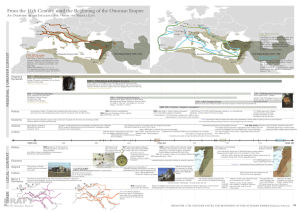
the impact of the crusades
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
From the 11th century until the beginning of the
... Sultan Baybar establishes a new sophisticated administration system, states in the Middle East, fall of Akkon effects that Muslims leave “holy cities” governor appointement from Cairo (citadel) or the Memluk princes (city) to the Christs for 10 years 1258 Mamluk conquer and destroy Bagdad, final end ...
... Sultan Baybar establishes a new sophisticated administration system, states in the Middle East, fall of Akkon effects that Muslims leave “holy cities” governor appointement from Cairo (citadel) or the Memluk princes (city) to the Christs for 10 years 1258 Mamluk conquer and destroy Bagdad, final end ...
Was the Crusades a successful failure?
... • After the Second Crusade (1144-1155)- 1187 Jerusalem was retaken by the Muslims led by Saladin • Third Crusade -1189, also known as the Kings Crusade, Frederick Barbarossa of Germany, Philip Augustus of France, and Richard the Lion Hearted of England • Other Crusades failed to establish the Christ ...
... • After the Second Crusade (1144-1155)- 1187 Jerusalem was retaken by the Muslims led by Saladin • Third Crusade -1189, also known as the Kings Crusade, Frederick Barbarossa of Germany, Philip Augustus of France, and Richard the Lion Hearted of England • Other Crusades failed to establish the Christ ...
(modern name: Akko or Akka) is a city in the western
... In 1191, the city was returned to Christian rule by Richard the Lionhearted during the Third Crusade. ...
... In 1191, the city was returned to Christian rule by Richard the Lionhearted during the Third Crusade. ...
The Crusades - Muslim Population
... lands. The city of Nicaea was taken first. Following that, the crusaders attacked and captured Antioch. Nearly all of the Muslims inside were killed by the merciless crusaders. Then the crusaders attacked Marrat an-Nu'man where the crusaders slaughtered a hundred thousand people. (The Templars did t ...
... lands. The city of Nicaea was taken first. Following that, the crusaders attacked and captured Antioch. Nearly all of the Muslims inside were killed by the merciless crusaders. Then the crusaders attacked Marrat an-Nu'man where the crusaders slaughtered a hundred thousand people. (The Templars did t ...
The Crusades: A Jigsaw Activity
... In 1187, the Holy City of Jerusalem fell to Muslim forces under Saladin. Three important rulers agreed to lead a Third Crusade. Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany (Holy Roman Empire), Richard I (The Lionheart) of England, and Phillip II Augustus, King of France. When members of the Third Crusad ...
... In 1187, the Holy City of Jerusalem fell to Muslim forces under Saladin. Three important rulers agreed to lead a Third Crusade. Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany (Holy Roman Empire), Richard I (The Lionheart) of England, and Phillip II Augustus, King of France. When members of the Third Crusad ...
The Crusades were a series of wars during the Middle Ages where
... longship had a long and narrow hull, as well as a shallow draft, in order to facilitate landings and troop deployments in shallow water. The knarr, on the other hand, was a slower merchant vessel with a greater cargo capacity than the longship. It was designed with a short and broad hull, and a deep ...
... longship had a long and narrow hull, as well as a shallow draft, in order to facilitate landings and troop deployments in shallow water. The knarr, on the other hand, was a slower merchant vessel with a greater cargo capacity than the longship. It was designed with a short and broad hull, and a deep ...
The Crusades - Mr. Kelleher
... • Also, it was during this time period that the Catholic Church, led by the pope, had tremendous political influence which was used to pressure various kings, etc., to seek the church’s favor. ...
... • Also, it was during this time period that the Catholic Church, led by the pope, had tremendous political influence which was used to pressure various kings, etc., to seek the church’s favor. ...
the crusades - Cobb Learning
... Saladin decided that neither Frankish Christians, nor the ones of oriental heritage should be pursued. Saladin placed guards around the church of the Holy grave as well as other holy places belonging to the non-Muslims, to avoid them being destroyed. Saladin encouraged the Franks to stay, and invit ...
... Saladin decided that neither Frankish Christians, nor the ones of oriental heritage should be pursued. Saladin placed guards around the church of the Holy grave as well as other holy places belonging to the non-Muslims, to avoid them being destroyed. Saladin encouraged the Franks to stay, and invit ...
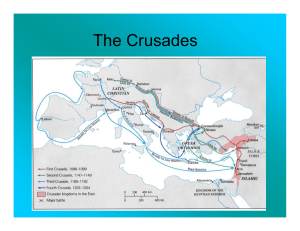
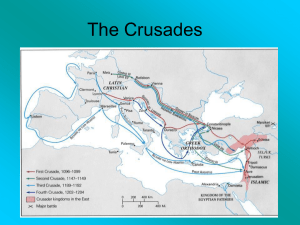
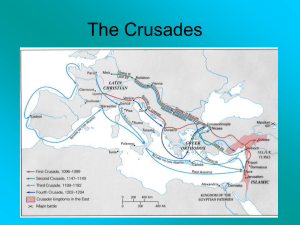
The Crusades
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
The Crusades - OnMyCalendar
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
The Crusades
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
Crusade
... Remember, you must be able to cite information from your text to show evidence proving your answer is true. ...
... Remember, you must be able to cite information from your text to show evidence proving your answer is true. ...
Chapter 10 - Packet (2017)
... Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades Directions: Read Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades (first part only) on page 119 in your textbook. 1. Why did the emperor of the Byzantine Empire appeal to Pope Urban for help in 1095 C.E.? ...
... Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades Directions: Read Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades (first part only) on page 119 in your textbook. 1. Why did the emperor of the Byzantine Empire appeal to Pope Urban for help in 1095 C.E.? ...
Task The Crusades
... Effects of the Crusades ■ Muslim Turks still rule the Holy Land ■ Byzantine Empire is weakened ■ Pope’s power declines ■ Power of feudal nobles weakens because they died or spent too much money on military ■ Kings become stronger ■ Religious intolerance grows ■ Italian cities expand trade and grow r ...
... Effects of the Crusades ■ Muslim Turks still rule the Holy Land ■ Byzantine Empire is weakened ■ Pope’s power declines ■ Power of feudal nobles weakens because they died or spent too much money on military ■ Kings become stronger ■ Religious intolerance grows ■ Italian cities expand trade and grow r ...
The Crusades: A Jigsaw Activity
... “Although, O sons of God, you have promised more firmly than ever to keep the peace among yourselves and to preserve the rights of the church, there remains still an important work for you to do. Freshly quickened by the divine correction, you must apply the strength of your righteousness to another ...
... “Although, O sons of God, you have promised more firmly than ever to keep the peace among yourselves and to preserve the rights of the church, there remains still an important work for you to do. Freshly quickened by the divine correction, you must apply the strength of your righteousness to another ...
Chapter 9 - Cloudfront.net
... Pope Urban II specifically appealed to sinners to repent their sins by joining the crusades. Yet, the pope was not alone in his effort in “preaching the crusades”. Blessed Peter the Hermit of Aimens traveled from city to city calling for a crusade. According to tradition, as Bl. Peter slept in the C ...
... Pope Urban II specifically appealed to sinners to repent their sins by joining the crusades. Yet, the pope was not alone in his effort in “preaching the crusades”. Blessed Peter the Hermit of Aimens traveled from city to city calling for a crusade. According to tradition, as Bl. Peter slept in the C ...
File - MrPadilla.net
... quickly organized armies to fight in the Holy Land. In addition to knights, regular people like craftsmen and peasants also joined the crusade. The main reason many joined the crusade was religion, but others went to earn money through trade and to gain property in the Holy Land. The First Crusade ( ...
... quickly organized armies to fight in the Holy Land. In addition to knights, regular people like craftsmen and peasants also joined the crusade. The main reason many joined the crusade was religion, but others went to earn money through trade and to gain property in the Holy Land. The First Crusade ( ...
The Crusades
... enough to attack the city. Salah al-Din’s forces had also grown weaker. In September 1192, the two leaders signed a peace treaty. The crusaders kept a chain of cities along the coast of Palestine. Muslims agreed to let Christian pilgrims enter Jerusalem. ...
... enough to attack the city. Salah al-Din’s forces had also grown weaker. In September 1192, the two leaders signed a peace treaty. The crusaders kept a chain of cities along the coast of Palestine. Muslims agreed to let Christian pilgrims enter Jerusalem. ...
Middle Ages
... – People endured cruel lords, unjust laws, and poor living conditions. – They believed that such hardships would earn them entry to heaven. As a result, the Middle Ages was not a time of rebellions and revolutions. ...
... – People endured cruel lords, unjust laws, and poor living conditions. – They believed that such hardships would earn them entry to heaven. As a result, the Middle Ages was not a time of rebellions and revolutions. ...
The Crusades
... The first crusade was conceived in the mid 11th century and was meant to reverse the capture of Jerusalem and the Holy Land from recent Muslim invasions Crusades had the effect of rallying the most violent members of Europe around the defense of the Christian religion Whether consciously conceived a ...
... The first crusade was conceived in the mid 11th century and was meant to reverse the capture of Jerusalem and the Holy Land from recent Muslim invasions Crusades had the effect of rallying the most violent members of Europe around the defense of the Christian religion Whether consciously conceived a ...
The Crusades Pages 326-331
... Crusades for several reasons. Jerusalem and the area around it was, and still is, sacred to Christians, Jews, and Muslims. Christians called this area the Holy Land. The Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem in 1071 made Christian pilgrimages to the Holy Land nearly impossible. Additionally, European feudal ...
... Crusades for several reasons. Jerusalem and the area around it was, and still is, sacred to Christians, Jews, and Muslims. Christians called this area the Holy Land. The Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem in 1071 made Christian pilgrimages to the Holy Land nearly impossible. Additionally, European feudal ...
The Third Crusade (1250)
... The Siege of Acre The English and French kings finally mustered their forces beneath the walls of Acre, which city the Christians were then besieging. It is estimated that 600,000 men were engaged i ...
... The Siege of Acre The English and French kings finally mustered their forces beneath the walls of Acre, which city the Christians were then besieging. It is estimated that 600,000 men were engaged i ...
Middle Ages - Crusades
... people called Muslim Turks. • The Empire of the Turks included Palestine, the land where Christ was born. • Several crusades (9 officially) between 1096 and 1291 failed to win the Holy Land, but nevertheless had important results for the people of Western Europe. ...
... people called Muslim Turks. • The Empire of the Turks included Palestine, the land where Christ was born. • Several crusades (9 officially) between 1096 and 1291 failed to win the Holy Land, but nevertheless had important results for the people of Western Europe. ...
Name___________________________________
... a. The Crusades did not achieve their original goals, but they brought about many desirable changes in Europe. b. Although the Crusaders captured the Holy Land, they were unable to bring about democratic reforms. c. The Crusades helped bring about the fall of the Roman Empire d. The Crusaders preven ...
... a. The Crusades did not achieve their original goals, but they brought about many desirable changes in Europe. b. Although the Crusaders captured the Holy Land, they were unable to bring about democratic reforms. c. The Crusades helped bring about the fall of the Roman Empire d. The Crusaders preven ...
Battle of Nicopolis

The Battle of Nicopolis (Turkish: Niğbolu Muharebesi) took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied crusader army of Hungarian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Wallachian, French, Burgundian, German and assorted troops (assisted by the Venetian navy) at the hands of an Ottoman force, raising of the siege of the Danubian fortress of Nicopolis and leading to the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire. It is often referred to as the Crusade of Nicopolis as it was one of the last large-scale Crusades of the Middle Ages, together with the Crusade of Varna in 1443–1444.