PDF Obsolete Data Sheets
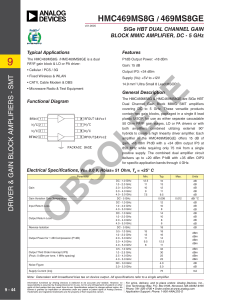
... Dual Channel Gain Block MMIC SMT amplifiers covering DC to 5 GHz. These versatile products contain two gain blocks, packaged in a single 8 lead plastic MSOP, for use as either separate cascadable 50 Ohm RF/IF gain stages, LO or PA drivers or with both amplifiers combined utilizing external 90° hybri ...
... Dual Channel Gain Block MMIC SMT amplifiers covering DC to 5 GHz. These versatile products contain two gain blocks, packaged in a single 8 lead plastic MSOP, for use as either separate cascadable 50 Ohm RF/IF gain stages, LO or PA drivers or with both amplifiers combined utilizing external 90° hybri ...
A New Fully Balanced Differential OTA with Common
... circuit is kept constant at 1.5 V, imposed as reference. The advantage of this configuration is given by the possibility of using the proposed circuit in application requiring d.c. coupling and also in those requiring a.c. coupling. The main disadvantage of using the common-mode tuning loop (CMFB) i ...
... circuit is kept constant at 1.5 V, imposed as reference. The advantage of this configuration is given by the possibility of using the proposed circuit in application requiring d.c. coupling and also in those requiring a.c. coupling. The main disadvantage of using the common-mode tuning loop (CMFB) i ...
+ R - Purdue Physics
... Ohmic resistor: resistor made of ohmic material Ohmic materials: materials in which conductivity is independent of the amount of current flowing through DV I= R ...
... Ohmic resistor: resistor made of ohmic material Ohmic materials: materials in which conductivity is independent of the amount of current flowing through DV I= R ...
Differential and Multistage Amplifiers
... Figure 7.19 Equivalence of the BJT differential amplifier in (a) to the two common-emitter amplifiers in (b). This equivalence applies only for differential input signals. Either of the two common-emitter amplifiers in (b) can be used to find the differential gain, differential input resistance, fr ...
... Figure 7.19 Equivalence of the BJT differential amplifier in (a) to the two common-emitter amplifiers in (b). This equivalence applies only for differential input signals. Either of the two common-emitter amplifiers in (b) can be used to find the differential gain, differential input resistance, fr ...
1.05 GHz MEMS Oscillator Based On Lateral-Field
... the required level by adding more fingers (i.e., resonator volume) to the AlN resonator depending on the specific application of interest. On the other hand, another important factor that can be negatively affecting the power handling capability of the LFE AlN resonators is the non-uniform distribut ...
... the required level by adding more fingers (i.e., resonator volume) to the AlN resonator depending on the specific application of interest. On the other hand, another important factor that can be negatively affecting the power handling capability of the LFE AlN resonators is the non-uniform distribut ...
Simultaneous-Switching Noise Analysis For Texas Instruments FIFO
... bounce.2 Surface-mount packages, such as PQFPs, are a better package option than through-hole packages, such as DIP or PGA, because the former have shortened pins or a lower-profile package. Another approach is to decrease the inductance of the ground pins by placing as many ground / power pins in t ...
... bounce.2 Surface-mount packages, such as PQFPs, are a better package option than through-hole packages, such as DIP or PGA, because the former have shortened pins or a lower-profile package. Another approach is to decrease the inductance of the ground pins by placing as many ground / power pins in t ...
DC/AC Fundamentals: A Systems Approach
... Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 • All Rights Reserved ...
... Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 • All Rights Reserved ...
2. Overview of Beyond CMOS Devices
... carriers might not have vacant states Parallel magnetizations = smaller R Anti-parallel = larger R (+) Switch magnetization for better off-current, reconfigurability. (-) For benchmarked circuits, the spin functionality not used. ...
... carriers might not have vacant states Parallel magnetizations = smaller R Anti-parallel = larger R (+) Switch magnetization for better off-current, reconfigurability. (-) For benchmarked circuits, the spin functionality not used. ...
Integrated circuit

An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small plate (""chip"") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. This can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components. ICs can be made very compact, having up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area the size of a fingernail. The width of each conducting line in a circuit can be made smaller and smaller as the technology advances; in 2008 it dropped below 100 nanometers, and has now been reduced to tens of nanometers.ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) as a result of the small size and close proximity of the components. As of 2012, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 450 mm2, with up to 9 million transistors per mm2.Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the low cost of integrated circuits.