RNA and Protein Synthesis - Port Washington School District
... acids to the ribosomes where they are eventually assembled into protein chains – Each amino acid is coded for by a different triplet codon on mRNA – tRNA has an anticodon that will pair up with codon on mRNA ...
... acids to the ribosomes where they are eventually assembled into protein chains – Each amino acid is coded for by a different triplet codon on mRNA – tRNA has an anticodon that will pair up with codon on mRNA ...
Chapter 23 Lecture PowerPoint
... • LTR are lacking in most retrotransposons • Most abundant type lacking LTR are LINEs and LINE-like elements – Long interspersed elements – Encode an endonuclease that nicks target DNA – Takes advantage of new DNA 3’-end to prime reverse transcriptase of element RNA – After 2nd strand synthesis, ele ...
... • LTR are lacking in most retrotransposons • Most abundant type lacking LTR are LINEs and LINE-like elements – Long interspersed elements – Encode an endonuclease that nicks target DNA – Takes advantage of new DNA 3’-end to prime reverse transcriptase of element RNA – After 2nd strand synthesis, ele ...
chapter review answers
... 7. Transcribe and translate the following DNA molecule: AAATATGGCCCGGAT mRNA: UUUAUACCGGGCCUA Protein: Phen- Iso - Pro - Gly - Leu 8. Name two major types of mutations. What do they have in common? How are they different? Give an example of each using the sequence above. Gene and chromosomal. Both c ...
... 7. Transcribe and translate the following DNA molecule: AAATATGGCCCGGAT mRNA: UUUAUACCGGGCCUA Protein: Phen- Iso - Pro - Gly - Leu 8. Name two major types of mutations. What do they have in common? How are they different? Give an example of each using the sequence above. Gene and chromosomal. Both c ...
HGNC future plans
... Aim 4: Naming small non-coding RNA genes Name microRNAs, transfer RNAs, small nucleolar RNAs and ribosomal RNAs, and investigate naming piRNA genes, create a “miscellaneous non-coding RNA” category for non-specific bioinformatically predicted genomic loci. ...
... Aim 4: Naming small non-coding RNA genes Name microRNAs, transfer RNAs, small nucleolar RNAs and ribosomal RNAs, and investigate naming piRNA genes, create a “miscellaneous non-coding RNA” category for non-specific bioinformatically predicted genomic loci. ...
Oxidative Metabolism - Plant Energy Biology
... (bhlh-Zip) transcription factors that heterodimerise and activate transcription of genes that contain an R Box -GTCAC Rtg2 acts upstream of Rtg1 and 3 sensor of mitochondrial dysfunction transducer of signals ...
... (bhlh-Zip) transcription factors that heterodimerise and activate transcription of genes that contain an R Box -GTCAC Rtg2 acts upstream of Rtg1 and 3 sensor of mitochondrial dysfunction transducer of signals ...
Heredity 1)Heredity is the ______ of the qualities that were passed
... 17) The sex of a child is determined by the ______ _______________. Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________ ...
... 17) The sex of a child is determined by the ______ _______________. Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________ ...
document
... are the same for a particular characteristic. • Bb or bB are said to be heterozygous as both genes for a particular characteristic are different. • Sometimes genes can be co-dominant where one gene is not entirely dominant over another gene. • Karyotype is a persons entire set of genetic material. • ...
... are the same for a particular characteristic. • Bb or bB are said to be heterozygous as both genes for a particular characteristic are different. • Sometimes genes can be co-dominant where one gene is not entirely dominant over another gene. • Karyotype is a persons entire set of genetic material. • ...
Workshop IX Fungal Genomics Chair: Peter Philippsen 206
... A new discovery method has been developed with the objective of finding secreted enzymes with unknown/undefined activity. It builds on direct selection in live cells (E.coli). It is named: Transposon assisted signal trapping (TAST).The method was designed to discover secreted proteins with special e ...
... A new discovery method has been developed with the objective of finding secreted enzymes with unknown/undefined activity. It builds on direct selection in live cells (E.coli). It is named: Transposon assisted signal trapping (TAST).The method was designed to discover secreted proteins with special e ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;11)(p21;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
... motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
Mutation detection and correction experiments in
... plant cell systems (Beetham et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 1999) have since been described. DNA sequence alterations have also been achieved in nuclear or cell-free extracts (Cole et al., 1999; Igoucheva et al., 1999). This novel RDO technology holds promise as a means to correct point mutations in disea ...
... plant cell systems (Beetham et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 1999) have since been described. DNA sequence alterations have also been achieved in nuclear or cell-free extracts (Cole et al., 1999; Igoucheva et al., 1999). This novel RDO technology holds promise as a means to correct point mutations in disea ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-central dogma
... polymerase then the sigma factor is released. - Termination: RNA polymerase encounter a stop signal or transcription terminator (e.g. rho protein in procaryotes). - the RNA polymerase dissociate from the DNA template - the RNA transcript is released. ...
... polymerase then the sigma factor is released. - Termination: RNA polymerase encounter a stop signal or transcription terminator (e.g. rho protein in procaryotes). - the RNA polymerase dissociate from the DNA template - the RNA transcript is released. ...
Overlapping gene structure of human VLCAD and
... et al., 1996). The VLCAD gene is about 5.4 kb long, contains 20 exons that encode a 655-amino-acid protein and is located on chromosome 17p13. VLCAD differs from the other three acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in that it is a homodimer of 70 kDa subunits bound to the inner membrane whereas the others are so ...
... et al., 1996). The VLCAD gene is about 5.4 kb long, contains 20 exons that encode a 655-amino-acid protein and is located on chromosome 17p13. VLCAD differs from the other three acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in that it is a homodimer of 70 kDa subunits bound to the inner membrane whereas the others are so ...
Gene Section POU2AF1 (POU domain, class 2, associating factor 1)
... Spans on a 30 kb genomic fragment; five exons; large fifth exon, with many 3'-UTR repetitive elements, two pyrimidine rich regions (a duplicated CT-rich region and a [CCTT]n tetranucleotide tandem repeat) and a ...
... Spans on a 30 kb genomic fragment; five exons; large fifth exon, with many 3'-UTR repetitive elements, two pyrimidine rich regions (a duplicated CT-rich region and a [CCTT]n tetranucleotide tandem repeat) and a ...
Bacterial Comparative Genomics
... • -log normalizes values between 0-1 such that 10-fold decrease in pvalue causes the normalized value to increase by 1 ...
... • -log normalizes values between 0-1 such that 10-fold decrease in pvalue causes the normalized value to increase by 1 ...
Document
... -Flexor pollicis longus -Flexor pollicis brevis -1st volar interosseus of Henle (80% of individuals present a pollical palmar interosseous muscle (of the thumb) as suggested by Henle's description in 1858) ...
... -Flexor pollicis longus -Flexor pollicis brevis -1st volar interosseus of Henle (80% of individuals present a pollical palmar interosseous muscle (of the thumb) as suggested by Henle's description in 1858) ...
Purpose of DNA
... past two days we talked about DNA replication and transcription (DNA to RNA) ► Today, we talk about translation (RNA to protein) ...
... past two days we talked about DNA replication and transcription (DNA to RNA) ► Today, we talk about translation (RNA to protein) ...
Gene Section AFF1 (AF4/FMR2 family, member 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... splice of exon 18 to the 3'-NTR, skipping exon 19 and 20. Therefore this protein comes in different flavors, as there are presumably three independent promotor, and one carboxy-terminal exon skipping. Bernard OA, Berger R. Molecular basis of 11q23 rearrangements in hematopoietic malignant proliferat ...
... splice of exon 18 to the 3'-NTR, skipping exon 19 and 20. Therefore this protein comes in different flavors, as there are presumably three independent promotor, and one carboxy-terminal exon skipping. Bernard OA, Berger R. Molecular basis of 11q23 rearrangements in hematopoietic malignant proliferat ...
1. Overview of Gene Expression Overview of Gene Expression Chapter 10B:
... • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small percentage of genes are special types of RNA molecules) ...
... • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small percentage of genes are special types of RNA molecules) ...
X-linked Inheritance - Great Ormond Street Hospital
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
Transcription & Translation
... – Making Proteins from RNA – amino acids are assembled from information encoded in mRNA 1. mRNA codons move through the ribosome 2. tRNAs add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain 3. Process continues until a stop codon is reached 4. Newly made protein is released ...
... – Making Proteins from RNA – amino acids are assembled from information encoded in mRNA 1. mRNA codons move through the ribosome 2. tRNAs add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain 3. Process continues until a stop codon is reached 4. Newly made protein is released ...
other_patterns_of_inheritance
... • Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses are said to be linked genes. • When genes are linked, they do not assort independently. ...
... • Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses are said to be linked genes. • When genes are linked, they do not assort independently. ...
Nuclear Hormone Receptor CloneSetTM
... Nuclear hormone receptors (NHR) are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate gene expression by interacting with specific DNA sequences upstream of their target genes. A two-step mechanism of action has been proposed for these receptors based upon observations of active and inactive stat ...
... Nuclear hormone receptors (NHR) are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate gene expression by interacting with specific DNA sequences upstream of their target genes. A two-step mechanism of action has been proposed for these receptors based upon observations of active and inactive stat ...
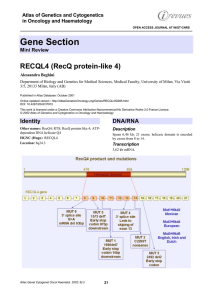
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
RNA-Seq

RNA-seq (RNA sequencing), also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing (WTSS), is a technology that uses the capabilities of next-generation sequencing to reveal a snapshot of RNA presence and quantity from a genome at a given moment in time.