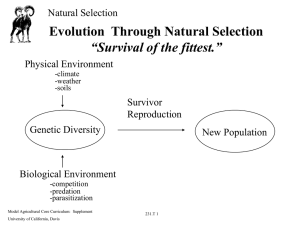
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
Chapter 4 Heredity and Evolution
... Genetic drift is directly related to population size. Genetic drift occurs when some individuals contribute a disproportionate share of genes to succeeding generations. Drift may also occur solely because the population is small: Alleles with low frequencies may simply not be passed on to offsprin ...
... Genetic drift is directly related to population size. Genetic drift occurs when some individuals contribute a disproportionate share of genes to succeeding generations. Drift may also occur solely because the population is small: Alleles with low frequencies may simply not be passed on to offsprin ...
Concept Review
... 6. Describe the Hardy-Weinberg equations. What does each part represent? Can you use it? 7. Give an example of a gene pool. Give examples of some alleles in the gene pool. (pg. 265) 13.6 8. What would need to occur within a population for it to remain in genetic equilibrium? What is ...
... 6. Describe the Hardy-Weinberg equations. What does each part represent? Can you use it? 7. Give an example of a gene pool. Give examples of some alleles in the gene pool. (pg. 265) 13.6 8. What would need to occur within a population for it to remain in genetic equilibrium? What is ...
Gene Pool - My Haiku
... • To calculate genotype and allele frequencies in a population. • To determine if a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. • To estimate what % of a population is carrying the allele for a ...
... • To calculate genotype and allele frequencies in a population. • To determine if a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. • To estimate what % of a population is carrying the allele for a ...
Founder effects in human populations
... only 2,600. After twelve to sixteen generations, with an eightyfold growth but only minimal gene dilution from intermarriage, Quebec has what geneticists call optimal linkage disequilibrium (genetic sharing).[15] The result: far fewer genetic variations, including those that have been wellstudied be ...
... only 2,600. After twelve to sixteen generations, with an eightyfold growth but only minimal gene dilution from intermarriage, Quebec has what geneticists call optimal linkage disequilibrium (genetic sharing).[15] The result: far fewer genetic variations, including those that have been wellstudied be ...
Evolution of Populations Summary of Natural Selection
... survive are more likely to pass down the beneficial traits to their offspring Over LONG periods of time the beneficial traits become prevalent throughout the population All species alive today are descended with modifications from ancestral species thus uniting all living things in a tree of life ...
... survive are more likely to pass down the beneficial traits to their offspring Over LONG periods of time the beneficial traits become prevalent throughout the population All species alive today are descended with modifications from ancestral species thus uniting all living things in a tree of life ...
1 Lecture 6 Migration, Genetic Drift and Nonrandom Mating I
... c. The result of constant introductions of alleles from the mainland is that this tends to homogenize the allele frequencies on the island. d. If natural selection did not oppose the effects of immigration, then the allele frequency on the island would come to resemble that on the mainland. III. Gen ...
... c. The result of constant introductions of alleles from the mainland is that this tends to homogenize the allele frequencies on the island. d. If natural selection did not oppose the effects of immigration, then the allele frequency on the island would come to resemble that on the mainland. III. Gen ...
chapter 8 - Palm Beach State College
... particular phenotype, as compared with the reproductive output of individuals with alternative phenotypes ...
... particular phenotype, as compared with the reproductive output of individuals with alternative phenotypes ...
Quiz #5
... Which of the following geological forces on our planet can lead to the separation of continents, formation of new islands or mountain ranges? A) continental drift B) volcanism C) biogeography D) rotational tilt E) both, a and b Q. 15: A structure of or within an animal’s body that was once functiona ...
... Which of the following geological forces on our planet can lead to the separation of continents, formation of new islands or mountain ranges? A) continental drift B) volcanism C) biogeography D) rotational tilt E) both, a and b Q. 15: A structure of or within an animal’s body that was once functiona ...
Unit 6 Practice and Answers (Answers or on "sticky note" on PDF file)
... 14) Mules are relatively long-lived and hardy organisms that cannot, generally speaking, perform successful meiosis. Consequently, which statement about mules is true? A) They have a relative evolutionary fitness of zero. B) Mutations cannot occur in their genomes. C) Their offspring have less genet ...
... 14) Mules are relatively long-lived and hardy organisms that cannot, generally speaking, perform successful meiosis. Consequently, which statement about mules is true? A) They have a relative evolutionary fitness of zero. B) Mutations cannot occur in their genomes. C) Their offspring have less genet ...
Adaptive Radiation
... Allele frequencies remain constant. this even possible in a changing environment?...... ...
... Allele frequencies remain constant. this even possible in a changing environment?...... ...
Chapter 17.1-Genes and Variation
... - Most organisms contain two sets of genes - One allele from each parent ...
... - Most organisms contain two sets of genes - One allele from each parent ...
Mutations - JeongAPbiology
... Population Genetics – study of how populations change genetically over time Population – groups of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time Gene Pool – all the alleles of all the individuals of a population ***if all members of a population are homozygous for the same ...
... Population Genetics – study of how populations change genetically over time Population – groups of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time Gene Pool – all the alleles of all the individuals of a population ***if all members of a population are homozygous for the same ...
013368718X_CH17_267-284.indd
... How Natural Selection Works Natural selection on a single-gene trait can lead to changes in allele frequencies and changes in phenotype frequencies. For polygenic traits, populations often exhibit a range of phenotypes for a trait. When graphed, this range usually forms a bell curve, with fewer indi ...
... How Natural Selection Works Natural selection on a single-gene trait can lead to changes in allele frequencies and changes in phenotype frequencies. For polygenic traits, populations often exhibit a range of phenotypes for a trait. When graphed, this range usually forms a bell curve, with fewer indi ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.























