above are correct. 40- The relation between the sequence of DNA and the sequence of corresponding protein is called…………….. a. mutation. b. Genetic code. c. nucleosome. d. Chromatin. 41- MRNA carry the same s ...
QCM2 - GIGA
... genetically linked with the disease gene in order to determine its chromosomal location, a procedure known as mapping. ...
... genetically linked with the disease gene in order to determine its chromosomal location, a procedure known as mapping. ...
downloadable file
... Sequencing DNA is a way to determine the order of the four nucleotides along a strand of DNA. Sequencing DNA has become vital to the fields of basic research, biotechnology, forensics and medical diagnostics. In the late 1970’s, biology saw the first two methods to sequence DNA. One method, Maxam-Gi ...
... Sequencing DNA is a way to determine the order of the four nucleotides along a strand of DNA. Sequencing DNA has become vital to the fields of basic research, biotechnology, forensics and medical diagnostics. In the late 1970’s, biology saw the first two methods to sequence DNA. One method, Maxam-Gi ...
pdf
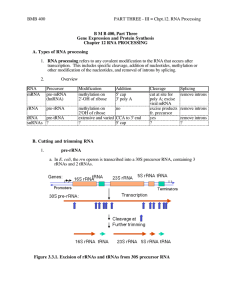
... CFI and CFII are cleavage factors. PAP is the polyA polymerase. CFI, CFII and PAP form a complex that binds to the nascent RNA at the cleavage site, directed by the CPSF specificity factor. CstF is an additional protein implicated in this process in vitro, but its precise function is currently unkno ...
... CFI and CFII are cleavage factors. PAP is the polyA polymerase. CFI, CFII and PAP form a complex that binds to the nascent RNA at the cleavage site, directed by the CPSF specificity factor. CstF is an additional protein implicated in this process in vitro, but its precise function is currently unkno ...
No Slide Title
... The first letter is the initial letter of the genus name of the organism from which the enzyme is isolated The second and third letters are usually the initial letters of the organisms species name. It is written in italic A fourth letter, if any, indicates a particular strain organism Origi ...
... The first letter is the initial letter of the genus name of the organism from which the enzyme is isolated The second and third letters are usually the initial letters of the organisms species name. It is written in italic A fourth letter, if any, indicates a particular strain organism Origi ...
Lecture8-Chap5 Sept26
... mouse and human genomes, and most functional genes are in a syntenic region. • synteny – A relationship between chromosomal regions of different species where homologous genes occur in the same order. Figure 05.08: Mouse chromosome 1 has 21 segments 1-25 Mb in length syntenic with regions correspond ...
... mouse and human genomes, and most functional genes are in a syntenic region. • synteny – A relationship between chromosomal regions of different species where homologous genes occur in the same order. Figure 05.08: Mouse chromosome 1 has 21 segments 1-25 Mb in length syntenic with regions correspond ...
Phenotype
... • Mechanistically predicting relationships between different data types is very difficult • Empirical mappings are important • Functions from Genome to Phenotype stands out in importance G is the most abundant data form - heritable and precise. F is of greatest interest. DNA ...
... • Mechanistically predicting relationships between different data types is very difficult • Empirical mappings are important • Functions from Genome to Phenotype stands out in importance G is the most abundant data form - heritable and precise. F is of greatest interest. DNA ...
Nature Biotechnology, 21(4) - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Sequences from genes that are transcribed from opposite strands of the same genomic locus and have overlapping expressed regions are aligned by LEADS into one cluster. We therefore designed an ‘Antisensor’ algorithm capable of detecting clusters with sequences from opposite strands (described in det ...
... Sequences from genes that are transcribed from opposite strands of the same genomic locus and have overlapping expressed regions are aligned by LEADS into one cluster. We therefore designed an ‘Antisensor’ algorithm capable of detecting clusters with sequences from opposite strands (described in det ...
Cis-regulatory modules in Drosophila
... A significant character of cis-regulatory sites: the multiple binding sites for different transcriptional factors tend to cluster together in one region around the gene, forming the Cis-Regulatory Modules (CRM). The searching of cis-regulatory sites gives out too many candidate positions, which make ...
... A significant character of cis-regulatory sites: the multiple binding sites for different transcriptional factors tend to cluster together in one region around the gene, forming the Cis-Regulatory Modules (CRM). The searching of cis-regulatory sites gives out too many candidate positions, which make ...
3.3.1: How is DNA Passed Through the Generations?
... called homologous chromosomes (one chromosome inherited from the father and one chromosome inherited from the mother). ...
... called homologous chromosomes (one chromosome inherited from the father and one chromosome inherited from the mother). ...
Mutations - The Super Heroes of Biology
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
Chapter 15
... 1. Promoter always capable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes in question are always transcribed (“on”) >genes that are always on are called constitutive genes 2. Promoter usually incapable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes are usually not transcribed (“off”) but ...
... 1. Promoter always capable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes in question are always transcribed (“on”) >genes that are always on are called constitutive genes 2. Promoter usually incapable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes are usually not transcribed (“off”) but ...
GENERAL ZOOLOGY LECTURE EXAM 2
... c. all will have stop codons inserted in locations where they do not belong d. all will have frameshift mutations e. none of the above will occur 9. The _______ of tRNA is ____________ to the ________ of mRNA. a. codon, identical, anticodon b. codon, complimentary, anticodon c. anticodon, identical, ...
... c. all will have stop codons inserted in locations where they do not belong d. all will have frameshift mutations e. none of the above will occur 9. The _______ of tRNA is ____________ to the ________ of mRNA. a. codon, identical, anticodon b. codon, complimentary, anticodon c. anticodon, identical, ...
Looking Beyond Our DNA - Federation of American Societies for
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
TGAC * Sequence Polymorphisms Module
... Codons in mRNA (5’-AUG-3’, etc.) have sequence equivalents in DNA (5’-ATG-3’, etc.). The DNA strand that is equivalent to mRNA is called the “coding strand.” The complementary strand is called the “template strand,” because it serves as the template for synthesizing mRNA. Non-spliced genes, wh ...
... Codons in mRNA (5’-AUG-3’, etc.) have sequence equivalents in DNA (5’-ATG-3’, etc.). The DNA strand that is equivalent to mRNA is called the “coding strand.” The complementary strand is called the “template strand,” because it serves as the template for synthesizing mRNA. Non-spliced genes, wh ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... Bacteria can reproduce in 4 different ways. Describe each of these: ...
... Bacteria can reproduce in 4 different ways. Describe each of these: ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.