Evolution: A Change In A Population
... small group of organisms colonize a new habitat. B. In small populations, an allele can become more or less common simply by chance. 1. Individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than others, just by chance. 2. Founder Effect - Allele frequencies change as a result of the ...
... small group of organisms colonize a new habitat. B. In small populations, an allele can become more or less common simply by chance. 1. Individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than others, just by chance. 2. Founder Effect - Allele frequencies change as a result of the ...
Allele Frequencyнаmeasure of how common a certain allele is in a
... cause a new allele to form. If in a reproductive cell it can be passed on. Increases genetic variation in a gene pool. ...
... cause a new allele to form. If in a reproductive cell it can be passed on. Increases genetic variation in a gene pool. ...
Mechanisms of Change
... generation would have a few more brown beetles than green (purely by chance) • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population. ...
... generation would have a few more brown beetles than green (purely by chance) • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population. ...
AP Biology - farishapbio
... ii. Founder effect – gen. Drift that occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population, with the result that the new population’s gene pool is not reflective of the original population 5. Explain why even though mutation can be a source of genetic variability, it contributes a n ...
... ii. Founder effect – gen. Drift that occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population, with the result that the new population’s gene pool is not reflective of the original population 5. Explain why even though mutation can be a source of genetic variability, it contributes a n ...
11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution
... flowers has genetic diversity that results in red, yellow and blue phenotypes. ...
... flowers has genetic diversity that results in red, yellow and blue phenotypes. ...
Population Genetics ppt - Liberty Union High School District
... - Reduced genetic variation - Smaller population have a hard time adapting ...
... - Reduced genetic variation - Smaller population have a hard time adapting ...
Chapter 4
... same locus on homologous chromosomes and govern the same trait. Because they are different, their action may result in different expressions of that trait. The term is often used synonymously with genes. ...
... same locus on homologous chromosomes and govern the same trait. Because they are different, their action may result in different expressions of that trait. The term is often used synonymously with genes. ...
Genetic Evolution Lecture
... Allele frequency aka relative frequency is the percentage of one allele in a gene pool. For example, 50% of the alleles might have been B’s, but after the change, it might have dropped to 10%. Recall that only GROUPS can evolve, not individuals. If this is true, then genetic evolution can only occur ...
... Allele frequency aka relative frequency is the percentage of one allele in a gene pool. For example, 50% of the alleles might have been B’s, but after the change, it might have dropped to 10%. Recall that only GROUPS can evolve, not individuals. If this is true, then genetic evolution can only occur ...
Microevolution ppt
... Once a mutation occurs, nearly all phenotypic variations will result from shuffling of existing alleles ...
... Once a mutation occurs, nearly all phenotypic variations will result from shuffling of existing alleles ...
Genetic Mutations
... Migration also contributes to genetic variation Individuals immigrating into a population bring new alleles with them. This causes a change in allele frequencies in a population. Read: Some individuals from a population of brown beetles might have joined a population of green beetles. That would mak ...
... Migration also contributes to genetic variation Individuals immigrating into a population bring new alleles with them. This causes a change in allele frequencies in a population. Read: Some individuals from a population of brown beetles might have joined a population of green beetles. That would mak ...
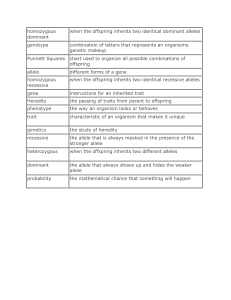
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... chart used to organize all possible combinations of offspring ...
... chart used to organize all possible combinations of offspring ...
BioA414 Handout VII-2017
... • The population achieves equilibrium – Nb of alleles undergoing forward mutation = Nb of alleles undergoing reverse mutation – At this point no change in allelic freq occur – The equilibrium q = … ...
... • The population achieves equilibrium – Nb of alleles undergoing forward mutation = Nb of alleles undergoing reverse mutation – At this point no change in allelic freq occur – The equilibrium q = … ...
Patterns of Evolution
... population a random assortment of traits will be passed on to the next generation • If parents are limited or selective in their choice of mates, a limited set of traits will be passed on (artificial selection) • Larger male iguanas on the Galapagos islands are more favorable ...
... population a random assortment of traits will be passed on to the next generation • If parents are limited or selective in their choice of mates, a limited set of traits will be passed on (artificial selection) • Larger male iguanas on the Galapagos islands are more favorable ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... - No migration: immigrants can change the frequency of an allele by bringing in new alleles to a population. - No net mutations: if alleles change from one to another, this will change the frequency of those alleles. - Random mating: if certain traits are more desirable, then individuals with those ...
... - No migration: immigrants can change the frequency of an allele by bringing in new alleles to a population. - No net mutations: if alleles change from one to another, this will change the frequency of those alleles. - Random mating: if certain traits are more desirable, then individuals with those ...
The Evolution of Populations
... Relative Fitness- the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals. Natural selection is the only evolutionary mechanism that continually leads to adaptive ...
... Relative Fitness- the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals. Natural selection is the only evolutionary mechanism that continually leads to adaptive ...
The Evolution of Populations
... (homozygous/heterozygous) • Fixed allele: all members of a population only have 1 allele for a particular trait • The more fixed alleles a population has, the LOWER the species’ diversity ...
... (homozygous/heterozygous) • Fixed allele: all members of a population only have 1 allele for a particular trait • The more fixed alleles a population has, the LOWER the species’ diversity ...
Lecture #10 Date ______
... • How to use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to calculate allelic frequencies and to test whether a population is evolving. ...
... • How to use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to calculate allelic frequencies and to test whether a population is evolving. ...
Evolution Study Guide Part 2
... These mutations can be neutral (no effect), negative (possible disease), or beneficial. Mutations are important for evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of gene ...
... These mutations can be neutral (no effect), negative (possible disease), or beneficial. Mutations are important for evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of gene ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.